前言: 在 第一篇文章 中,我们讨论了 如何用 pygame 写一个小游戏,并用键盘交互控制 。接下来,我们将分别用 DFS 、BFS 、DRL 实现自动控制。DFS 已经在 这篇文章 中讨论过,现在来看 BFS 。
使用广度优先搜索方法实现游戏的自动控制
本文涉及一个 .py 文件:
bfs_play.py

如上图,我们将使用“广度优先搜索”的方法,来控制黑色方块自动闯关。
所谓“广度优先搜索”,即:
- 搜索:精准预测行一步操作后,黑色方块将到达什么位置;并再次精准预测在这个位置进行操作后,黑色方块将到达什么位置…直到触发终止条件,即找到最终得分的路径;
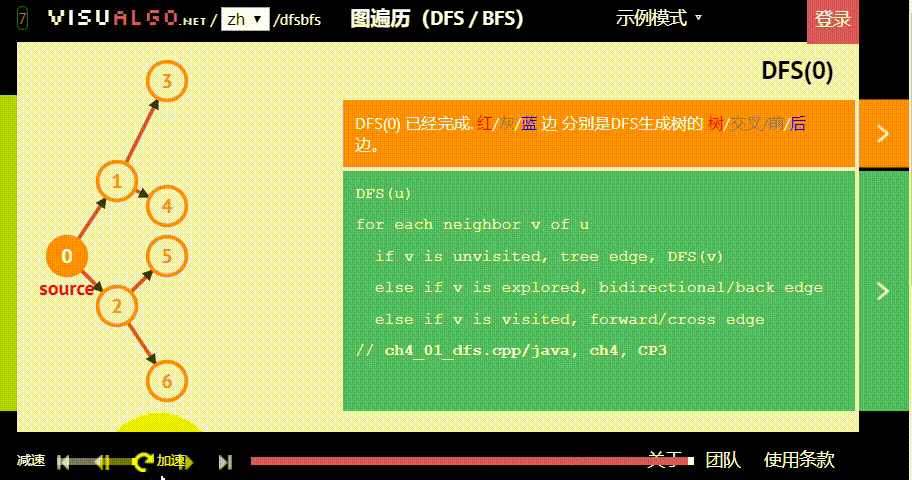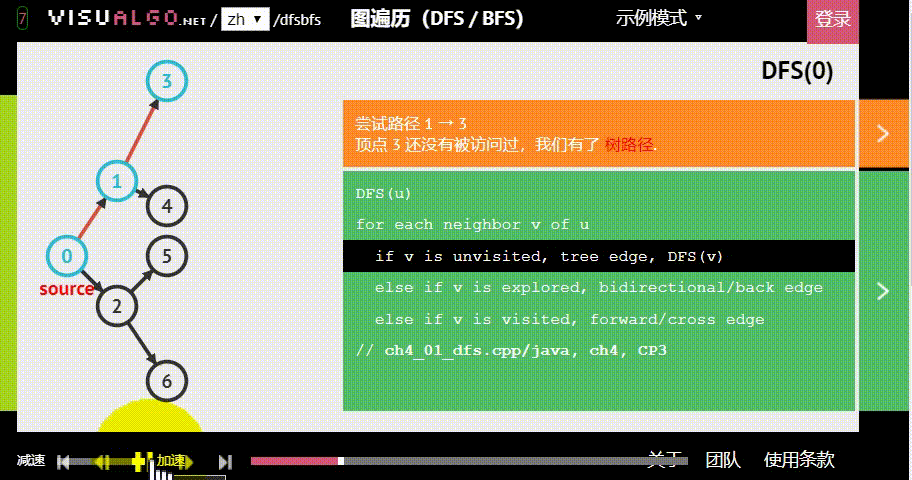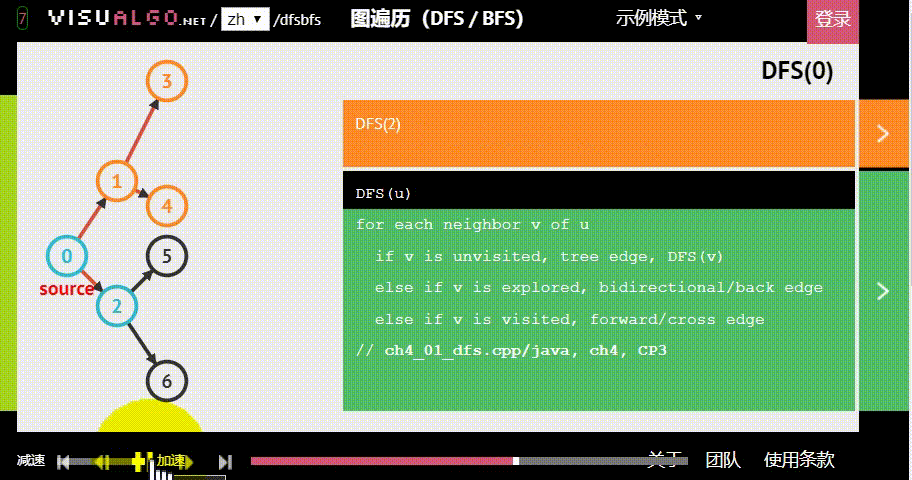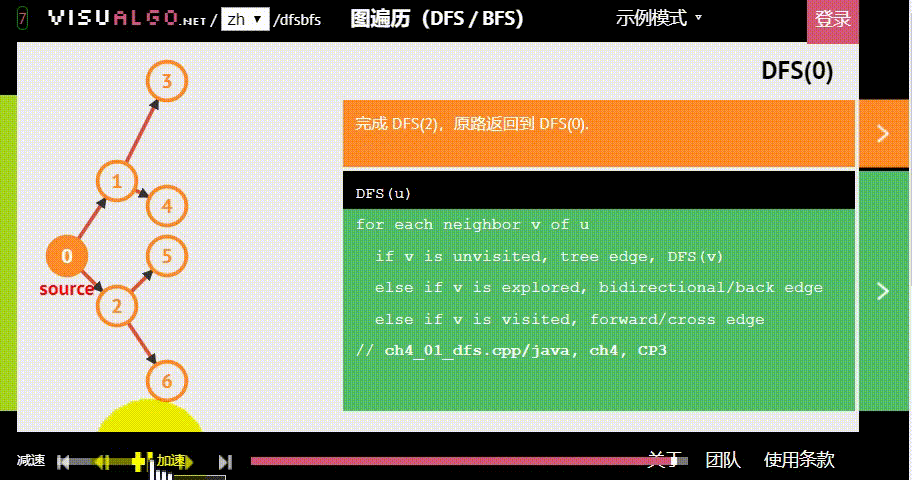
- 广度优先:假设黑色方块有两个动作可以选择:A与B,那么黑色方块做出“选择A后应该到达的位置”的预测后,不继续接着这条路径预测;而是去预测在初始状态下“选择B后应该到达的位置”。具体原理如下图。
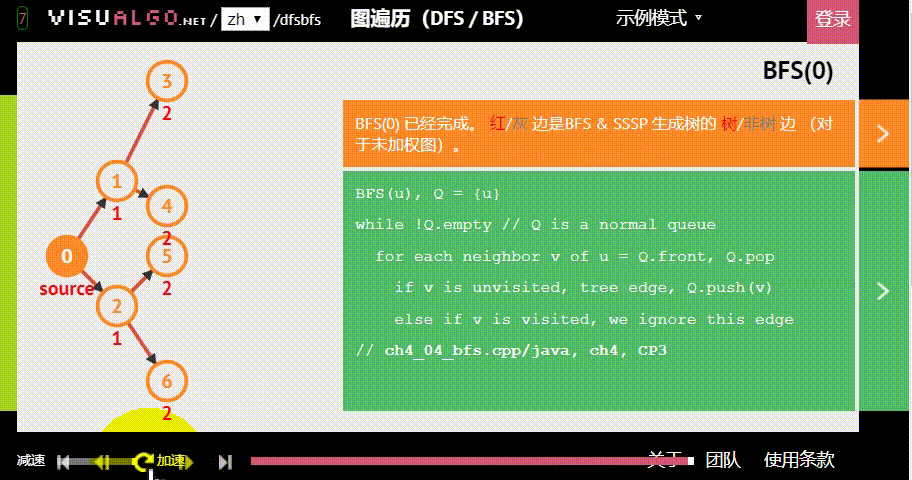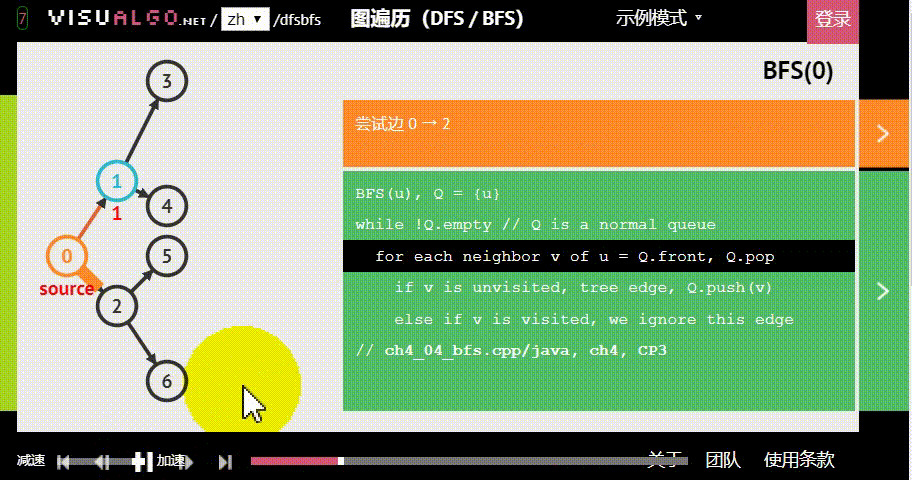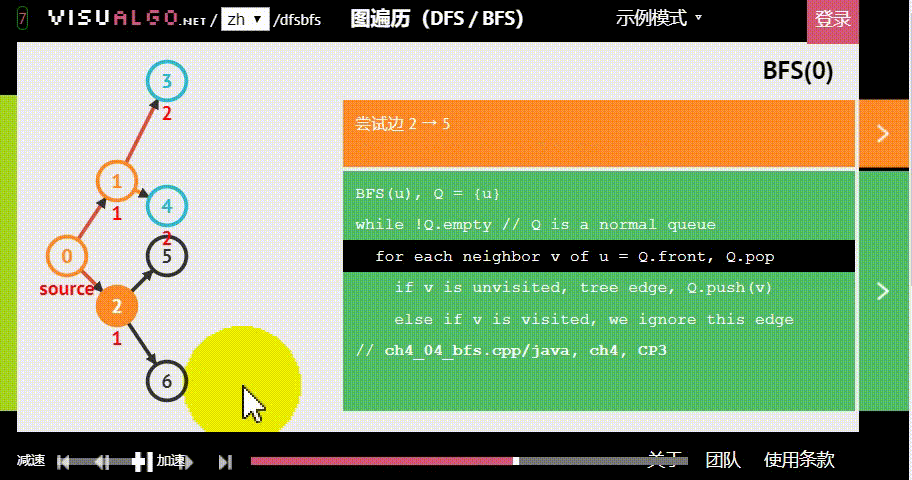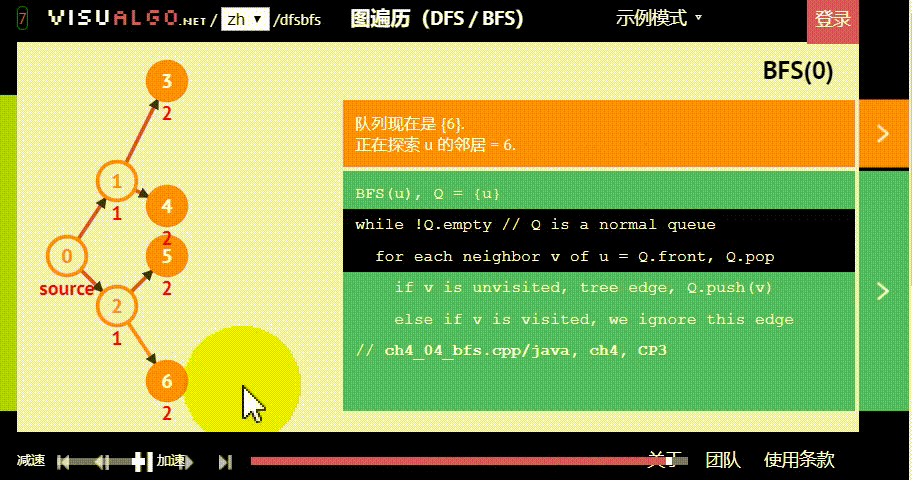
图片生成自:https://visualgo.net/zh/dfsbfs
为了更好地了解 BFS 的特性,你可以用 DFS(深度优先搜索) 进行对比:
如何用 BFS 匹配我们的小游戏
在我写的小游戏(小游戏项目地址,小游戏代码结构详解)中,我们的小方块时刻面临三个选择:
- 给自己一个左上的力;
- 给自己一个右上的力;
- 什么也不做,这一时刻任由自己受重力牵制而掉落。
因此,我们每层也就有三个结点,如下图:

但是因为算法本身的时间复杂度过大,我们可以不考虑“什么也不做”这一动作。这样,每层的父结点就只有两个子结点,大大减少需要遍历的空间。否则,需要搜索的结点过多,导致程序运行过慢或内存溢出。
使用队列的实现
我使用队列来实现 BFS 算法,我大概描述一下这个过程。数据结构不够硬的同学,应该静下心来读读我的源码、或者其他经典的 BFS 教程、或者刷刷 LeetCode 。
我的源码见:https://github.com/PiperLiu/Amazing-Brick-DFS-and-DRL/bfs_play.py
Node = namedtuple("Node", ['sta' , 'act', 'father'])
game_state = GameState(True)
# 为了避免搜索空间过大
# 这里调高了游戏的力学参数
game_state.player.velMaxY = 20
game_state.player.AccY = 5
ACTIONS = (0, 1, 2)
def bfs_forward(root_state, show=False):
# 保存结点的队列
q = Queue()
for action in ACTIONS:
node = Node(root_state.copy(), action, None)
q.put(node)
while True:
# 如果队列为空
# 则说明所有可行结点已经遍历
if q.empty():
break
father_node = q.get()
father_state = father_node.sta
if check_for_score(father_state):
# 如果得分
# 说明可行路径已经找到
# 跳出循环
if show:
pygame.draw.rect(SCREEN, (0, 0, 255), \
(father_state['x'] - game_state.s_c.x, father_state['y'] - game_state.s_c.y, game_state.player.width, game_state.player.height))
pygame.display.update()
break
# 只考虑动作 1 和 2
for action in ACTIONS[1:]:
# father_state = move_forward(father_state, ACTIONS[0])
new_state = move_forward(father_state, action)
if check_crash(new_state):
if show:
pygame.draw.rect(SCREEN, (255, 0, 0), \
(new_state['x'] - game_state.s_c.x, new_state['y'] - game_state.s_c.y, game_state.player.width, game_state.player.height))
pygame.display.update()
else:
if show:
pygame.draw.rect(SCREEN, (100, 100, 100), \
(new_state['x'] - game_state.s_c.x, new_state['y'] - game_state.s_c.y, game_state.player.width, game_state.player.height))
pygame.display.update()
node = Node(new_state, action, father_node)
q.put(node)
return father_node
我这里 BFS 算法效果不好:
python bfs_play.py
输入参数 --display 可以查看寻路过程:
python bfs_play.py --display

源码:https://github.com/PiperLiu/Amazing-Brick-DFS-and-DRL
欢迎 star 。