写在前面
数据结构的实现是多种多样的,在本篇实现多种数据结构的过程中会尽可能的使用动态内存的形式,避免使用宏定义的形式,宏定义的形式是很老旧的版本,在实际运用中很少使用,掌握动态运用内存是必备的技能
对于二叉树的遍历创建方法有多种多样,这里使用的是leetcode等平台力荐的递归形式,递归完成二叉树遍历是较为标准和简单的方式
如果对二叉树的遍历不熟悉,最好优先复习二叉树是如何进行递归遍历和创建的
assert函数仅仅是编写代码时便于调试所加,可以删除,不会造成影响
下载链接
数制转换
问题描述
将十进制数N和其他d进制数之间进行转换是计算机实现计算的基本问题,解决方案很多,其中最简单的方法是除d取余法。例如,(1348)10=(2504)8,其转化过程如下所示:
N N div 8 N mod 8
1348 168 4
168 21 0
21 2 5
2 0 2
从中可以看出,最先产生的余数4是转换结果的最低位,这正好符合栈的“后进先出”的特性。所以可以用顺序栈来模拟这个过程。
题目解析
很简单的题,写一个栈入余数即可

需要注意的是,超过十进制的数有字母的参与,因此可以提前写一个数组,然后把栈内元素当成下标,再用下标元素访问数组内元素,就可以达到输出数字和字母的效果
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//1. 将十进制数N和其他d进制数之间进行转换是计算机实现计算的基本问题,解决方案很多,其中最简单的方法是除d取余法。
// 例如,(1348)10 = (2504)8,其转化过程如下所示:
//N N div 8 N mod 8
//1348 168 4
//168 21 0
//21 2 5
//2 0 2
//从中可以看出,最先产生的余数4是转换结果的最低位,这正好符合栈的“后进先出”的特性。所以可以用顺序栈来模拟这个过程。
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int capacity;
int top;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (pst->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->capacity = 4;
pst->top = 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top);
pst->top--;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->capacity = pst->top)
{
STDataType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = pst->capacity * 2;
tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
if (pst->top == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//被除数 dividend
//除数 divisor
//商 result
//余数 remainder
void Calculate(Stack* pst, int dividend, int divisor)
{
int remainder;
while (dividend)
{
remainder = dividend % divisor;
StackPush(pst, remainder);
dividend = dividend / divisor;
}
}
void Print(Stack* pst, int dividend, int divisor)
{
char array[16] = {
'0', '1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F' };
printf("%d(10)=", dividend);
while (!StackEmpty(pst))
{
printf("%c", array[StackTop(pst)]);
StackPop(pst);
}
printf("(8)\n");
}
int main()
{
int dividend = 1348;
printf("输入十进制数->");
scanf("%d", ÷nd);
int divisor = 8;
printf("输入要改变的进制数->");
scanf("%d", &divisor);
Stack st;
StackInit(&st);
Calculate(&st, dividend, divisor);
Print(&st, dividend, divisor);
return 0;
}
表达式求值
题目描述
从键盘输入一个算术表达式并输出它的结果,算术表达式可包含加、减、乘、除、十进制整数和小括号,利用栈实现。
题目解析
本题难度较高,属于高阶题目,需要先转后缀表达式再计算,这里展示一种解法,后续学习了高阶解决方法会更新该题目,下面代码由本人进行一定程度改造所写,基本功能可以实现,如有其他bug自行解决
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#define N 30
typedef struct my_stack
{
int a[N];
int top;
}ST;
int isempty(ST* T)
{
if (T->top < 0)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int isfull(ST* T)
{
if (T->top == N - 1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int gettop(ST* T)
{
return T->a[T->top];
}
int pop(ST* T)
{
int x;
if (T->top < 0)
{
printf("Zhan is empty,can not pop!\n");
exit(0);
}
else
{
x = T->a[T->top];
(T->top)--;
return x;
}
}
void push(ST* T, int s)
{
if (T->top == N - 1)
{
printf("Zhan is full,can not push,you can modify N and then you can push again.\n");
exit(0);
}
else
{
(T->top)++;
T->a[T->top] = s;
}
}
void transfer(char* in, char* post)
{
ST T;
int i, j, flag = 0;
int count;
int right = 0, left = 0;
T.top = -1;
for (i = 0, j = 0; in[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
switch (in[i])
{
case '0':
case '1':
case '2':
case '3':
case '4':
case '5':
case '6':
case '7':
case '8':
case '9':
for (count = 0; (in[i] <= '9' && in[i] >= '0') || in[i] == '.'; i++, j++)
{
post[j] = in[i];
if (in[i] == '.')
count++;
}
i--;
if (count > 1)
{
printf("数中有两个小数点\n");
exit(0);
}
post[j] = ' ';
j++;
flag = 1;
break;
case '(':
if (flag)
{
printf("数字后直接跟括号\n");
exit(0);
}
push(&T, in[i]);
left++;
break;
case ')':
right++;
while (gettop(&T) != '(')
{
post[j] = pop(&T);
j++;
}
pop(&T);
break;
case '+':
case '-':
if (!flag && i != 0)
{
printf("有连续两个运算符之间没有数字\n");
exit(0);
}
while (!isempty(&T) && gettop(&T) != '(')
{
post[j] = pop(&T);
j++;
}
push(&T, in[i]);
flag = 0;
break;
case '*':
case '/':
if (!flag)
{
printf("有连续两个运算符之间没有数字\n");
exit(0);
}
while (!isempty(&T) && (gettop(&T) == '/' || gettop(&T) == '*'))
{
post[j] = pop(&T);
j++;
}
push(&T, in[i]);
flag = 0;
break;
default:
printf("输入非法字符,无法试别\n");
exit(0);
}
}
if (left != right)
{
printf("左右括号不匹配\n");
exit(0);
}
while (!isempty(&T))
{
post[j] = pop(&T);
j++;
}
post[j] = '\0';
}
float Calculate_zhong(char* post)
{
int i, j, top = -1, flag;
int len;
float temp, aa[N]={
0};
char ch[N];
for (i = 0; post[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
if (post[i] >= '0' && post[i] <= '9')
{
flag = 0;
j = 0;
while (post[i] != ' ')
{
if (post[i] == '.')
{
flag = 1;
}
ch[j] = post[i];
i++;
j++;
}
ch[j] = '\0';
if (flag)
{
for (j = 0; ch[j] != '.'; j++);
len = j - 1;
for (j = 0, temp = 0.; ch[j] != '.'; j++)
{
temp += (ch[j] - '0') * (float)pow(10, len - j);
}
for (j++, len++; ch[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
temp += (ch[j] - '0') * (float)pow(10, len - j);
}
}
else
{
for (j = 0; ch[j] != '\0'; j++);
len = j - 1;
for (j = 0, temp = 0.; ch[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
temp += (ch[j] - '0') * (float)pow(10, len - j);
}
}
top++;
aa[top] = temp;
}
else
{
switch (post[i])
{
case'+':
temp = aa[top];
top--;
temp += aa[top];
aa[top] = temp;
break;
case'-':
temp = aa[top];
top--;
temp = aa[top] - temp;
aa[top] = temp;
break;
case'*':
temp = aa[top];
top--;
temp = temp * aa[top];
aa[top] = temp;
break;
case'/':
temp = aa[top];
top--;
temp = aa[top] / temp;
aa[top] = temp;
}
}
}
return aa[top];
}
int main()
{
char zhong[N], hou[N];
float answer;
printf("需要计算的中缀表达式为:");
scanf("%s", zhong);
transfer(zhong, hou);
answer = Calculate_zhong(hou);
printf("%.2f\n", answer);
}
回文判断
题目描述
假设称正读和反读都相同的字符序列为“回文”,例如,’abba’和’abcba’是回文,’abcde’和’ababab’则不是回文。请编写一个程序判别读入的一个以’@’为结束符的字符序列是否是“回文”。提示:由于依次输入的字符序列中不含特殊的分隔符,则在判别是否是“回文”时,一种比较合适的做法是,同时利用“栈”和“队列”两种结构。
题目解析
本题也很简单,创建队列和栈两个数据结构,分别取Top比较再Pop,放到while循环里即可
//3. 假设称正读和反读都相同的字符序列为“回文”,例如,’abba’和’abcba’是回文,’abcde’和’ababab’则不是回文。
//请编写一个程序判别读入的一个以’@’为结束符的字符序列是否是“回文”。
//提示:由于依次输入的字符序列中不含特殊的分隔符,则在判别是否是“回文”时,一种比较合适的做法是,同时利用“栈”和“队列”两种结构。\
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef char QueueDataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
QueueDataType data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->ptail = NULL;
}
QNode* BuynewQNode(QueueDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QueueDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = BuynewQNode(x);
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
}
QueueDataType QueueTop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
typedef char STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int capacity;
int top;
}Stack;
void StackInit(Stack* pst)
{
pst->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (pst->a == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return;
}
pst->capacity = 4;
pst->top = 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
void StackPop(Stack* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top);
pst->top--;
}
void StackPush(Stack* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->capacity = pst->top)
{
STDataType* tmp = NULL;
int newcapacity = pst->capacity * 2;
tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
bool StackEmpty(Stack* pst)
{
if (pst->top == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void Input(Queue* pq, Stack* ps)
{
char ret;
printf("输入回文字符,以@结尾->");
while (1)
{
scanf("%c", &ret);
if (ret == '@')
break;
QueuePush(pq, ret);
StackPush(ps, ret);
}
}
void Judge(Queue* pq, Stack* ps)
{
while (!QueueEmpty(pq))
{
char que = QueueTop(pq);
QueuePop(pq);
char st = StackTop(ps);
StackPop(ps);
if (que!=st)
{
printf("不是回文\n");
return;
}
}
printf("是回文\n");
return;
}
int main()
{
Queue q;
Stack s;
QueueInit(&q);
StackInit(&s);
Input(&q, &s);
Judge(&q, &s);
return 0;
}
二叉树的创建、遍历及其它基本操作的实现
问题描述
- 以二叉链表作存储结构创建如下二叉树:
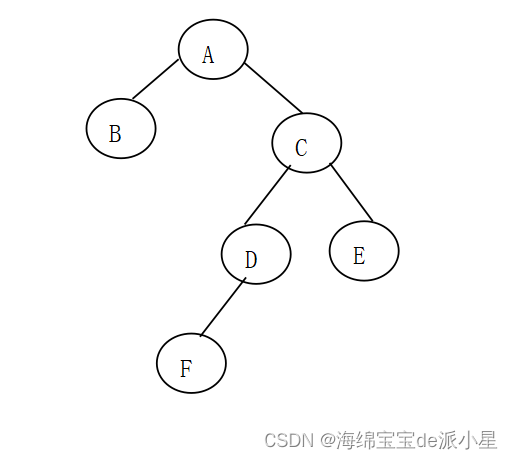
-
输出二叉树的中序遍历序列和后序遍历序列,以验证所建二叉树的正确性;
-
按二叉树的层次输出所建二叉树各层的结点,要求同层的结点自左向右排列。(提示:用到两个队列P、Q。其中P存放当前层上的结点,Q存放下一层的结点。)
题目解析
本实验就是对二叉树的简单操作,熟悉二叉树即可
二叉树介绍链接:
注意:
创建二叉树的方法有很多种,标准的创建二叉树的方法是用递归调用进行创建,基本原理可以在上文链接寻找
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QNode
{
QDataType data;
struct QNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
QNode* BuyQnode(QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = BuyQnode(x);
if (pq->ptail == NULL)
{
assert(pq->phead == NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
if (pq->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* newhead = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = newhead;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType a)
{
BTNode* newnode = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
newnode->data = a;
newnode->left = NULL;
newnode->left = NULL;
return newnode;
}
BTNode* BinaryTreeCreate(BTDataType* a, int* pi)
{
if (a[*pi] == '#')
{
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
BTNode* root = BuyNode(a[*pi]);
(*pi)++;
root->left = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);
root->right = BinaryTreeCreate(a, pi);
return root;
}
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinaryTreeDestory(root->left);
BinaryTreeDestory(root->right);
free(root);
}
void BinaryTreePrevOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
//printf("N ");
return;
}
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreePrevOrder(root->right);
}
void BinaryTreeInOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
//printf("N ");
return;
}
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ", root->data);
BinaryTreeInOrder(root->right);
}
void BinaryTreePostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
//printf("N ");
return;
}
BinaryTreePostOrder(root->left);
BinaryTreePostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c ", root->data);
}
void BinaryTreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
{
QueuePush(&q, root);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
printf("%c ", front->data);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
printf("\n");
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
char ch[] = "AB##CDF###E##";
int pos = 0;
BTNode* tree = BinaryTreeCreate(ch, &pos);
printf("前序遍历:");
BinaryTreePrevOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
printf("中序遍历:");
BinaryTreeInOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
printf("后序遍历:");
BinaryTreePostOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
printf("层序遍历:");
BinaryTreeLevelOrder(tree);
printf("\n");
BinaryTreeDestory(tree);
tree = NULL;
return 0;
}