写在前面:
对于此题,下面提供了三种写法,都是基于最小错误贝叶斯决策来实现的,并且对于wine_data的预测准确率都是100%。注释也已经写好,需要数据集的人可以点击这里获取:链接:
wine_data数据集链接
提取码:ciba
方法一:通过sklearn库中GaussianNB实现
运行结果如下:
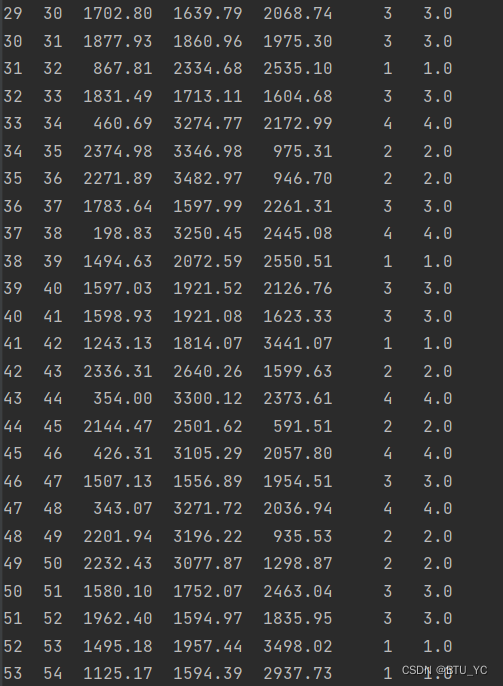
图表 1判别结果

图表 2正确率
运行代码如下:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
import pandas as pd
#导入数据
data_all = pd.read_excel('wine_data.xlsx')
# split the train data and test data
data = data_all.iloc[:,1:4]
target = data_all.iloc[:,4]
# #拆分训练集和测试集
train_size = len(data[0:29])/len(data)
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(data,target,train_size=train_size,shuffle=False)
#高斯模型
clf_G2 = GaussianNB().fit(x_train,y_train)
#给出测试集的预测类别输出
y_pred = clf_G2.predict(x_test)
y_pred = pd.DataFrame(y_pred)
#给出测试集样本在各个类别上预测的概率
y_pred_proba = clf_G2.predict_proba(x_test)
#给出测试集样本在各个类别上预测概率的对数转化
y_pred_log_proba = clf_G2.predict_log_proba(x_test)
print(y_pred)
print(y_test)
data_all.iloc[29:,5] = y_pred.iloc[:]
# plt.plot(y_test)
# print(y_pred_proba[:5])
print(y_pred_log_proba[:5])
print("训练集评分:",clf_G2.score(x_train,y_train))
print("测试集评分:",clf_G2.score(x_test,y_test))
print("精准率:",metrics.accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred))
data_all.to_excel('result_new1.xlsx',index = None)
print(data_all)方法二:通过基于正太分布的最小错误率分类
运行结果:
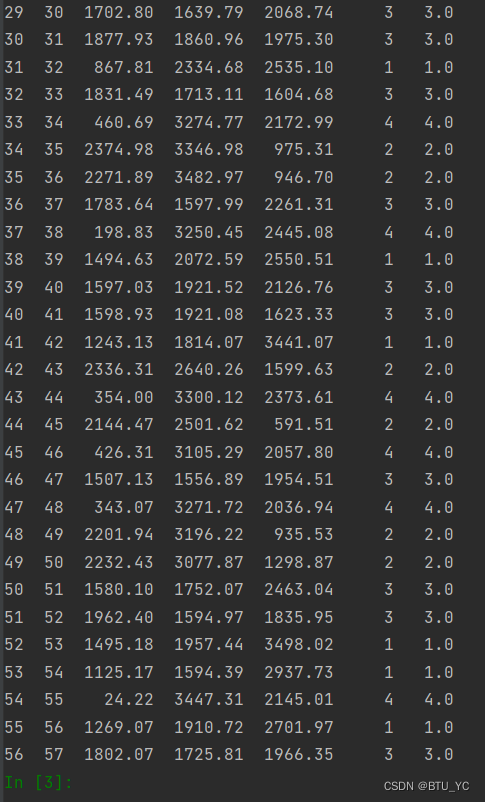
图表 3判别结果
![]()
图表 4正确率
代码如下:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import math
# read the simple data
data = pd.read_excel('wine_data.xlsx')
# split the train data and test data
data_tr = data[0:29]
data_te = data[29:]
# 初始化
N = len(data_tr) # N test simples
#data.iloc[ 0:2 ,1:2 ] # take all the data that intersects rows 0-2 and columns 1-2
w = len(set(data.iloc[:,4])) # w catagory
n = 3 # n characterristics
# count(1) is the number of ones in the list
N1 = list(data_tr['所属类别']).count(1) # The number of the type 1 in the test simple
N2 = list(data_tr['所属类别']).count(2) # The number of the type 2 in the test simple
N3 = list(data_tr['所属类别']).count(3) # The number of the type 3 in the test simple
N4 = list(data_tr['所属类别']).count(4) # The number of the type 4 in the test simple
#From 0 to 4 is in the first category ,so copy the three characteristics from 0 to 4 of the first category to A
A = data.iloc[:N1,1:4] # A belongs to w1
B = data.iloc[N1:N2+N1,1:4] # B belongs to w2
C = data.iloc[N2+N1:N1+N2+N3,1:4] # C belongs to w3
D = data.iloc[N1+N2+N3:N1+N2+N3+N4,1:4] # D belongs to w4
# prior probablity
pw1 = N1/N
pw2 = N2/N
pw3 = N3/N
pw4 = N4/N
def get_p(A,pw):
P_ls = []
x1 = np.array(A.mean()) # 求样本均值
sigma2 = np.array(A.var())
s1 = np.mat(A.cov()) # 求样本协方差矩阵
s1_ = s1.I # 求协方差矩阵的逆矩阵
s11 = np.linalg.det(s1) # 求协方差矩阵的行列式
for i in range(30):
x_u = np.mat(data_te.iloc[i,1:4]-x1) # x-u
# P1=-1/2*x_u*s1_*x_u.T+math.log(pw)-1/2*math.log(s11)
P1 = 1/(np.sqrt(2*np.pi*sigma2))*(np.exp(-x_u*x_u.T/(2*sigma2)).T)*pw
P_ls.append(P1)
return P_ls
#Determine the correct number
cnt = 0
P1 = get_p(A,pw1)
P2 = get_p(B,pw2)
P3 = get_p(C,pw3)
P4 = get_p(D,pw4)
for i in range(30):
P = [P1[i],P2[i],P3[i],P4[i]]
data.iloc[i+29,5] = P.index(max(P))+1
if data.iloc[i+29,5] == data.iloc[i+29,4]:
cnt += 1
accuracy = cnt/len(data_te)
print("精确率:",accuracy)
data.to_excel('result_new.xlsx',index = None)
print(data)方式三:与方法二一样,不过在此基础上将函数封装起来
运行结果:
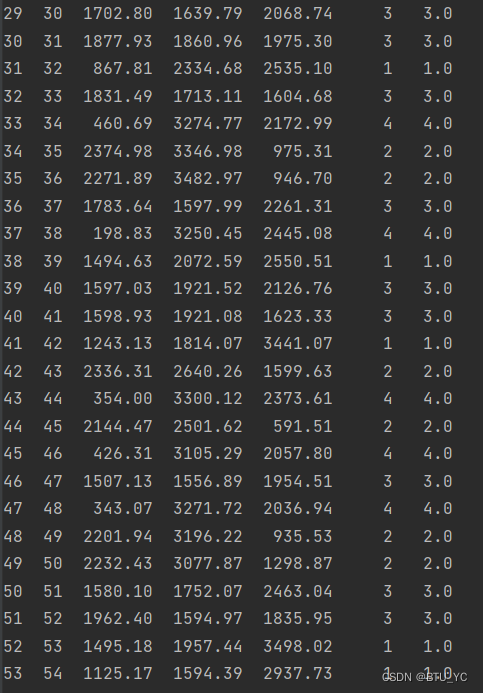
图表 5判别结果
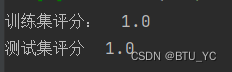
图表 6正确率
代码如下:
import time
import math
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True)
class My_Gaussian(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def fit(self, X_train, y_train):
self.train_data = X_train.copy() #将训练集拷贝
self._y_train = pd.DataFrame(y_train.values, columns=['label'])#训练集的类
self.train_data['label'] = y_train.values #将训练集的类放入,以方便之后用
self.mean_mat = self.train_data.groupby("label").mean() #对每个类的各个特征求均值
self.var_mat = self.train_data.groupby("label").var() #对每个类的各个特征求方差
self.prior_rate = self.__Calculate_prior_probability() #先验概率
return self
#预测
def predict(self, X_test):
pred = [self.__Condition_formula(self.mean_mat, self.var_mat, row) * self.prior_rate for row in X_test.values] # 得到正太分布后的后验概率
class_result = np.argmax(pred,axis=1) # 得到最大值,并将索引分类。
class_result += np.ones(len(class_result)).astype(int)
return class_result
# 先验概率
def __Calculate_prior_probability(self):
la = self._y_train['label'].value_counts().sort_index()
prior_rate = np.array([i / sum(la) for i in la])
return prior_rate
# 高斯贝叶斯条件公式
def __Condition_formula(self, mu, sigma2, row):#row表示每个测试集的三个特征,sigma2表示的是每个类的方差,mu表示每个类的均值
P_mat = 1 / np.sqrt(2 * math.pi * sigma2) * np.exp(-(row - mu) ** 2 / (2 * sigma2)) #通过正太分布得到类条件概率p(x|wi)
P_mat = pd.DataFrame(P_mat).prod(axis=1) #对类条件概率乘积:p(x1|wi)*p(x2|wi)*p(x3|wi)
return P_mat
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
start_time = time.time()
#导入数据
data_all = pd.read_excel('wine_data.xlsx')
# split the train data and test data
data = data_all.iloc[:,1:4]
target = data_all.iloc[:,4]
# #拆分训练集和测试集
train_size = len(data[0:29])/len(data)
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(data,target,train_size=train_size,shuffle=False)
#进行训练
NB = My_Gaussian()
NB.fit(X_train, y_train)
#预测
y_train_NB = NB.predict(X_train)
y_test_NB = NB.predict(X_test)
data_all.iloc[29:,5] = y_test_NB[:]
print("训练集评分: ",accuracy_score(y_train,y_train_NB ),"\n测试集评分 ",accuracy_score(y_test,y_test_NB))
data_all.to_excel('result_new1.xlsx',index = None)
print(data_all)