动态规划(dynamic programming)是运筹学的一个分支,是求解决策过程(decision process)最优化的数学方法。20世纪50年代初美国数学家R.E.Bellman等人在研究多阶段决策过程(multistep decision process)的优化问题时,提出了著名的最优化原理(principle of optimality),把多阶段过程转化为一系列单阶段问题,利用各阶段之间的关系,逐个求解,创立了解决这类过程优化问题的新方法——动态规划。
c++动态规划类算法编程汇总(二)全排列| O(n)排序 | manacher法
c++策略类O(n)编程问题汇总(扑克的顺子|约瑟夫环|整数1出现的次数|股票最大利润)
目录

一、加油站与油O(n)
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/gas-station/submissions/
问题:共n个加油站,123456....n个加油站,每个站点 i 能加 add[ i ] 升汽油, 但是到下一个站点需要花费 sub[ i ] 升汽油。只能从一个站点 i 到下一个站点 i+1 ,从n 到 1,是一个环状的路程,但是不能往回走。问从哪里出发能走完全程?
1.1 思路
问题转换
先把每个站点构造数列 score[ i ] = add[ i ] - sub[ i ],
这个问题就转换成环状的 score [i] 从哪个位置出发,可以实现他们的和 大于0
Sum(score)>0则可以实现,证明:全局>0则局部必然存在>0。问题是在于找出局部在哪里?从哪里开始
解法
选择score最大的节点,两个指针之间,一个fast,一个slow,从前往后加入sum,大于零则继续往后加,小于则用下一个节点加,往前加。如果可以使得sum>0且两指针重合,则满足。
1.2 解法
按照如上思路编写程序。
- 只要输入变量不加const修饰,可直接用相应的输入的变量存储中间结果节省运算,例如直接用cost=gas-cost
- 用 fast%length来实现相应的取地址操作和环形的循环操作
- 第一个循环中判断,slow == fast - 1 && slow<length-1,要用length-1来防止循环溢出,或者用slow == fast - 1 && fast<length
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int canCompleteCircuit(vector<int>& gas, vector<int>& cost) {
int length = gas.size();
if (length < 1 || length!=cost.size())return -1;
for (int idx = 0; idx < length; idx++){
cost[idx] = gas[idx] - cost[idx];
}
int fast=1; int slow=0;
int sum = cost[0];
for (slow = 0; slow < length; slow++){
while (sum < 0 && slow == fast - 1 && slow<length-1){
slow++;
fast++;
sum = cost[slow];
}
while (sum >= 0){
if (fast>slow && fast%length == slow){
return slow;
}
sum += cost[fast%length];
fast++;
}
sum -= cost[slow];
}
return -1;
}
};
int main(){
vector<int>gas = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int>cost = { 3, 4, 5, 1, 2};
Solution s1;
cout << s1.canCompleteCircuit(gas, cost) << endl;
//cout << s1.minPathSum(grid) << endl;
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}二、01矩阵中到0的最小步数
问题:输入一个0,1矩阵,比如
0 0 0 1
1 0 1 1
1 1 1 1
0 0 1 0问矩阵中每个位置到最近的0的曼哈顿距离(只能上下左右走,走到0的步数)。比如此题答案就是
2.1 思路
笨方法:
遍历所有的距离0距离是1的位置,填入1,
然后遍历所有距离1距离是1并且没有填过的位置填入2,依次类推,直到最长边m,但此算法复杂度高,需要O(m*mn),mn为矩阵大小。
动态规划方法
从左上到右下和从右下到左上分别遍历两次。
左上到右下的遍历就是,当前到来自左上方0的距离为:左块和上块最小值加1 current_distance=min(left_distance, up_distance)+1
右下到左上的遍历类推。最终的矩阵为 min(左上距离,右下距离)
OJ与程序待补充。
三、不用冒泡的稳定O(n)
1 2 3 5 0 5 6 2 4 0 0 0 0 0 5
如何将序列的0移到最后,且不变换非0值的顺序。算法复杂度O(n)
3.1 思路
不可行方案:
原始思路就像冒泡排序那样,不可取,因为复杂度O(n*n)
快速排序不可取,因为快速排序是不稳定排序,打算非零值的顺序。
正确思路:
先遍历一次,找出非零值的数量(这步可以省略)。
然后两个指针,一个fast,一个slow,一起往下遍历。fast移一次只能指向非0值,slow只能从前往后遍历
每次把fast的值填入slow,当fast到末尾的时候,slow后面的值置0
OJ与程序待补充。
四、滑动窗口最大值
给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,找出所有滑动窗口里数值的最大值。例如,如果输入数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,他们的最大值分别为{4,4,6,6,6,5}; 针对数组{2,3,4,2,6,2,5,1}的滑动窗口有以下6个: {[2,3,4],2,6,2,5,1}, {2,[3,4,2],6,2,5,1}, {2,3,[4,2,6],2,5,1}, {2,3,4,[2,6,2],5,1}, {2,3,4,2,[6,2,5],1}, {2,3,4,2,6,[2,5,1]}。
4.1 要求O(n)的算法复杂度
采用方法:https://cuijiahua.com/blog/2018/02/basis_64.html
错误写法:
此题本地可以正常运行,但是到了OJ就总显示段错误。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxInWindows(const vector<int>& num, unsigned int size)
{
int length = num.size();
vector<int> max_value;
if (length < 1 || length < size || length < 1)return max_value;
deque<int> buffer;
for (int idx = 0; idx < size; idx++){
while (!buffer.empty() ){
if (num[idx] >= num[buffer[buffer.size() - 1]])
buffer.pop_back();
else
break;
}
buffer.push_back(idx);
}
for (int idx = size; idx < length; idx++){
max_value.push_back(num[buffer[0]]);
while (!buffer.empty() ){
if (num[idx] >= num[buffer[buffer.size() - 1]]){
if (num[idx] >= num[buffer[buffer.size() - 1]])
buffer.pop_back();
else
break;
}
else
break;
}
buffer.push_back(idx);
while (idx-size+1>buffer[0]){
buffer.pop_front();
}
}
max_value.push_back(num[buffer[0]]);
return max_value;
}
};
int main(){
vector<int> test = { 2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 4,3,2,1,0 };
Solution s1;
int window_size = 3;
vector<int> result = s1.maxInWindows(test, window_size);
//input
for (auto item : test){
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// output
for (int idx = 0; idx < window_size - 1; idx++){
cout << " ";
}
for (auto item : result){
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}
问题描述:
您的代码已保存
段错误:您的程序发生段错误,可能是数组越界,堆栈溢出(比如,递归调用层数太多)等情况引起
case通过率为0.00%
这里我们需要弄明白几个问题:
- 判断中,A&&B,如果第一个A语句为假了,B语句是否会执行?
- 判断中, A||B,如果第一个A为真了,第二个B语句是否会执行?
- 段错误到底来自于什么?
4.2 判断语句的执行问题
答案是,如果第一个语句可以完成判断,则第二个语句不被执行。例如:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
bool print1(){
cout << "Whats your problem?11111" << endl;
return true;
}
bool print2(){
cout << "Whats your problem?22222" << endl;
return true;
}
int main(){
if (print1() || print2())
cout << "yes,next" << endl;
bool pr1 = print1();
bool pr2 = print2();
if (pr1&&pr2)
cout << "verfied" << endl;
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}
/* 输出
Whats your problem?11111
yes,next
Whats your problem?11111
Whats your problem?22222
verfied
*/4.3 段错误来自什么地方?
为什么本地IDE可以运行但是服务器就显示段错误?
待检查
五、类似排序的奇偶排序
第一题:输入乱序数组,使奇数值排在偶数值之前(要求O(n)时间复杂度,O(1)空间复杂度)
第二题:输入乱序链表,使奇数值排在偶数值之前(要求O(n)时间复杂度,O(1)空间复杂度)
5.1 解法
输入乱序数组
作者:offer从天上来
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/discuss/226064?type=post&order=time&pos=&page=1
来源:牛客网
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//乱序数组,使奇数值排在偶数值之前(要求O(n)时间复杂度,O(1)空间复杂度)
void func(vector<int> &array)
{
if (array.size() < 2)
return;
int start = 0, end = array.size() - 1;
while (start < end)
{
while (array[start] & 0x0001)
{
if (start == end)
break;
++start;
}
while ((array[end] & 0x0001) == 0)
{
if (end == start)
break;
--end;
}
if (start == end)
break;
int temp = array[start];
array[start] = array[end];
array[end] = temp;
++start;
--end;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n)
{
vector<int> input;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> temp;
input.push_back(temp);
}
func(input);
for (auto it : input)
cout << it << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}5.2 输入乱序链表
作者:offer从天上来
链接:https://www.nowcoder.com/discuss/226064?type=post&order=time&pos=&page=1
来源:牛客网
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//乱序链表,使奇数值排在偶数值之前(要求O(n)时间复杂度,O(1)空间复杂度)
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int x) :val(x), next(NULL){}
};
void func(ListNode** root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
ListNode* pNode = *root;
ListNode* preNode = *root;
pNode = pNode->next;
while (pNode)
{
if (pNode->val & 0x0001)
{
preNode->next = pNode->next;
pNode->next = *root;
*root = pNode;
pNode = preNode->next;
}
else
{
preNode = pNode;
pNode = pNode->next;
}
}
}
ListNode* constructList(const vector<int> &array)
{
if (array.size() == 0)
return NULL;
ListNode* root = new ListNode(array[0]);
ListNode* pNode = root;
for (int i = 1; i < array.size(); ++i)
{
pNode->next = new ListNode(array[i]);
pNode = pNode->next;
}
return root;
}
void printList(ListNode* root)
{
ListNode* pNode = root;
while (pNode)
{
cout << pNode->val << ' ';
pNode = pNode->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while (cin >> n)
{
vector<int> input;
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
cin >> temp;
input.push_back(temp);
}
ListNode* root = constructList(input);
func(&root);
printList(root);
}
return 0;
}六、全排列
输入一个字符串,按字典序打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a,b,c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc,acb,bac,bca,cab和cba。
思路要清晰,
- 每个节点idx与后面所有的互换,
- 然后往下递归,将idx+1与后面互换。
- 互换到idx=最后一个(size-1)的时候,将结果存入set
6.1 非最佳方案
此方法算法复杂度较高,并且思路不太对:
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> Permutation(string str) {
loc_Permutation(str, 0);
vector<string> result;
if (str.size() == 0)return result;
for (auto item : all_str){
result.push_back(item);
}
return result;
}
void loc_Permutation(string str, int loc){
all_str.insert(str);
int size = str.size();
if (loc == size - 1)return;
for (int idx = loc; idx < size-1; idx++){
for (int idx_swap = idx + 1; idx_swap < size; idx_swap++){
swap(str[idx],str[idx_swap]);
loc_Permutation(str, loc + 1);
swap(str[idx], str[idx_swap]);
}
}
}
public:
set<string> all_str;
};
int main(){
string a = "123";
Solution s1;
for (auto item : s1.Permutation(a)){
cout << item << endl;
}
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}
- 注意一点,set头文件可以不重复的输入进去,当作集合,用insert函数。对于aa,输出只有aa,而不是[aa,aa],所以必须用set
- 编程序的时候,涉及到下标的,要画出来具体化。
- class中可以设置全局变量
swap(str[idx],str[idx_swap]);
loc_Permutation(str, loc + 1);
swap(str[idx], str[idx_swap]);运用loc+1的时候
遍历的完整性与不重不漏:
例如:可以在每个void函数后面输出当前str,输出当前idx,与idx_swap
123
0 1 213
1 2 231
0 2 321
1 2 312
1 2 132
1 2 123可以看作程序如此运行
123
循环中换位置 213 递归231
循环中换位置 321 递归312
循环中换位置 132 递归123(此步导致重复)
此处可以重新改进程序,即当前位置交换之后,即可swap后面改为idx+1也可以
for (int idx = loc; idx < size - 1; idx++){
for (int idx_swap = idx + 1; idx_swap < size; idx_swap++){
//cout << idx << " " << idx_swap << " ";
swap(str[idx], str[idx_swap]);
loc_Permutation(str, idx + 1);
swap(str[idx], str[idx_swap]);
}
}但是必须用set
6.2 最终方案
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> Permutation(string str) {
loc_Permutation(str, 0);
vector<string> result;
if (str.size() == 0)return result;
for (auto item : all_str){
result.push_back(item);
}
//result = all_str;
return result;
}
void loc_Permutation(string str, int loc){
all_str.insert(str);
//all_str.push_back(str);
//cout << str << endl;
int size = str.size();
if (loc == size - 1)return;
//loc_Permutation(str, loc + 1);
for (int idx_swap = loc ; idx_swap < size; idx_swap++){
//cout << loc << " " << idx_swap << " ";
swap(str[loc], str[idx_swap]);
loc_Permutation(str, loc + 1);
swap(str[loc], str[idx_swap]);
}
}
public:
set<string> all_str;
};
七、最长回文串
7.1 题干
Leetcode 5
Leetcode5
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-palindromic-substring/
暴力求解方法可以先做:
输入: "babad"
输出: "bab"
注意: "aba" 也是一个有效答案。
输入: "cbbd"
输出: "bb"
需要注意,substr函数是这样用的,string.substr(初始位置,字串长度)
不可行,总是存在算法复杂度过高的问题,本题算法复杂度O(N*N*N)
7.2 暴力解法
这种算法复杂度 O(N^3)的显然不可以。OJ也不会通过
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
bool if_reverse(string s){
int len = s.size();
for (int idx = 0; idx <= (len / 2); idx++){
if (s[idx] != s[len - idx - 1]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int str_size = s.size();
string max_str = s.substr(0, 1);
int max_length = 1;
for (int start_loc = 0; start_loc < str_size - max_length; start_loc++){
for (int sub_size = str_size - start_loc; sub_size>max_length; sub_size--){
string sub = s.substr(start_loc, sub_size);
if (if_reverse(sub) && sub_size>max_length){
max_str = sub;
max_length = sub_size;
}
}
}
return max_str;
}
};
int main(){
//string A; cin >> A;
string A = "babad";
string B = "cbbd";
Solution Solution;
cout << A << endl;
cout << Solution.longestPalindrome(A) << endl;
cout << B << endl;
cout << Solution.longestPalindrome(B) << endl;
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}7.3 动态规划
动态规划的算法复杂度为O(N^2),即当前节点回文,则(节点最左往左==节点最左往右)这两个转换条件可以达到下一个节点回文。算法复杂度依然较高,但是此时已经可以通过OJ的测试了。
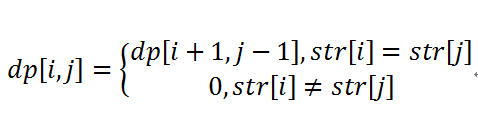
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int str_size = s.size();
int location = 0;
int max_length = 0;
//odd size
for (int loc_idx = 0; loc_idx < str_size; loc_idx++){
int length=0;
while (loc_idx - length >= 0 && loc_idx + length < str_size && s[loc_idx - length] == s[loc_idx + length]){
length++;
}
if (2*length-1 >max_length){
max_length = 2 * length - 1;
location = loc_idx - length + 1;
}
}
//even size
for (int loc_idx = 0; loc_idx < str_size; loc_idx++){
int length=0;
while (loc_idx - length >= 0 && loc_idx + length + 1 < str_size && s[loc_idx - length] == s[loc_idx + length + 1]){
length++;
}
if (2 * length > max_length){
max_length = 2 * length;
location = loc_idx-length+1;
}
}
return s.substr(location, max_length);
}
};
int main(){
//string A; cin >> A;
string A = "babad";
string B = "cbbd";
string C = "bb";
Solution Solution;
cout << A << endl;
cout << Solution.longestPalindrome(A) << endl;
cout << B << endl;
cout << Solution.longestPalindrome(B) << endl;
cout << C << endl;
cout << Solution.longestPalindrome(C) << endl;
int end; cin >> end;
return 0;
}
实际操作的时候,一定要找好映射与边界,最好将实际的string画出来,相应的index标上。
- 单映射,比如ababa的时候,需要将loc_idx表示为中间元素的位置
- 满足条件的前面边界为loc_idx-length>=0, 后面边界<str_size
- while循环退出的时候,length多加了1
- 映射到字符串的前面边界为 loc_idx-length +1
- 映射到子字符串的长度为 2*length-1
- 偶数长度比如abba的字符串类推
7.4 插入#简化映射
先加#,加#之后的映射变得比之前更简单和易得

class Solution {
public:
string longestPalindrome(string s) {
int str_size = s.size();
//add #
string add_s = "#";
for (int idx = 0; idx < str_size; idx++){
add_s += s[idx];
add_s += "#";
}
int add_length = 2 * str_size + 1;
//找出加了#后的最长长度和位置
int location = 0;
int max_length = 0;
for (int loc_idx = 0; loc_idx < add_length; loc_idx++){
int length = 0;
while (loc_idx - length >= 0 && loc_idx + length < add_length && add_s[loc_idx - length] == add_s[loc_idx + length]){
length++;
}
if (length>max_length){
max_length = length;
location = loc_idx;
}
}
// 找出映射
int begin=location-max_length+1;
return s.substr(begin/2, max_length-1);
}
};7.5 manacher法
原理参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/mini-coconut/p/9074315.html

程序待补充
