数据结构–栈实现综合计算器(中缀表达式)(Java)
博客说明
文章所涉及的资料来自互联网整理和个人总结,意在于个人学习和经验汇总,如有什么地方侵权,请联系本人删除,谢谢!
介绍
计算一个表达式,通过栈来实现,创建两个栈,一个存储数,一个存储符号,通过栈先进后出的特点,实现表达式的计算
思路
-
通过一个 index 值(索引),来遍历我们的表达式
-
如果遍历是一个数字, 就直接入数栈
-
如果遍历的是一个符号, 就分如下情况
3.1 如果发现当前的符号栈为空,就直接入栈
3.2 如果符号栈有操作符,就进行比较
如果当前的操作符的优先级小于或者等于栈中的操作符, 就需要从数栈中pop出两个数,在从符号栈中pop出一个符号,进行运算,将得到结果,入数栈,然后将当前的操作符入符号栈。
如果当前的操作符的优先级大于栈中的操作符, 就直接入符号栈.
-
当表达式扫描完毕,就顺序的从 数栈和符号栈中pop出相应的数和符号,并运行.
-
最后在数栈只有一个数字,就是表达式的结果
-
优化多位数的计算,在入数栈的时候判断下一位是数字还是符号,如果下一位是数字则作为一个数存入数栈
代码实现
package stack;
/**
* @author guizimo
* @date 2020/4/6 9:53 上午
*/
public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个表达式
String expression = "26+7*2-15";
//创建数栈和符号栈
ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
//计算时表达式的变量
int index = 0; //索引
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' '; //存入符号到ch
String keepNum = ""; //用于多位数的
//循环获取expression表达式的每个字符
while(true) {
ch = expression.substring(index, index+1).charAt(0);
if(operStack.isOper(ch)) { //判断字符是什么
if(!operStack.isEmpty()) { //栈空判断
if(operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {
//获取计算的表达式
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
//结果入数栈
numStack.push(res);
//符号入符号栈
operStack.push(ch);
} else {
//如果优先级大,直接入符号栈
operStack.push(ch);
}
}else {
//如果为空,直接入符号栈
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else { //如果是数,入数栈
keepNum += ch;
//判断是否是最后一个元素
if (index == expression.length() - 1) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
}else{
//判断下一个元素是否是数字
if (operStack.isOper(expression.substring(index+1,index+2).charAt(0))) {
//如果是运算符,入栈
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum)); //转化为int类型
//将keepNum置空
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
//判断是否到表达式最后
index++;
if (index >= expression.length()) {
break;
}
}
//扫描完成之后,按照顺序取出数栈和符号栈的元素进行计算
while(true) {
//为空时得到最后的结果
if(operStack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);//结果入数栈
}
//数栈最后一个元素就是结果
int res2 = numStack.pop();
System.out.printf("表达式ʽ %s = %d", expression, res2);
}
}
//定义一个栈
class ArrayStack2 {
private int maxSize; // 大小
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1;// 栈顶
//构造器
public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[this.maxSize];
}
//返回当前的栈顶元素
public int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
//栈满
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
//栈空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//push
public void push(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
//pop
public int pop() {
if(isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空");
}
int value = stack[top];
top--;
return value;
}
//遍历
public void list() {
if(isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空");
return;
}
for(int i = top; i >= 0 ; i--) {
System.out.printf("stack[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
//符号优先级
public int priority(int oper) {
if(oper == '*' || oper == '/'){
return 1;
} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {
return 0;
} else {
return -1; //无效
}
}
//是否是运算符
public boolean isOper(char val) {
return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';
}
//计算
public int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {
int res = 0; // res 结果
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;//顺序
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
}
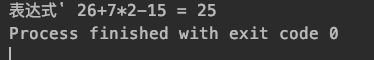
结果
感谢
尚硅谷
以及勤劳的自己
