1、请求转发
(1)直接书写要转发的页面:
@Controller
public class HelloController{
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","nihao");
return "/test.jsp";
}
}

注意:请求转发和重定向是不需要视图解析器参与的,因为这里已经写了完整的路径,有视图解析器的话拼接地址后会出错
(2)添加forward关键字:
@Controller public class HelloController{ @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","nihao"); return "forward:/test.jsp"; } }
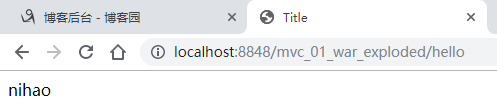
2、重定向
@Controller public class HelloController{ @RequestMapping("/hello") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","nihao"); return "redirect:/test.jsp"; } }

可以看到地址栏已经发生变化,但是由于重定向的时候不能携带数据,因此,jsp页面的内容不能显示
3、数据的接收
(1)提交的域名称和处理的方法的参数名一致
@Controller @RequestMapping("/teacher") public class TeacherController { @GetMapping("/t1") public String testTeacher(String tname, Model model){ //接收前端的参数,要注意要和函数中的参数保持一致 System.out.println("接收到前端的参数为:"+tname); //将返回的结果传递给前端 model.addAttribute("msg",tname); return "test"; } }
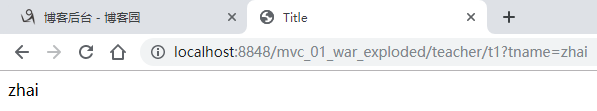
(2)提交的域名称和处理的方法的参数名不一致
@Controller @RequestMapping("/teacher") public class TeacherController { @GetMapping("/t1") public String testTeacher(@RequestParam("name") String tname, Model model){ //接收前端的参数,要注意要和函数中的参数保持一致 System.out.println("接收到前端的参数为:"+tname); //将返回的结果传递给前端 model.addAttribute("msg",tname); return "test"; } }

4、接收一个对象
@Controller @RequestMapping("/teacher") public class TeacherController { @GetMapping("/t1") public String testTeacher(Teacher teacher){ System.out.println("接收到前端的数据为:"+teacher); return "test"; } }

在控制台打印出前端传递的数据:
Teacher(teacherno=null, tname=null, major=jsj, prof=null, department=null)
注意:前端传递数据的时候的参数名要和对象的属性名对应
5、数据的回显
(1)Model
@Controller @RequestMapping("nihao") public class HelloController{ @RequestMapping("/haha") public String hello(Model model){ model.addAttribute("msg","Good Morning!!");//封装数据 return "hello";//被视图解析器处理 } }
(2)ModelAndView
public class HelloController implements Controller { public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception { ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("msg","HelloSpringMVC"); modelAndView.setViewName("hello");//hello.jsp return modelAndView; } }
(3)ModelMap
@Controller @RequestMapping("/teacher") public class TeacherController { @GetMapping("/t1") public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){ modelMap.addAttribute("msg","hhhha"); return "test"; } }

(4)三种方式的比较:
Model:方法较少,只适合于存储数据
ModelMap:继承了LinkedMap,除了实现自身的一些方法,同样的继承了LinkedMap的方法和特性
ModelAndView:可以在存储数据的同时进行设置返回的逻辑视图,进行控制展示层的跳转