GUI编程
1.简介
GUI的核心技术:
Swing
AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit)抽象窗口工具包
缺点:
-
界面不美观
-
需要jre环境
为什么我们要学习?
了解MVC架构,了解监听
2.Awt组件和容器
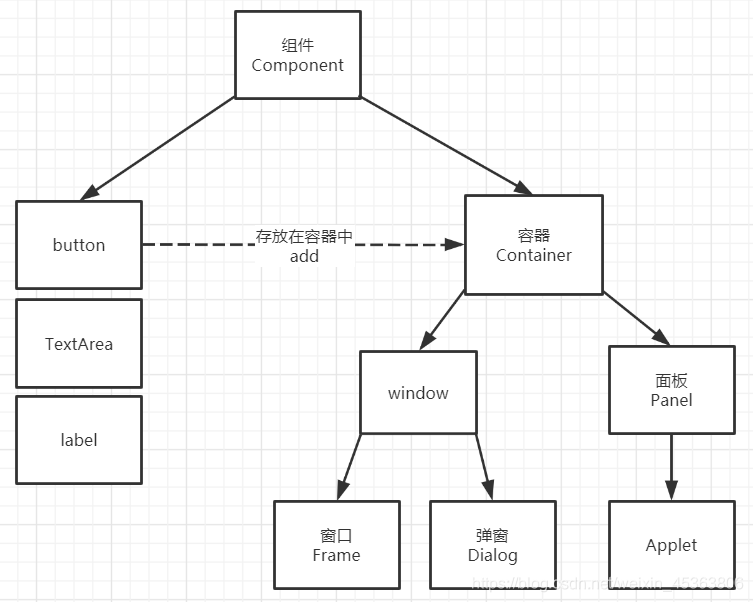
2.1.Frame
展示一个窗口
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Frame,JDK,看源码!
Frame frame = new Frame("我的第一个JAVA图像界面窗口");
//需要设置可见性
frame.setVisible(true);
//设置窗口大小
frame.setSize(400,400);
//设置背景颜色
frame.setBackground(new Color(163, 63, 68));
//弹出的初始位置
frame.setLocation(500,500);
//设置大小固定
frame.setResizable(false);
}
}
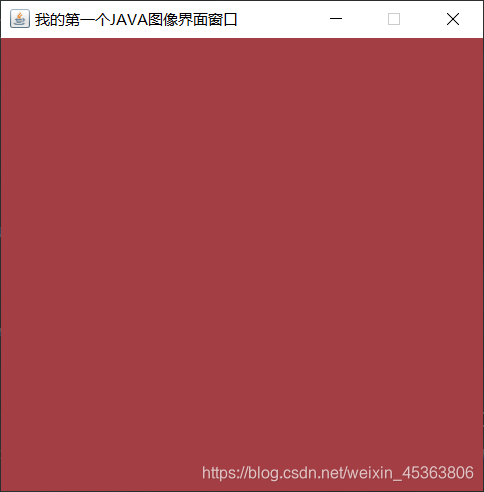
问题:发现窗口关闭不掉
停止java程序
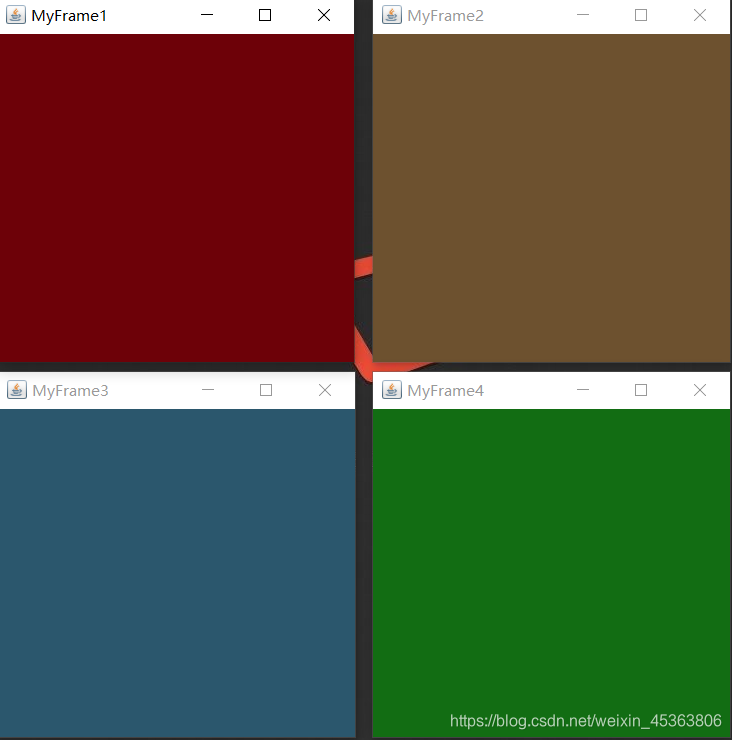
展示多个窗口
public class test2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//展示多个窗口
Frame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(500,200,300,300,new Color(109,1, 8));
Frame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(800,200,300,300,new Color(109, 81, 47));
Frame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(500,500,300,300,new Color(43, 87, 109));
Frame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(800,500,300,300,new Color(18, 109, 19));
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
//可能存在多个窗口,我们需要一个计数器
static int id = 0;
public MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color){
//调用父类Frame的构造函数
super("MyFrame"+(++id));
setBackground(color);
setBounds(x,y,w,h);
setVisible(true);
}
}
2.2.Panel
在这里同时解决了窗口关闭的问题
public class TestPanel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
//Panel可以看成一个空间,但是不能单独存在,必须添加到容器中
Panel panel = new Panel();
//设置布局,不设置Frame会置顶
frame.setLayout(null);
frame.setBounds(200,200,200,200);
frame.setBackground(new Color(62, 163, 171));
frame.setVisible(true);
panel.setBounds(100,100,100,100);
panel.setBackground(new Color(103, 188, 47));
frame.add(panel);
//监听事件,监听窗口关闭时间 System.exit(0)
//适配器模式 不直接new WindowListener(){},直接new它的实现类 可以避免需要实现其所有办法
frame.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override//窗口点击关闭时,需要做的事情
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}

2.3.布局管理器
-
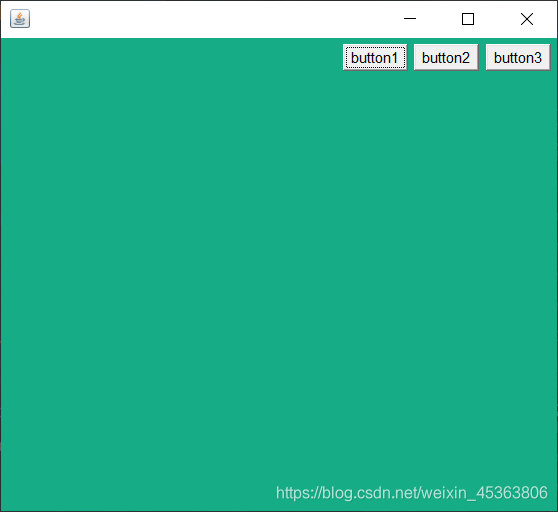
流式布局
public class TestFlowLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame(); frame.setBounds(300,300,300,300); frame.setBackground(new Color(22, 173, 134)); frame.setVisible(true); //组件-按钮 Button button1 = new Button("button1"); Button button2 = new Button("button2"); Button button3 = new Button("button3"); //添加按钮 frame.add(button1); frame.add(button2); frame.add(button3); //设置为流式布局,不添加参数默认为FlowLayout.CENTER frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.RIGHT)); } }
-
东西南北中
public class TestBorderLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame(); frame.setBounds(300,300,300,300); frame.setBackground(new Color(60, 121, 173)); frame.setVisible(true); Button east = new Button("east"); Button west = new Button("west"); Button south = new Button("south"); Button north = new Button("north"); Button center = new Button("center"); frame.add(east,BorderLayout.EAST); frame.add(west,BorderLayout.WEST); frame.add(south,BorderLayout.SOUTH); frame.add(north,BorderLayout.NORTH); frame.add(center,BorderLayout.CENTER); } }
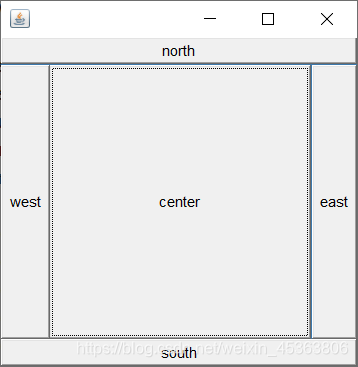
-
表格布局
public class TestGridLayout { public static void main(String[] args) { Frame frame = new Frame(); frame.setBounds(200,200,200,200); frame.setVisible(true); Button button1 = new Button("button1"); Button button2 = new Button("button2"); Button button3 = new Button("button3"); Button button4 = new Button("button4"); Button button5 = new Button("button5"); Button button6 = new Button("button6"); frame.add(button1); frame.add(button2); frame.add(button3); frame.add(button4); frame.add(button5); frame.add(button6); //第一个参数rows为行,第二个参数cols为列 frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(3,2)); } }

2.4布局练习
如何得到一个这样的图?
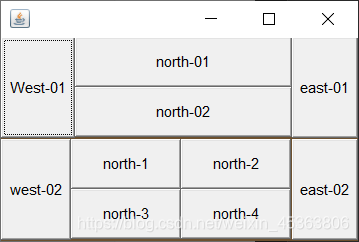
答案:
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame frame = new Frame();
frame.setBounds(500,200,300,200);
frame.setBackground(new Color(109, 81, 47));
frame.setVisible(true);
//整体布局为两行一列的表格
frame.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1));
//上面
Panel panel = new Panel(new BorderLayout());
Panel pane2 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2,1));
panel.add(new Button("West-01"),BorderLayout.WEST);
panel.add(new Button("east-01"),BorderLayout.EAST);
pane2.add(new Button("north-01"));
pane2.add(new Button("north-02"));
//将面板二添加到面板一的CENTER中
panel.add(pane2,BorderLayout.CENTER);
//下面
Panel pane3 = new Panel(new BorderLayout());
Panel pane4 = new Panel(new GridLayout(2,2));
pane3.add(new Button("west-02"),BorderLayout.WEST);
pane3.add(new Button("east-02"),BorderLayout.EAST);
for (int i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
pane4.add(new Button("north-"+i));
}
//将面板四添加到面板三的CENTER中
pane3.add(pane4,BorderLayout.CENTER);
//将面板一和面板三添加到窗口中
frame.add(panel);
frame.add(pane3);
}
}
