文章目录
- 1 介绍
- 2 [语法说明](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/index.html)
- 2.1 [$schema字段](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/schema.html)
- 2.2 [通用关键字段](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/generic.html)
- 2.2.1 注释字段
- 2.2.2 验证关键字
- 2.3 [特定类型关键字:type](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/type.html)
- 2.4 [字符串 string](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/string.html)
- 2.5 [数值类型](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/numeric.html#multiples)
- 2.6 [对象object](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/object.html)
- 2.7 [数组 array](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/array.html)
- 2.8 [布尔值 boolean](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/boolean.html)
- 2.9 [空值 null](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/null.html)
- 2.10 [组合模式](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/combining.html)
- 2.11 [逻辑结构](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/reference/conditionals.html)
- 2.12 [构建复杂的模式](https://json-schema.org/understanding-json-schema/structuring.html)
- 3 实战演练:生成json schema
- 4 集成至jmeter
1 介绍
Json Schema定义了一套词汇和规则,这套词汇和规则用来定义Json元数据,且元数据也是通过Json数据形式表达的。Json元数据定义了Json数据需要满足的规范,规范包括成员、结构、类型、约束等。
1.1 使用Json Schema做接口测试的步骤
- 将响应json转换成json schema格式,(在线转换工具:jsonschema.net)
- 优化修改生成的json schema,使其更符合该接口的各种场景;
- 校验修改后的json schema是否符合规范(在线校验工具:jsonschemalint.com/#!/version/draft-07/markup/json)。
- 进行断言操作。
1.2 优点
- 一个个参数的去验证,测试用例会非常多,代码也会很冗长。如果我们使用 json schema去验证的话,就会大大减少用例和代码数量。
- json schema描述json的数据格式,是一种元数据,它非常简单易读。只要返回的json符合json schema的要求,就可以通过测试。
- 多语言支持。
2 语法说明
2.1 $schema字段
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| $schema | 声明了针对该架构编写的JSON Schema标准版本。 | 如"$schema": “http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema”, http://json-schema.org/draft/2019-09/schema# |
截止到目前,Json Schema一共有8个版本(版本迭代记录),最新的是Draft 8(2019-09)。
不同版本之间语法并不完全兼容,所以最佳实践是在写json schema的时候使用$schema关键字标记当前使用的是哪个规范。
2.2 通用关键字段
2.2.1 注释字段
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| $id | 架构关键字,定义模式的URI,并解析模式中其他URI引用的基URI。 | 如"$id": “http://example.com/example.json” |
| title | 文档标题,关键字是描述性的,用来对文档作补充说明 | |
| description | 文档描述,关键字是描述性的,用来对文档作补充说明 | |
| default | 描述字段 | |
| example | 描述字段,用于展示转换前的json | in draft 6 |
| $comment | 描述字段,用于 schema 开发人员对文档进行注释,不需要展示给最终用户看。 | in draft 7 |
注:注释字段都是非必须字段。
- 举例:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"$id": "http://example.com/example.json",
"type": "object",
"title": "The root schema",
"description": "The root schema comprises the entire JSON document.",
"default": {}
}
2.2.2 验证关键字
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| const | 验证值必须等于该常量,此关键字的值可以是任何类型,包括null。 | 如:“const”: 200,“const”: “success” 。注意,该关键字强类型语言不支持 |
| enum | 验证枚举值,即值只能是enum数组中的某一项 | 如:“enum”: [200,404] |
- 举例1:const
{
"properties": {
"country": {
"const": "success"
}
}
}
{ "country": "success" } # pass
{ "country": "fail" } # fail
- 举例2:enum
{
"enum": ["red", "amber", "green", null, 42]
}
"red" # pass
null # pass
42 # pass
0 # fail
2.3 特定类型关键字:type
- 字段说明:
| 类型 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| string | 字符串 | |
| integer | 整型 | |
| number | 数字 | |
| object | 对象 | properties 关键字是必需的 |
| boolean | 布尔值 | items 关键字是必需的 |
| array | 列 | |
| null | 空 | |
| any | 任意 |
- 举例:
{ "type": "number" }
42 # pass
42.0 # pass
"42" # fail
2.4 字符串 string
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| maxLength | 字符串最大长度 | x <= maxLength |
| minLength | 字符串最小长度 | x >= minLength |
| pattern | 正则匹配字符串 | 如{“type”: “string”, “pattern”: “^(([0-9]{3}))?[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}$”} |
| format | 字符串格式化引擎 | 这些是提案草稿内置的一些格式化校验方式见(#### 附1) |
| contentMediaType | 指定MIME类型的字符串的内容 | 如字符串包含一个HTML文档:{“type”:“string”,“contentMediaType”:“text/html”} |
| contentEncoding | 指定指定的编码用于存储内容 | 如字符串包含使用Base64编码的PNG图像:{“type”:“string”,“contentEncoding”:“base64”,“contentMediaType”:“image/png”} |
- 举例1:Length
{
"type": "string",
"minLength": 2,
"maxLength": 3
}
"A" # fail
"AB" # pass
"ABC" # pass
"ABCD" # fail
- 举例2:正则表达式
{
"type": "string",
"pattern": "^(\\([0-9]{3}\\))?[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{4}$"
}
"555-1212" # pass
"(888)555-1212" # pass
"(888)555-1212 ext. 532" # fail
"(800)FLOWERS" # fail
- 举例3:contentMediaType
{
"type": "string",
"contentMediaType": "text/html"
}
"<!DOCTYPE html><html xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml\"><head></head></html>" # pass
- 举例4:contentEncoding
{
"type": "string",
"contentEncoding": "base64",
"contentMediaType": "image/png"
}
"iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABgAAAAYCAYAAADgdz34AAAABmJLR0QA/wD/AP+gvaeTAAAA..." # pass
附1:format内置有:
日期和时间
- “date-time”:例如 2018-11-13T20:20:39+00:00。
- “time”:例如,20:20:39+00:00
- “date”:例如,2018-11-13。
电子邮件地址
- “email”:互联网电子邮件地址,请参阅RFC 5322,第3.4.1节。
- “idn-email”:Internet电子邮件地址的国际化形式,请参阅 RFC 6531。
Hostnames
- “hostname”:互联网主机名,请参阅RFC 1034第3.1节。
- “idn-hostname”:国际化的Internet主机名,请参阅 RFC5890第2.3.2.3节。
IP地址 - “ipv4”:IPv4地址,根据RFC 2673第3.2节中定义的点分四进制ABNF语法。
- “ipv6”:IPv6地址,如RFC 2373第2.2节中所定义。
资源标识符
- “uri”:根据RFC3986的通用资源标识符(URI) 。
- “uri-reference”:草案6中的新增内容 URI参考(URI或相对参考),根据RFC3986第4.1节。
- “iri”:根据RFC3987,“ uri”的国际化等效项。
- “iri-reference”:根据RFC3987,“ uri-reference”的国际化等效项
如果架构中的值具有相对于特定源路径(例如,来自网页的链接)的能力,则通常更好的做法是使用 “uri-reference”(或"iri-reference")而不是"uri"(或 “iri”)。"uri"仅在路径必须为绝对路径时才应使用。
URI模板
- “uri-template”:根据RFC6570的 URI模板(任何级别) 。如果您尚不知道URI模板是什么,则可能不需要此值。
JSON指针
- “json-pointer”:在构造复杂的架构时,会更多地讨论在JSON架构中使用JSON指针。请注意,仅当整个字符串仅包含JSON指针内容时,才应使用此属性 /foo/bar。JSON指针URI片段,例如#/foo/bar/应使用 “uri-reference”。
- “relative-json-pointer”:相对JSON指针。
正则表达式
- “regex”:草案7中的新增内容一个正则表达式。
2.5 数值类型
- 数值类型包含integer(整形)和number(任何数字类型,整数或浮点数)。
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| multipleOf | 倍数 | |
| minimum | 最小值 | x >= minimum |
| maximum | 最大值 | x ≤ maximum |
| exclusiveMinimum | 不包含最小值, 设置为true | false可以包含minimum的情况 |
| exclusiveMaximum | 不包含最大值,设置为true | false可以包含maximum的情况 |
- 举例1:integer
{
"type": "integer"
}
42 # pass
-1 # pass
3.1415926 # fail
"42" # fail
- 举例2:number:
{
"type": "number",
"minimum": 0,
"exclusiveMaximum": 100
}
-1 # fail 少于minimum
0 # pass
10 # pass
99 # pass
100 # fail exclusiveMaximum 是排他性的,因此100无效
101 # fail 大于maximum
- 举例3:multipleOf
{
"type" : "number",
"multipleOf" : 10
}
0 # pass
10 # pass
20 # pass
23 # fail 不是10的倍数
- 举例4:精确小数点后几位
{
"type": "number",
"multipleOf": 1.0
}
42 # pass
42.0 # pass
3.14156926 # fail
2.6 对象object
- object(对象)是JSON中的映射类型。他们将“键”映射到“值”。在JSON中,“键”必须始终为字符串。这些对中的每对通常都称为“属性”。
- 字段说明:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| properties | json串出现的属性(字段) | 每个属性又可以按照嵌套的方式使用 |
| required | 存放必要属性列表。json串必须出现required要求的属性 | 通常用于判断响应中的必要字段 |
| additionalProperties | true:json串允许properties之外的属性出现;false:json串不可以出现properties之外的属性; | 默认情况,允许出现其他属性 |
| propertyNames.pattern | 可以根据模式验证属性的名称的合法性 | |
| minProperties | 最少属性数量 | x >= minProperties |
| maxProperties | 最大属性数量 | X <= maxProperties |
| dependencies | 定义Key属性依赖的Value属性 | 如{“dependencies”: {“a”: [“b”]}}表示a属性必须依赖于b属性存在,才可以存在, |
| patternProperties | 所有属性名称可以定义为一个正则 |
- 举例1:additionalProperties限制出现属性
如,json串为:
{
"status": 200,
"msg": "success"
}
转换成json schema:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"required": [
"status",
"msg"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"status": {
"type": "integer"
},
"msg": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
-
当设置additionalProperties = true时,原json的status同级再增加一个属性,也能被校验通过:
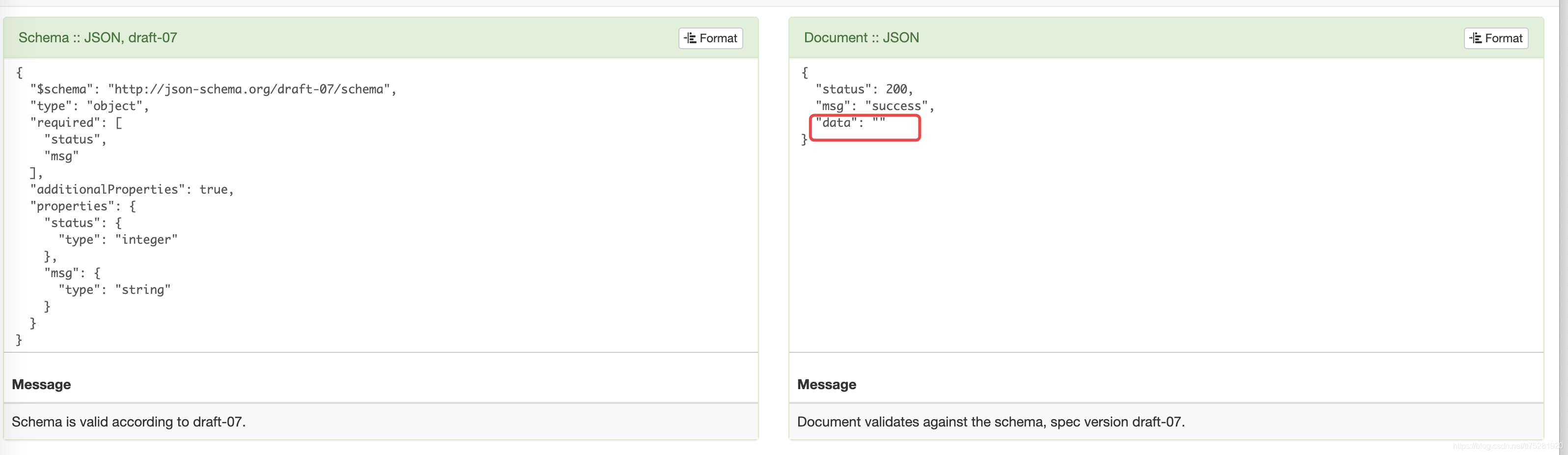
-
但当设置为false时,就会校验失败,报错"should NOT have additional properties":
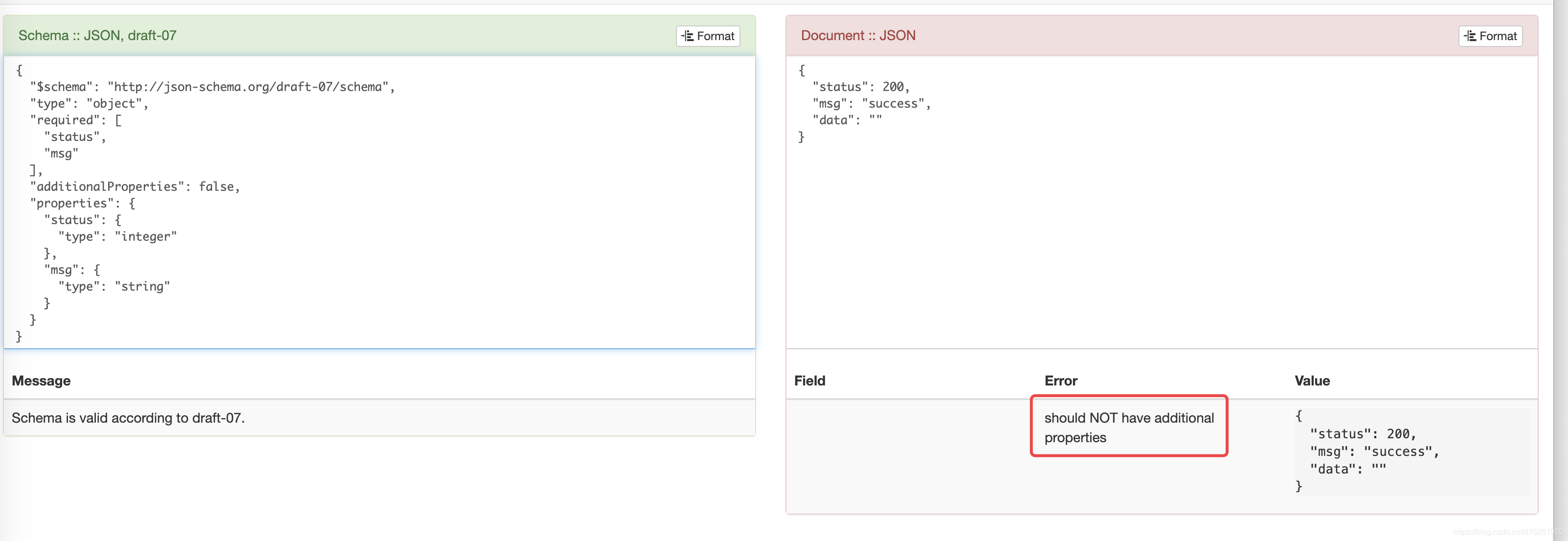
-
举2:additionalProperties限制属性类型
可以允许其他属性,但前提是每个属性都是一个字符串:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"number": { "type": "number" },
"street_name": { "type": "string" },
"street_type": { "type": "string",
"enum": ["Street", "Avenue", "Boulevard"]
}
},
"additionalProperties": { "type": "string" }
}
{ "number": 1600, "street_name": "Pennsylvania", "street_type": "Avenue" } # pass
{ "number": 1600, "street_name": "Pennsylvania", "street_type": "Avenue", "direction": "NW" } # pass 附加属性的值是一个字符串
{ "number": 1600, "street_name": "Pennsylvania", "street_type": "Avenue", "office_number": 201 } # fail 附加属性的值不是字符串
- 举例3:propertyNames.pattern关键字说明:
如:
{
"type": "object",
"propertyNames": {
"pattern": "^[A-Za-z_][A-Za-z0-9_]*$"
}
}
{"_a_proper_token_001": "value"} # pass
{"001 invalid": "value"} # fail
- 举例4:dependencies关键字说明:
如:
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "string" },
"credit_card": { "type": "number" },
"billing_address": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["name"],
"dependencies": {
"credit_card": ["billing_address"]
}
}
示例中credit_card依赖billing_address的出现,则:

- 属性全部存在:
# pass
{
"name": "John Doe",
"credit_card": 5555555555555555,
"billing_address": "555 Debtor's Lane"
}
- 属性全部都不存在:
# pass
{
"name": "John Doe"
}
- 只存在属性billing_address:
# pass
{
"name": "John Doe",
"billing_address": "555 Debtor's Lane"
}
只存在属性credit_card:
# fail
{
"name": "John Doe",
"credit_card": 5555555555555555
}
- 举例5:patternProperties关键字说明:
{
"type": "object",
"patternProperties": {
"^S_": { "type": "string" },
"^I_": { "type": "integer" }
},
"additionalProperties": false
}
{ "S_25": "This is a string" } # pass
{ "I_0": 42 } # pass
{ "S_0": 42 } # fail 如果名称以开头S_,则必须为字符串
{ "I_42": "This is a string" } # fail 如果名称以开头I_,则必须为整数
{ "keyword": "value" } # fail 这是一个与任何正则表达式都不匹配的键
2.7 数组 array
- 数组用于有序元素。 在JSON中,数组中的每个元素都可以具有不同的类型。包含列表验证(任意长度的序列,其中每个项目都匹配相同的架构。)和元组验证(固定长度的序列,其中每个项目可能具有不同的模式)。
- 字段格式:
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| items | 验证数组中的所有元素的类型 | |
| contains | 仅针对数组中的一个或多个项目进行验证 | 如:一个“数字”就足以通过认证:{“type”:“array”,“contains”:{“type”:“number”}}。注意:该关键字,官方说明中支持,但是,有可能你使用的平台或者第三方工具不支持(强类型语言不支持)。所以,使用需谨慎。 |
| additionalItems | 控制是否有效有超出了所定义的数组中的其他项目items:true为允许,false为不允许 | 如果只含有一个items,那additionalItems没有效果 |
| minItems | 数组最小长度验证,必须为非负数 | x >= minItems |
| maxItems | 数组最大长度验证,必须为非负数 | x <= maxItems |
| uniqueItems | 数组内元素唯一性验证,设置为true表示数组项不能有重复的元素 |
- 举例1:items
定义数组中的每个项目都是一个数字:
{
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "number"
}
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # pass 单个“非数字”会导致整个数组无效
[1, 2, "3", 4, 5] # fail 空数组始终有效
[] # pass
- 举例2:contains
{
"type": "array",
"contains": {
"type": "number"
}
}
["life", "universe", "everything", 42] # pass 一个“数字”就足以通过此认证
["life", "universe", "everything", "forty-two"] # fail 如果我们没有数字,验证失败
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # pass
- 举例3:additionalItems
- additionalItems为false,其效果是不允许在数组中添加其他项:
{
"type": "array",
"items": [
{
"type": "number"
},
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Street", "Avenue", "Boulevard"]
},
{
"type": "string",
"enum": ["NW", "NE", "SW", "SE"]
}
],
"additionalItems": false
}
[1600, "Pennsylvania", "Avenue", "NW"] # pass
[1600, "Pennsylvania", "Avenue"] # pass
[1600, "Pennsylvania", "Avenue", "NW", "Washington"] # fail
- additionalItems关键字也可以是验证对所述阵列中的每个元素的类型:
{
"type": "array",
"items": [
{
"type": "number"
},
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"type": "string",
"enum": ["Street", "Avenue", "Boulevard"]
},
{
"type": "string",
"enum": ["NW", "NE", "SW", "SE"]
}
],
"additionalItems": { "type": "string" }
}
[1600, "Pennsylvania", "Avenue", "NW", "Washington"] # pass
[1600, "Pennsylvania", "Avenue", "NW", 20500] # fail
- 举例4:数组长度
{
"type": "array",
"minItems": 2,
"maxItems": 3
}
[] # fail
[1] # fail
[1, 2] # pass
[1, 2, 3] # pass
[1, 2, 3, 4] # fail
- 举例5:uniqueItems
{
"type": "array",
"uniqueItems": true
}
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] # pass
[1, 2, 3, 3, 4] # fail
[] # pass 空数组总是通过
2.8 布尔值 boolean
-
布尔类型仅匹配两个特殊值:true和false。
-
举例:
{
"type": "boolean"
}
true # pass
false # pass
"true" # fail
0 # fail
2.9 空值 null
- 当模式指定null类型时,它只有一个可接受的值:null,也就是只有null才能被校验通过。
- 举例:
{
"type": "null"
}
null # pass
false # fail
0 # fail
"" # fail
2.10 组合模式
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| allOf | 必须对所有子方案有效 | |
| anyOf | 对任意给定子方案有效 | |
| oneOf | 必须对给定的子方案之一有效。 | |
| not | 给定的子方案都没有效 |
- 举例1:allOf
{
"allOf": [
{ "type": "string" },
{ "maxLength": 5 }
]
}
"short" # pass
"too long" # fail
- 举例2:anyOf
{
"anyOf": [
{ "type": "string" },
{ "type": "number" }
]
}
"Yes" # pass
42 # pass
{ "Not a": "string or number" } # fail
- 举例3:oneOf
{
"oneOf": [
{ "type": "number", "multipleOf": 5 },
{ "type": "number", "multipleOf": 3 }
]
}
10 # pass
9 # pass
2 # fail 不是5或3的倍数
15 # fail 5和3的倍数均fail
- 举例4:not
{
"not": {
"type": "string"
}
}
42 # pass
{ "key": "value" } # pass
"I am a string" # fail
2.11 逻辑结构
| 字段 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| if | if控制了哪个“then”或“else”关键字被判断。 | |
| then | 如果if生效,则then必须生效,然后else会被忽略。 | |
| else | 如果if无效,则else必须生效,then会被忽略。 |
举例1:
假设您想编写一个模式来处理美国和加拿大的地址。这些国家/地区有不同的邮政编码格式,我们希望根据国家/地区选择要验证的格式。如果地址在美国,则该postal_code字段为“zipcode”:五个数字后跟可选的四位数后缀。如果地址位于加拿大,则该postal_code字段是六位数的字母数字字符串,其中字母和数字交替显示。
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"street_address": {
"type": "string"
},
"country": {
"enum": ["United States of America", "Canada"]
}
},
"if": {
"properties": { "country": { "const": "United States of America" } }
},
"then": {
"properties": { "postal_code": { "pattern": "[0-9]{5}(-[0-9]{4})?" } }
},
"else": {
"properties": { "postal_code": { "pattern": "[A-Z][0-9][A-Z] [0-9][A-Z][0-9]" } }
}
}
- pass
{
"street_address": "1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW",
"country": "United States of America",
"postal_code": "20500"
}
- pass
{
"street_address": "24 Sussex Drive",
"country": "Canada",
"postal_code": "K1M 1M4"
}
- fail
{
"street_address": "24 Sussex Drive",
"country": "Canada",
"postal_code": "10000"
}
2.12 构建复杂的模式
在编写代码时,通常会使用抽象的概念,将程序“结构化”为可重用的功能,要好于在各处使用并复制和粘贴重复的代码。同样,在Json Schema,将模式结构化为可在许多地方重用的部分非常有用。
2.12.1 重用
假设定义一个客户记录,其中每个客户可能都具有送货地址和帐单邮寄地址。地址始终是相同的特征(它们具有街道地址,城市和州名),因此我们不想在要存储地址的所有地方重复该模式的那部分。这不仅会使架构变得更加冗长,而且使将来的更新更加困难。
- 首先让我们从定义地址的json:
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"street_address": { "type": "string" },
"city": { "type": "string" },
"state": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["street_address", "city", "state"]
}
- 接着我们重构此json,将其放置在父架构关键字definitions下:
"definitions": {
"address": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"street_address": { "type": "string" },
"city": { "type": "string" },
"state": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["street_address", "city", "state"]
}
}
}
- 然后就可以使用$ref关键字从其他地方引用此模式片段:
{ "$ref": "#/definitions/address" }
- 将其放在一起,并使用我们的地址架构为客户创建架构
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"definitions": {
"address": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"street_address": { "type": "string" },
"city": { "type": "string" },
"state": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["street_address", "city", "state"]
}
},
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"billing_address": { "$ref": "#/definitions/address" },
"shipping_address": { "$ref": "#/definitions/address" }
}
}
# pass
{
"shipping_address": {
"street_address": "1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW",
"city": "Washington",
"state": "DC"
},
"billing_address": {
"street_address": "1st Street SE",
"city": "Washington",
"state": "DC"
}
}
$ref也可以是相对或绝对URI,因此如果您希望将定义包含在单独的文件中,也可以这样做,将从另一个文件中加载地址模式。
{ "$ref": "definitions.json#/address" }
2.12.2 递归
$ref元素可用于创建引用自己的递归模式。例如,您可能有一个person包含的数组的架构children,每个数组也是person实例:
json schema:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"definitions": {
"person": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": { "type": "string" },
"children": {
"type": "array",
"items": { "$ref": "#/definitions/person" },
"default": []
}
}
}
},
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"person": { "$ref": "#/definitions/person" }
}
}
# pass
{
"person": {
"name": "Elizabeth",
"children": [
{
"name": "Charles",
"children": [
{
"name": "William",
"children": [
{ "name": "George" },
{ "name": "Charlotte" }
]
},
{
"name": "Harry"
}
]
}
]
}
}
2.12.3 扩展
将 ref一起使用,$id还提供了一种无需使用JSON指针即可引用子模式的方法。这意味着您可以通过唯一名称而不是在JSON树中出现的位置来引用它们。
重用上面的地址示例,我们可以$id向地址架构添加一个属性,然后通过该属性来引用它。
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"definitions": {
"address": {
"$id": "#address",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"street_address": { "type": "string" },
"city": { "type": "string" },
"state": { "type": "string" }
},
"required": ["street_address", "city", "state"]
}
},
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"billing_address": { "$ref": "#address" },
"shipping_address": { "$ref": "#address" }
}
}
注意:Python jsonschema 库当前不支持此功能。
3 实战演练:生成json schema
3.1 将json转换成json schema格式
利用在线json生成schema工具(jsonschema.net)可以快捷的将接口响应转换成json schema的数据格式。
原json:
{
"status": 200,
"msg": "success",
"data": {
"time": "1530236444",
"version": [{
"versionCode": 60000,
"versionName": "6.0.0"
}]
}
}
转换后:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"$id": "http://example.com/example.json",
"type": "object",
"title": "The root schema",
"description": "The root schema comprises the entire JSON document.",
"default": {},
"examples": [
{
"status": 2000,
"msg": "success",
"data": {
"time": "1530236444",
"version": [
{
"versionCode": 60000,
"versionName": "6.0.0"
}
]
}
}
],
"required": [
"status",
"msg",
"data"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"status": {
"$id": "#/properties/status",
"type": "integer",
"title": "The status schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": 0,
"examples": [
2000
]
},
"msg": {
"$id": "#/properties/msg",
"type": "string",
"title": "The msg schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": "",
"examples": [
"success"
]
},
"data": {
"$id": "#/properties/data",
"type": "object",
"title": "The data schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": {},
"examples": [
{
"time": "1530236444",
"version": [
{
"versionCode": 60000,
"versionName": "6.0.0"
}
]
}
],
"required": [
"time",
"version"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"time": {
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/time",
"type": "string",
"title": "The time schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": "",
"examples": [
"1530236444"
]
},
"version": {
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/version",
"type": "array",
"title": "The version schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": [],
"examples": [
[
{
"versionCode": 60000,
"versionName": "6.0.0"
}
]
],
"additionalItems": true,
"items": {
"anyOf": [
{
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/version/items/anyOf/0",
"type": "object",
"title": "The first anyOf schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": {},
"examples": [
{
"versionCode": 60000,
"versionName": "6.0.0"
}
],
"required": [
"versionCode",
"versionName"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"versionCode": {
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/version/items/anyOf/0/properties/versionCode",
"type": "integer",
"title": "The versionCode schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": 0,
"examples": [
60000
]
},
"versionName": {
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/version/items/anyOf/0/properties/versionName",
"type": "string",
"title": "The versionName schema",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"default": "",
"examples": [
"6.0.0"
]
}
}
}
],
"$id": "#/properties/data/properties/version/items"
}
}
}
}
}
}
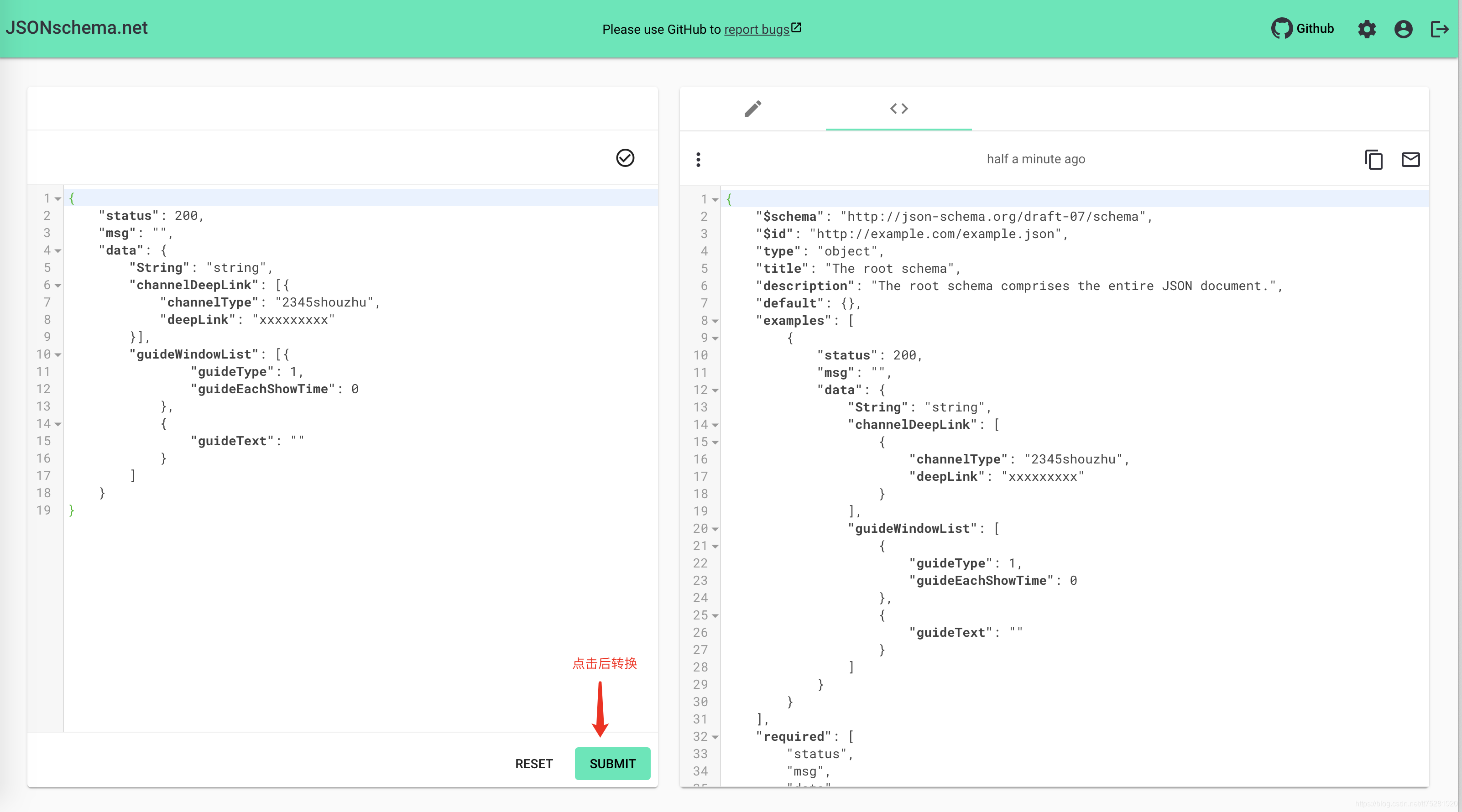
使用生成的json schema已经可以直接用于做接口的判断,但最好需要做修改优化,因为你生成的json数据不仅有很多的冗余字段你,而且只代表着这种条件下的接口响应,比如线上哪些配置下掉了,某个字段的值有多种状态,这种都是要做修改的。
3.2 修改优化json schema格式字符串
推荐使用在线编辑器"www.bejson.com"进行编辑。
在实际使用中一般会把$id、title、description、default、examples都去掉,因为这些都是些可有可无的东西,反而是太多了,造成干扰不是那么直观、简洁。
一般会根据数据节点的特征,只留下Type,需要用正则表达式匹配的留下pattern;需要特定长度的留下maxLengh和minLength等。

修改完的json schema如下:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema",
"type": "object",
"additionalProperties": true,
"required": [
"status",
"msg",
"data"
],
"properties": {
"status": {
"type": "integer",
"enum": [
200,
500
]
},
"msg": {
"type": "string",
"const": "success"
},
"data": {
"type": "object",
"required": [
"time",
"version"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"time": {
"type": "string"
},
"version": {
"type": "array",
"additionalItems": true,
"items": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "object",
"required": [
"versionCode",
"versionName"
],
"additionalProperties": true,
"properties": {
"versionCode": {
"type": "integer"
},
"versionName": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.3 校验修改后的json schema
生成的json schema可以使用在线校验工具来验证。
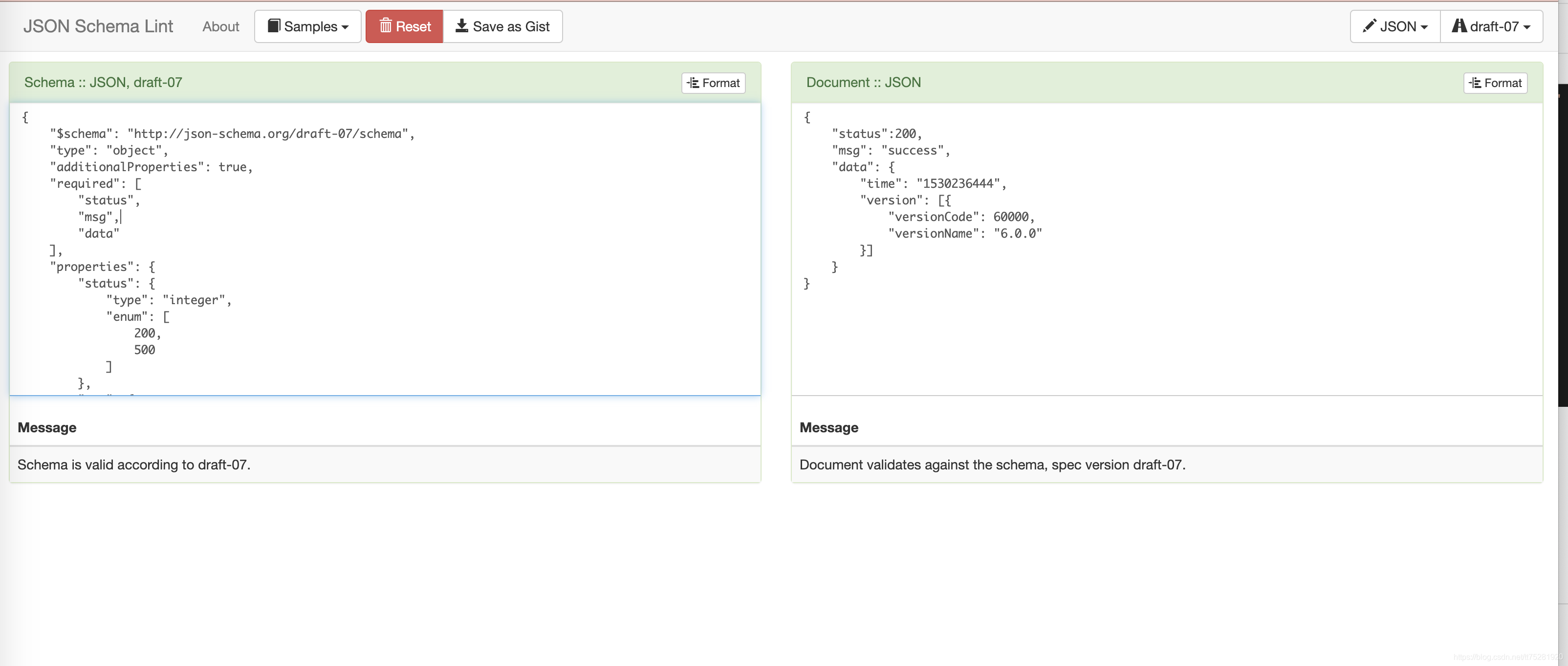
4 集成至jmeter
4.1 生成jar包
4.1.1 选择断言库
在java中,有如下几个库可拿来做json schema断言:
-
everit-org/json-schema [draft-07, -06, -04 (Apache License 2.0)]
-
Justify [draft-07, -06, -04 (Apache License 2.0)]
-
networknt/json-schema-validator [draft-07, -06, -04 Support OpenAPI 3.0 with Jackson parser (Apache License 2.0)]
-
java-json-tools (本文使用)
4.1.2 maven集成
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.java-json-tools</groupId>
<artifactId>json-schema-validator</artifactId>
<version>2.2.12</version>
</dependency>
4.1.3 编写代码
代码里有两个断言方法,满足两个场景,json schema直接传字符串或者读变量的值:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.github.fge.jackson.JsonLoader;
import com.github.fge.jsonschema.core.exceptions.ProcessingException;
import com.github.fge.jsonschema.core.report.ProcessingReport;
import com.github.fge.jsonschema.main.JsonSchema;
import com.github.fge.jsonschema.main.JsonSchemaFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 响应json格式断言类
* @author tangbincheng
* @date 2020-05-23
*/
public class AssertJson {
/**
* 通过json schema断言json是否符合要求
* @param schemaFileName 存放schema的文件名(包含路径)
* @param jsonStr json字符串
* @return 返回"test pass" or "test fail 与错误报告" or "test fail 与Excerption"
*/
public String verifyJsonSchemaByFile(String schemaFileName, String jsonStr) {
try{
String PKGBASE = String.valueOf('/') ;
JsonNode fstabSchema = JsonLoader.fromResource(PKGBASE + schemaFileName);
return new AssertJson().verifyJsonSchemaByJsonNode(fstabSchema, jsonStr);
}catch (IOException e){//Jmeter 的bean shell 使用java代码必须catch所有异常,不能Throw
return "IOException " + e.getMessage();
}catch (ProcessingException e){
return "ProcessingException" + e.getMessage();
}
}
/**
* 通过json schema断言json是否符合要求
* @param schemaStr json schema格式的字符串
* @param jsonStr json格式的字符串
* @return 返回"test pass" or "test fail 与错误报告" or "test fail 与Excerption"
*/
public String verifyJsonSchema(String schemaStr, String jsonStr) {
try{
JsonNode fstabSchema = JsonLoader.fromString(schemaStr);
return new AssertJson().verifyJsonSchemaByJsonNode(fstabSchema, jsonStr);
}catch (IOException e){//Jmeter 的bean shell 使用java代码必须catch所有异常,不能Throw
return "IOException " + e.getMessage();
}catch (ProcessingException e){
return "ProcessingException" + e.getMessage();
}
}
/**
*
* @param jsonSchemaNode
* @param jsonStr
* @return 返回"test pass" or "test fail 与错误报告" or "test fail 与Excerption"
* @throws IOException
* @throws ProcessingException
*/
public String verifyJsonSchemaByJsonNode(JsonNode jsonSchemaNode, String jsonStr) throws IOException, ProcessingException {
JsonNode respJson = JsonLoader.fromString(jsonStr);
JsonSchemaFactory factory = JsonSchemaFactory.byDefault();
JsonSchema schema = factory.getJsonSchema(jsonSchemaNode);
ProcessingReport report;
report = schema.validate(respJson);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (report.toString().contains("ListProcessingReport: success")){
sb.append("test pass");
}
if (report.toString().contains("ListProcessingReport: failure")){
sb.append("test fail") ;
sb.append("\n") ;
sb.append(report.toString()) ;
}
if(report.toString().contains("level: \"warning\"")){
sb.append("\n") ;
sb.append(" with warning!!!");
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
4.1.4 生成jar包
直接使用idel导出jar包即可
4.2 集成jmeter
4.2.1 jar包导入jmeter
将4.1中生成的jar包放置在jmeter目录的 /apache-jmeter-5.1.1/lib/ext/ 下
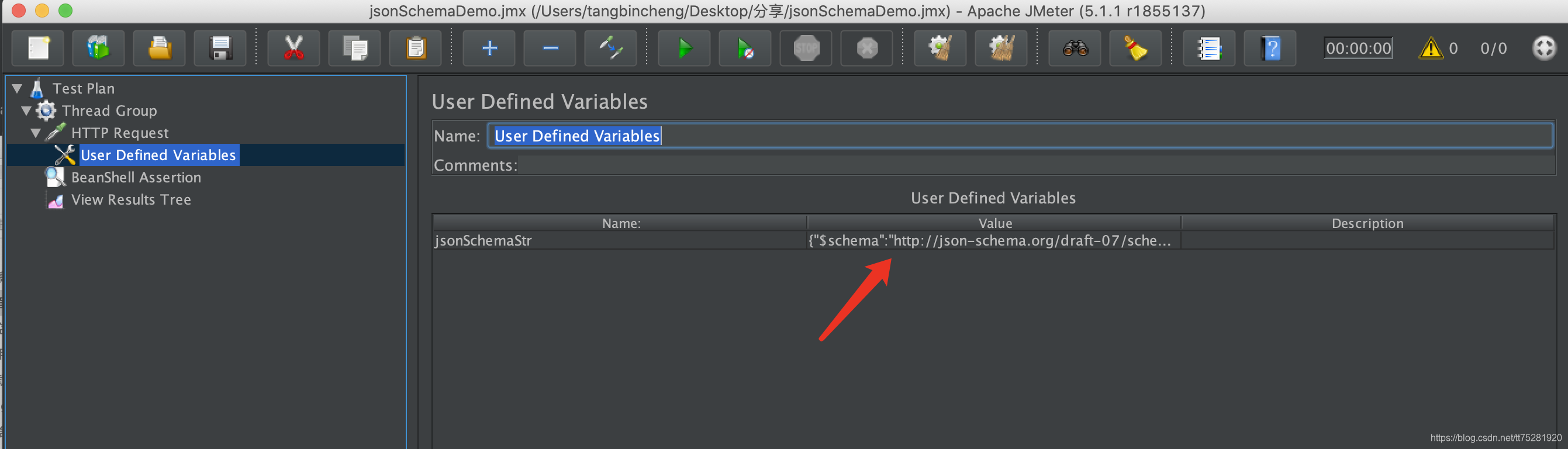
4.2.2 创建变量管理器User Defined Variables
用于放置生成的json schema字符串
4.2.3 创建响应断言器BeanShell Assertion
代码如下:
import com.xq.check.*;
String responseData = prev.getResponseDataAsString();
log.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>responseData: " + responseData);
String schemaData = vars.get("jsonSchemaStr");
log.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>schemaData: " + schemaData);
String assertResult = "";
try{
assertResult = new AssertJson().verifyJsonSchema(schemaData , responseData);
log.info(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>assertResult:" + assertResult);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
log.error("Beanshell failure: ", ex);
throw ex;
}
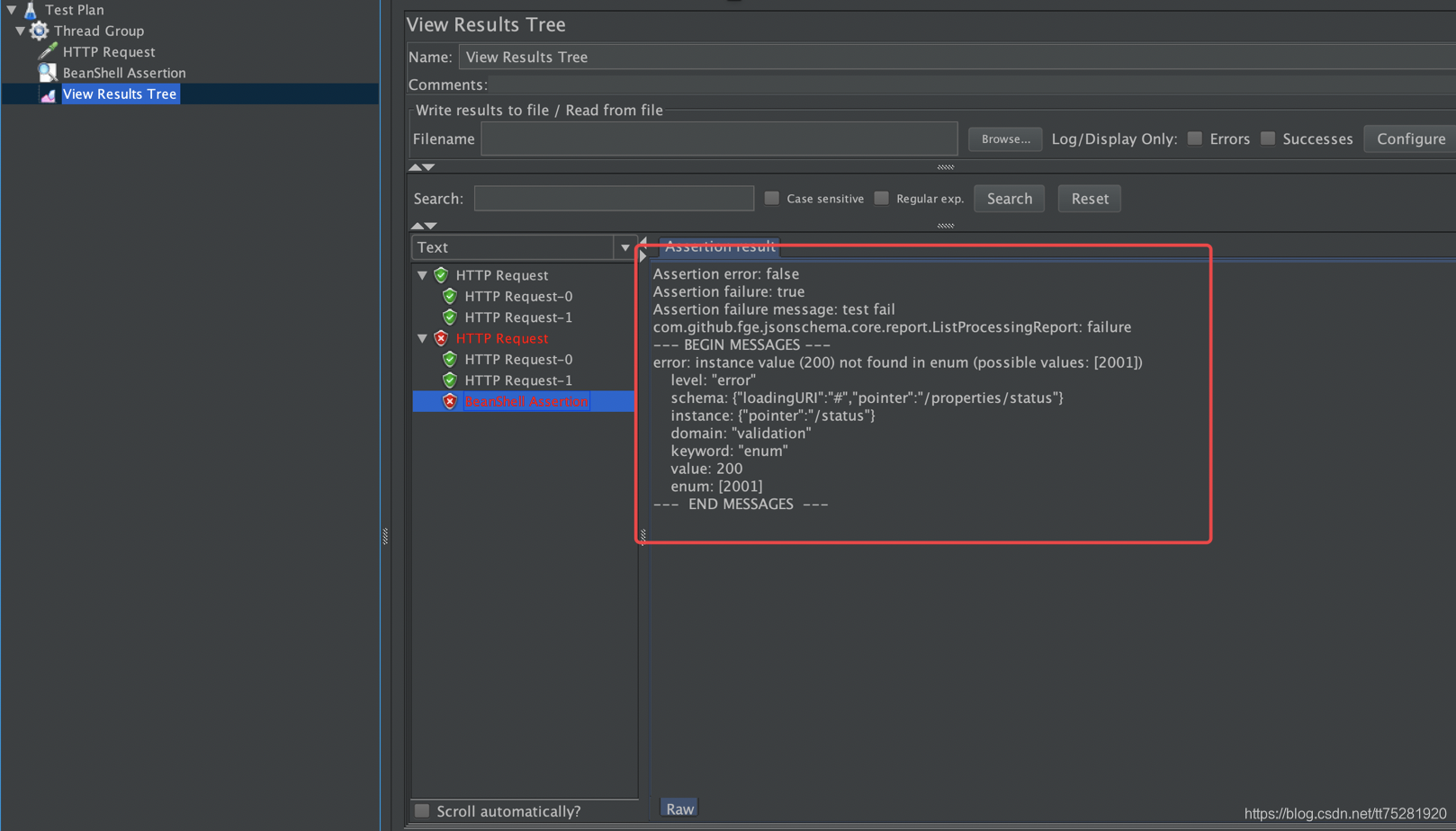
if(assertResult.contains("test fail")){
Failure = true;
FailureMessage = assertResult;
}

4.2.4运行查看结果