HashMap
Map接口的实现类有HashMap测试:
package cn.yzy.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class testMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("one", 1);
map.put("two", 2);
map.put("three", 3);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.get("one"));
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map.isEmpty());
System.out.println(map.containsKey("one"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(2));
System.out.println(map.containsKey("four"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(4));
Map<String, Integer> map1 = new HashMap<>();
map1.put("four", 4);
map1.put("five", 5);
map.putAll(map1);
System.out.println(map);
// map中键不能重复,如果重复新的会覆盖旧的(键的重复与否是通过equals方法判断的)
map.put("four", 404);
System.out.println(map);
map.remove("four");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
测试Map的实现类HashMap存储自定义类型
package cn.yzy.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/*
* 测试Map的实现类HashMap存储自定义类型
*/
public class testMap2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e1 = new Employee(202007171, "入门", 8000);
Employee e2 = new Employee(202007172, "专业", 12000);
Employee e3 = new Employee(202007173, "大神", 30000);
Map<Integer, Employee> map = new HashMap<Integer, Employee>();
map.put(1, e1);
map.put(2, e2);
map.put(3, e3);
System.out.println(map.get(1).toString());
System.out.println(map);
}
}
//雇员信息类
class Employee{
private int id;
private String name;
private double salary;
public Employee(int id, String name, double salary) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String toString() {
return "id:"+getId()+" name:"+getName()+" salary"+getSalary();
}
}
(1) 数组:占用空间连续。寻址容易,查询速度快。但是,增加和删除效率非常低。
(2) 链表:占用空间不连续。寻址困难,查询速度慢。但是,增加和删除效率非常高。
HashMap底层实现采用了哈希算法哈希表1,哈希表的本质就是“数组+链表, 因此HashMap在查找、删除、修改方面都有非常高的效率,HashMap是Map接口最常用的实现类。
由于底层采用了哈希表存储数据,我们要求键不能重复,如果发生重复,新的键值对会替换旧的键值对。
HashMap与HashTable的区别:
-
HashMap: 线程不安全,效率高。允许key或value为null。
-
HashTable: 线程安全,效率低。不允许key或value为null。
HashTable类和HashMap用法几乎一样,底层实现几乎一样,只不过HashTable的方法添加了synchronized关键字确保线程同步检查,效率较低。

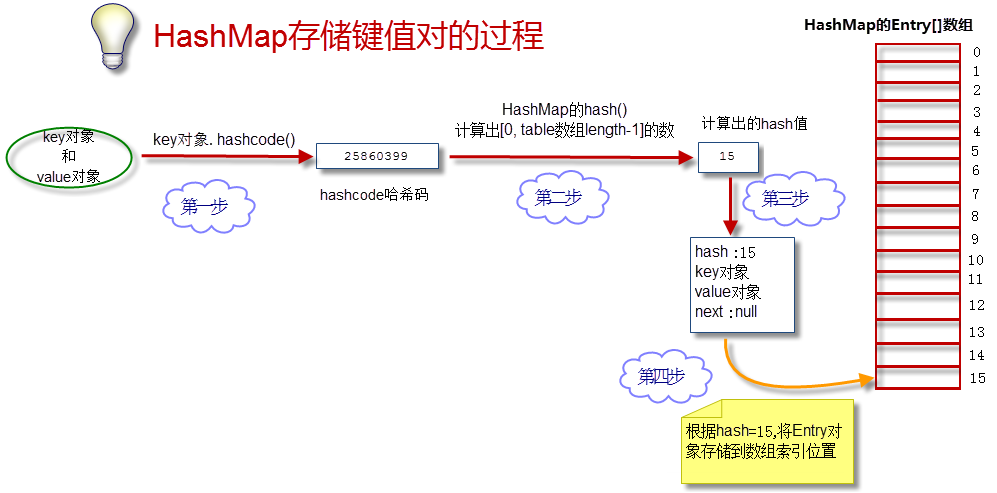
计算哈希值:
简单和常用的算法是(相除取余算法):
hash值 = hashcode%数组长度
“除法”,效率低下。JDK后来改进了算法。首先约定数组长度必须为2的整数幂,这样采用位运算即可实现取余的效果:hash值 = hashcode&(数组长度-1)
JDK8中,当链表长度大于8时,链表就转换为红黑树,这样又大大提高了查找的效率。
模拟实现HashMap
实现节点:
package mycollection;
public class sEntry<K, V> {
int hash; //哈希值
K keyK;
V vaV;
sEntry<K, V> nextEntry;
public sEntry() {
super();
}
public sEntry(int hash, K keyK, V vaV, sEntry<K, V> nextEntry) {
this.hash = hash;
this.keyK = keyK;
this.vaV = vaV;
this.nextEntry = nextEntry;
}
}
实现HashMap
package mycollection;
public class sHashMap<K, V> {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
sEntry[] table; //位桶数组 bucket array
int size; //存放的键值对个数
public sHashMap() {
table = new sEntry[16]; //长度一般定义成2的整数幂
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V get(K key) {
int hash = myHash(key.hashCode(), table.length);
sEntry<K, V> findEntry = table[hash];
while(findEntry != null) {
if(findEntry.keyK.equals(key))
return (V)findEntry.vaV;
findEntry = findEntry.nextEntry;
}return null;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
//是否需要扩容:
//定义新的节点对象
sEntry<K, V> newSEntry = new sEntry<K, V>();
newSEntry.hash = myHash(key.hashCode(), table.length);
newSEntry.keyK = key;
newSEntry.vaV = value;
newSEntry.nextEntry = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
sEntry<K, V> tmpEntry = table[newSEntry.hash];
sEntry<K, V> iSEntry = tmpEntry;
if(tmpEntry == null)
table[newSEntry.hash] = newSEntry;
else {
while(tmpEntry != null) {
//判断键值是否重复,重复就覆盖并结束
if(newSEntry.keyK.equals(tmpEntry.keyK)) {
tmpEntry.vaV = newSEntry.vaV;
return;
}
iSEntry = tmpEntry;
tmpEntry = tmpEntry.nextEntry;
}
//键值不重复尾插
iSEntry.nextEntry = newSEntry;
}
size++;
}
public int myHash(int k, int length) {
// System.out.println(v&(length-1));
// System.out.println(v%(length-1));
return k&(length-1);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("{");
for(int i=0; i<table.length; ++i) {
sb.append(i + ":");
sEntry<K, V> tmpEntry = table[i];
while(tmpEntry != null) {
sb.append("["+tmpEntry.keyK+","+tmpEntry.vaV+"]-->");
tmpEntry = tmpEntry.nextEntry;
}sb.append("null\n");
}sb.setCharAt(sb.length()-1, '}');
return sb.toString();
}
public void remove(K key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
sEntry<K, V> tmpEntry = table[myHash(key.hashCode(), table.length)];
sEntry<K, V> preEntry = tmpEntry;
sEntry<K, V> curEntry = tmpEntry;
if(curEntry.nextEntry == null) {
table[myHash(key.hashCode(), table.length)] = null;
size--;
return ;
}
while(curEntry != null) {
if(curEntry.keyK.equals(key)) {
preEntry.nextEntry = curEntry.nextEntry;
curEntry = null; //???????????
size--;
return ;
}
preEntry = curEntry;
curEntry = curEntry.nextEntry;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
sHashMap<Integer, String> sm = new sHashMap<Integer, String>();
sm.put(10, "aa");
sm.put(20, "bb");
sm.put(30, "dd");
sm.put(30, "cc");
sm.put(46, "ee");
sm.put(62, "ff");
System.out.println(sm);
System.out.println(sm.get(10));
System.out.println(sm.get(20));
System.out.println(sm.get(30));
System.out.println(sm.get(46));
System.out.println(sm.get(62));
System.out.println(sm.size());
sm.remove(46);
System.out.println(sm.size());
// System.out.println(sm);
sm.remove(62);
System.out.println(sm.size());
// System.out.println(sm);
sm.remove(30);
System.out.println(sm.size());
System.out.println(sm);
}
}
思考以上模拟实现的HashMap的remove方法是否存在内存泄露问题?
哈希表,这是一种非常重要的数据结构。对于我们以后理解很多技术都非常有帮助(比如:redis数据库的核心技术和HashMap一样)
结合数组和链表的优点(即查询快,增删效率也高) 就是“哈希表”,哈希表的本质就是“数组+链表 ↩︎