利用opendir函数实现tree功能
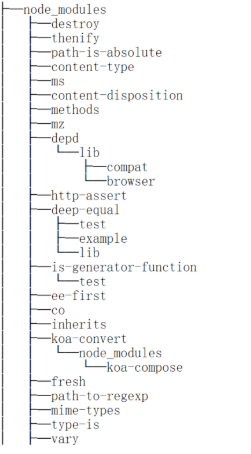
在ubuntu中tree的效果图
编写代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
int fun(const char *path_name,int i);
int main(int argc,const char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
{
perror("input error\n");
return 0;
}
fun(argv[1],0);
return 0;
}
int fun(const char *path_name,int i)
{
DIR *dp = opendir(path_name);
struct dirent*ep = NULL;
char phname[512]={
0};
while(1)
{
ep = readdir(dp);
if(ep==NULL)
{
return -1;
}
if(ep->d_name[0]!='.')
{
//&& (readdir(dp)!=NULL)
for(int n=0; n<i; n++)
{
if(n%2==0)
printf("|");
printf(" ");
}
printf("|__%s",ep->d_name);
printf("\n");
if(ep->d_type==4)
{
sprintf(phname,"%s/%s",path_name,ep->d_name);
fun(phname,i+2);
}
}
//printf("%d\n",ep->d_type);
}
}
编译运行,虽然不是完全一模一样,但是也实现了tree的效果
