__format__()方法
__format__()传参方法:someobject.__format__(specification)
specification为指定格式,当应用程序中出现"{0:specification}".format(someobject)或format(someobject, specification)时,会默认以这种方式调用
当specification为" "时,一种合理的返回值是return str(self),这为各种对象的字符串表示形式提供了明确的一致性
注意,"{0!s}".format()和"{0!r}".format()并不会调用__format__()方法,他们会直接调用__str__()或者__repr__()
例:自定义我们自己的__format__()格式
#coding=utf-8 class formatest: def __init__(self, name, age): self.name,self.age = name, age def __format__(self,specification): if specification == "": return str(self) strformat = specification.replace("%s",self.name).replace("%r",self.age) return strformat if __name__ == "__main__": people = formatest("zhanglin", "31") print ("{}".format(people)) print ("{0:%s-%r}".format(people)) print (format(people, "%s-%r"))
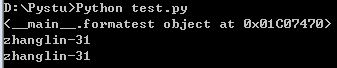
例:格式化对象中的集合
#coding=utf-8 class people: def __init__(self, name, age): self.name,self.age = name, age def __format__(self,specification): if specification == "": return str(self) strformat = specification.replace("%s",self.name).replace("%r",self.age) return strformat class hand: def __init__(self, *people): self.peoples = [] self.peoples= list(people) def __format__(self, specification): if specification == "": return str(self) return ",".join("{:{fs}}".format(c, fs=specification) for c in self.peoples) if __name__ == "__main__": handobj = hand(people("zhangsan", "18"), people("lisi", "28"), people("zhanglin", "38")) print ("{:%s-%r}".format(handobj))
