概述
如果流程围绕失误的状态流转,这时候就要用到状态机,状态机描述一个事务,有多种状态,不同的动作作用再状态上导致抓状态的转换,这里面有三个重点
- 状态 : 睡觉,工作,吃饭
- 事件 : 起床,饥饿,疲惫
- 动作 : 比如说闹铃触发了
起床事件导致状态 从睡觉->工作(可以省略)
总体就是,首先触发某个事件,导致了状态的改变, 闹铃触发起床事件,导致状态的改变睡觉-->工作
而Android中提供了状态机,在frameworks层源码frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/util,如果项目中需要使用可以把对应的三个类拷贝到项目中StateMachine.java、State、IState
源码分析
IState
public interface IState {
/**
* Returned by processMessage to indicate the the message was processed.
* 由 processMessage 返回以指示消息已处理。
*/
static final boolean HANDLED = true;
/**
* Returned by processMessage to indicate the the message was NOT processed.
* 由 processMessage 返回以指示消息未被处理。
*/
static final boolean NOT_HANDLED = false;
/**
* Called when a state is entered.
* 进入状态时调用
*
*/
void enter();
/**
* Called when a state is exited.
* 退出一个状态时调用
*/
void exit();
/**
* Called when a message is to be processed by the
* state machine.
*
* This routine is never reentered thus no synchronization
* is needed as only one processMessage method will ever be
* executing within a state machine at any given time. This
* does mean that processing by this routine must be completed
* as expeditiously as possible as no subsequent messages will
* be processed until this routine returns.
*
* @param msg to process
* @return HANDLED if processing has completed and NOT_HANDLED
* if the message wasn't processed.
*/
boolean processMessage(Message msg);
/**
* Name of State for debugging purposes.
*
* @return name of state.返回状态的名字
*/
String getName();
}
状态的接口,定义了基本的方法,State实现了IState,我们自定义的状态需要直接继承State
StateMachine
构造方法
private void initStateMachine(String name, Looper looper) {
mName = name;
mSmHandler = new SmHandler(looper, this);
}
protected StateMachine(String name) {
mSmThread = new HandlerThread(name);
mSmThread.start();
Looper looper = mSmThread.getLooper();
initStateMachine(name, looper);
}
public StateMachine(String name, Looper looper) {
initStateMachine(name, looper);
}
private void initStateMachine(String name, Looper looper) {
mName = name;
mSmHandler = new SmHandler(looper, this);
}
有三个构造方法,可以外部传入Looper,如果外部不传入就自动 new HandlerThread,最终创建SmHandler,他是StateMachine的内部类,他的角色相当于上面说的动作
addState
private HashMap<State, StateInfo> mStateInfo =new HashMap<State, StateInfo>();
private final StateInfo addState(State state, State parent) {
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "addStateInternal: E state=" + state.getName()
+ ",parent=" + ((parent == null) ? "" : parent.getName()));
}
StateInfo parentStateInfo = null;
if (parent != null) {
parentStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(parent);
if (parentStateInfo == null) {
// Recursively add our parent as it's not been added yet.
parentStateInfo = addState(parent, null);
}
}
StateInfo stateInfo = mStateInfo.get(state);
if (stateInfo == null) {
stateInfo = new StateInfo();
mStateInfo.put(state, stateInfo);
}
// Validate that we aren't adding the same state in two different hierarchies.
if ((stateInfo.parentStateInfo != null) &&
(stateInfo.parentStateInfo != parentStateInfo)) {
throw new RuntimeException("state already added");
}
stateInfo.state = state;
stateInfo.parentStateInfo = parentStateInfo;
stateInfo.active = false;
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "addStateInternal: X stateInfo: " + stateInfo);
return stateInfo;
}
private class StateInfo {
/** The state */
State state;
/** The parent of this state, null if there is no parent */
StateInfo parentStateInfo;
/** True when the state has been entered and on the stack */
boolean active;
/**
* Convert StateInfo to string
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "state=" + state.getName() + ",active=" + active
+ ",parent=" + ((parentStateInfo == null) ?
"null" : parentStateInfo.state.getName());
}
}
像状态机添加状态,可以看到最外层使用HashMap存储key=State,value=StateInfo,而StateInfo中储存了当前状态和是否激活,和当前状态的父节点
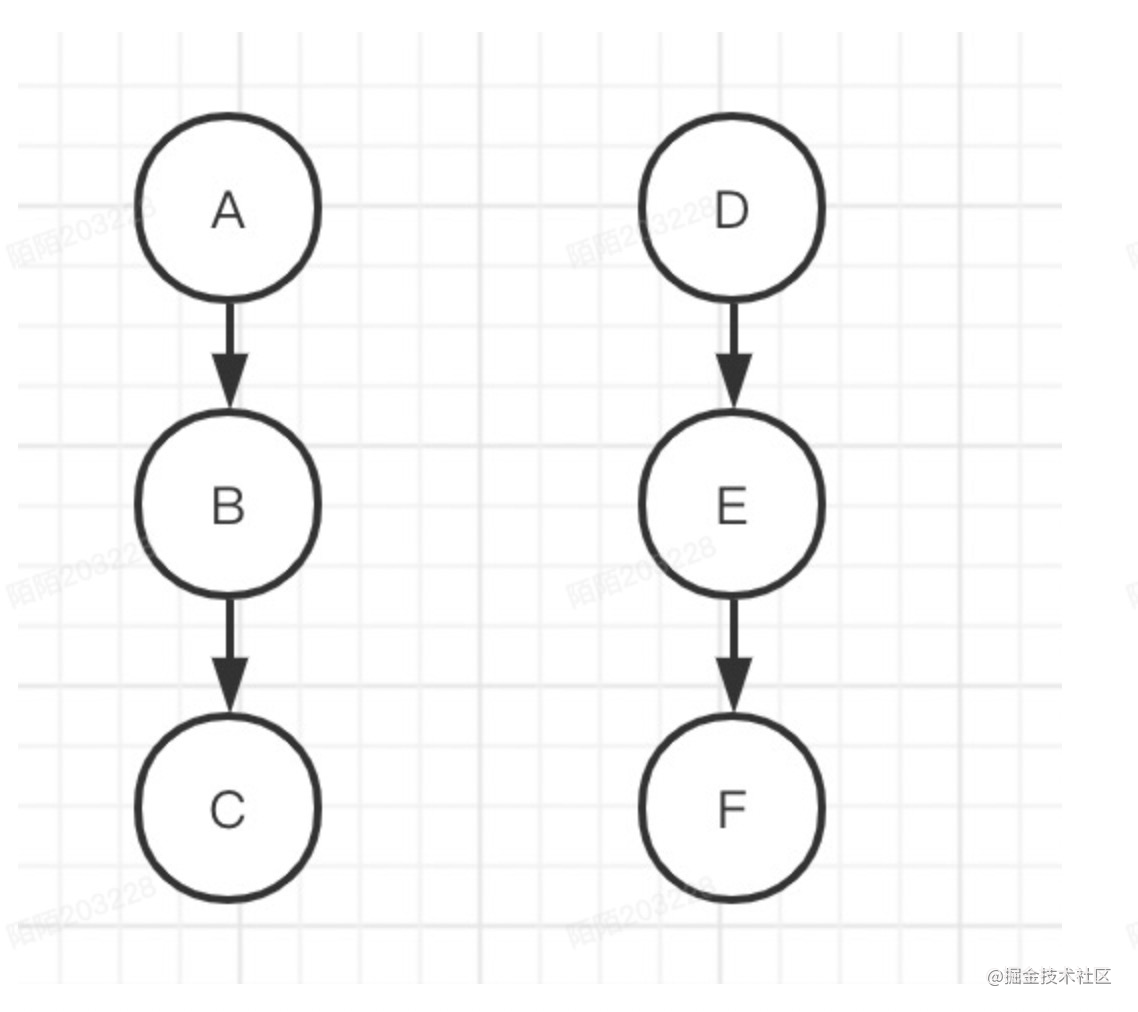
假如说目前有六个状态,A->B->C 和 D->E->F,C是B的父节点,B是A的父节点
setInitialState 设置除初始化状态
public final void setInitialState(State initialState) {
mSmHandler.setInitialState(initialState);
}
private final void setInitialState(State initialState) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "setInitialState: initialState=" + initialState.getName());
mInitialState = initialState;
}
假如现在设的初始状态为 C
状态机开始
public void start() {
// mSmHandler can be null if the state machine has quit.
if (mSmHandler == null) return;
/** Send the complete construction message */
mSmHandler.completeConstruction();
}
private final void completeConstruction() {
//首先拿到状态树的最大深度
int maxDepth = 0;
for (StateInfo si : mStateInfo.values()) {
int depth = 0;
for (StateInfo i = si; i != null; depth++) {
i = i.parentStateInfo;
}
if (maxDepth < depth) {
maxDepth = depth;
}
}
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "completeConstruction: maxDepth=" + maxDepth);
//根据最大深度初始化状态栈,和临时状态栈
mStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
mTempStateStack = new StateInfo[maxDepth];
setupInitialStateStack();
/** Sending SM_INIT_CMD message to invoke enter methods asynchronously */
//发送初始化消息给Handler
sendMessageAtFrontOfQueue(obtainMessage(SM_INIT_CMD, mSmHandlerObj));
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "completeConstruction: X");
}
//根据初始状态填充mTempStateStack 临时栈
private final void setupInitialStateStack() {
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "setupInitialStateStack: E mInitialState="
+ mInitialState.getName());
}
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(mInitialState);
for (mTempStateStackCount = 0; curStateInfo != null; mTempStateStackCount++) {
mTempStateStack[mTempStateStackCount] = curStateInfo;
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
}
// Empty the StateStack
mStateStackTopIndex = -1;
moveTempStateStackToStateStack();
}
//然后把mTempStateStack翻转填充mStateStack
private final int moveTempStateStackToStateStack() {
int startingIndex = mStateStackTopIndex + 1;
int i = mTempStateStackCount - 1;
int j = startingIndex;
while (i >= 0) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "moveTempStackToStateStack: i=" + i + ",j=" + j);
mStateStack[j] = mTempStateStack[i];
j += 1;
i -= 1;
}
mStateStackTopIndex = j - 1;
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop="
+ mStateStackTopIndex + ",startingIndex=" + startingIndex
+ ",Top=" + mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].state.getName());
}
return startingIndex;
}
这里一共做了一下几件事情
- 计算出状态树的最大深度
- 根据最大深度初始化俩个数组
- 然后根据初始的State 填充数组
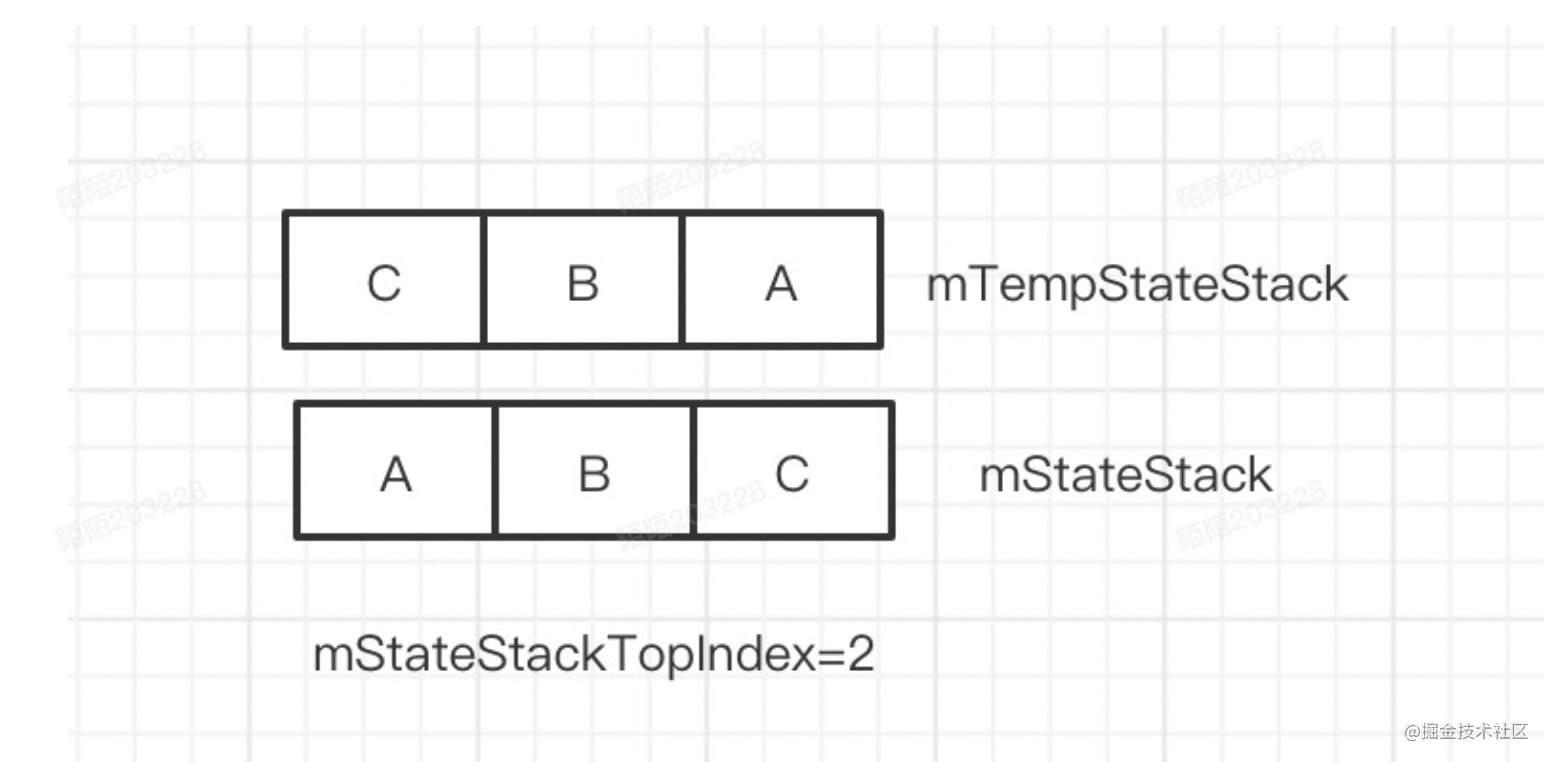
此时数组状态,也就是说从mStateStack按照mStateStackTopIndex取出的状态是C
Handler处理初始化
public final void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "handleMessage: E msg.what=" + msg.what);
/** Save the current message */
mMsg = msg;
if (mIsConstructionCompleted) {
/** Normal path */
processMsg(msg);
} else if (!mIsConstructionCompleted &&
(mMsg.what == SM_INIT_CMD) && (mMsg.obj == mSmHandlerObj)) {
/** Initial one time path. */
//第一次初始化走这里
mIsConstructionCompleted = true;
invokeEnterMethods(0);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("StateMachine.handleMessage: " +
"The start method not called, received msg: " + msg);
}
//处理状态的切换
performTransitions();
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "handleMessage: X");
}
private final void invokeEnterMethods(int stateStackEnteringIndex) {
for (int i = stateStackEnteringIndex; i <= mStateStackTopIndex; i++) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "invokeEnterMethods: " + mStateStack[i].state.getName());
mStateStack[i].state.enter();
mStateStack[i].active = true;
}
}
第一次初始化做了俩件事情
- 首先把`mIsConstructionCompleted = true;
- 然后把invokeEnterMethods(0)方法,由于传入的是0,所以把mStateStack中所有的状态都调用
mStateStack[i].state.enter();mStateStack[i].active = true;全部激活
如果已经初始化完成了调用processMsg
private final void processMsg(Message msg) {
//首先从mStateStack取出顶部状态
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex];
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "processMsg: " + curStateInfo.state.getName());
}
if (isQuit(msg)) {
transitionTo(mQuittingState);
} else {
//调用状态的processMessage方法,如果没处理就调用父节点,如果父节点也不处理,就提跳出循环
while (!curStateInfo.state.processMessage(msg)) {
/**
* Not processed
*/
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
if (curStateInfo == null) {
/**
* No parents left so it's not handled
*/
mSm.unhandledMessage(msg);
break;
}
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "processMsg: " + curStateInfo.state.getName());
}
}
}
这个就做了俩件事情
- 首先从
mStateStack取出顶部状态(目前来说就是取出了C) - 调用
State的processMessage方法,如果没处理就调用父节点,如果父节点也不处理,就提跳出循环
怎么切换状态呢?
private final void transitionTo(IState destState) {
mDestState = (State) destState;
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "transitionTo: destState=" + mDestState.getName());
}
用这个方法切换状态,参数就是目标状态,我们看到再handleMessage中,除了调用State的processMessage方法,还调用了performTransitions来处理状态的切换,看下这个方法
private void performTransitions() {
/**
* If transitionTo has been called, exit and then enter
* the appropriate states. We loop on this to allow
* enter and exit methods to use transitionTo.
*/
State destState = null;
while (mDestState != null) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "handleMessage: new destination call exit");
/**
* Save mDestState locally and set to null
* to know if enter/exit use transitionTo.
*/
destState = mDestState;
mDestState = null;
/**
* Determine the states to exit and enter and return the
* common ancestor state of the enter/exit states. Then
* invoke the exit methods then the enter methods.
*/
StateInfo commonStateInfo = setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter(destState);
invokeExitMethods(commonStateInfo);
int stateStackEnteringIndex = moveTempStateStackToStateStack();
invokeEnterMethods(stateStackEnteringIndex);
/**
* Since we have transitioned to a new state we need to have
* any deferred messages moved to the front of the message queue
* so they will be processed before any other messages in the
* message queue.
*/
moveDeferredMessageAtFrontOfQueue();
}
}
假如目标状态为F,先走setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter
private final StateInfo setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter(State destState) {
/**
* Search up the parent list of the destination state for an active
* state. Use a do while() loop as the destState must always be entered
* even if it is active. This can happen if we are exiting/entering
* the current state.
*/
mTempStateStackCount = 0;
StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateInfo.get(destState);
do {
mTempStateStack[mTempStateStackCount++] = curStateInfo;
curStateInfo = curStateInfo.parentStateInfo;
} while ((curStateInfo != null) && !curStateInfo.active);
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "setupTempStateStackWithStatesToEnter: X mTempStateStackCount="
+ mTempStateStackCount + ",curStateInfo: " + curStateInfo);
}
return curStateInfo;
}
这个就是按照顺序把destState和他的父节点依次填入mTempStateStack,这里返回值为null,因为新的状态都没有被激活过,此时mTemStateStack数据为
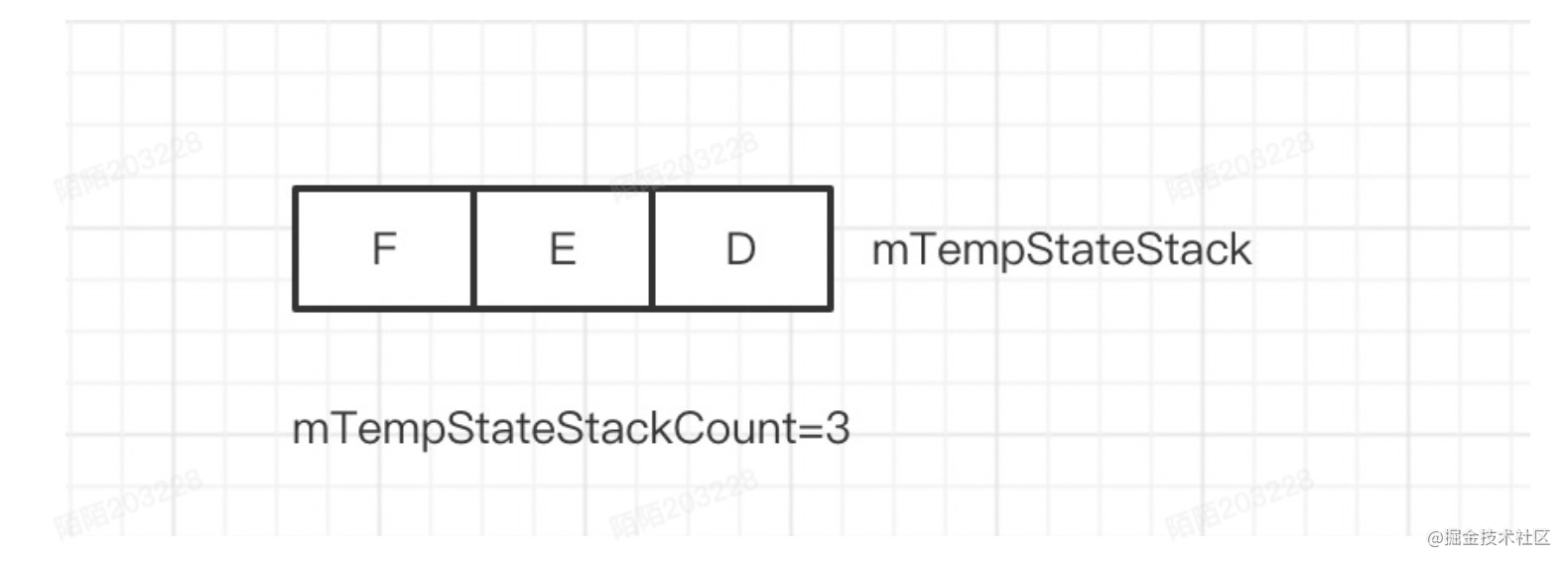
然后调用invokeExitMethods(commonStateInfo);
private final void invokeExitMethods(StateInfo commonStateInfo) {
while ((mStateStackTopIndex >= 0) &&
(mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex] != commonStateInfo)) {
State curState = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].state;
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "invokeExitMethods: " + curState.getName());
curState.exit();
mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].active = false;
mStateStackTopIndex -= 1;
}
}
这里表示把之前mStateStack数据exit,并且active = false,此时mStateStack状态为
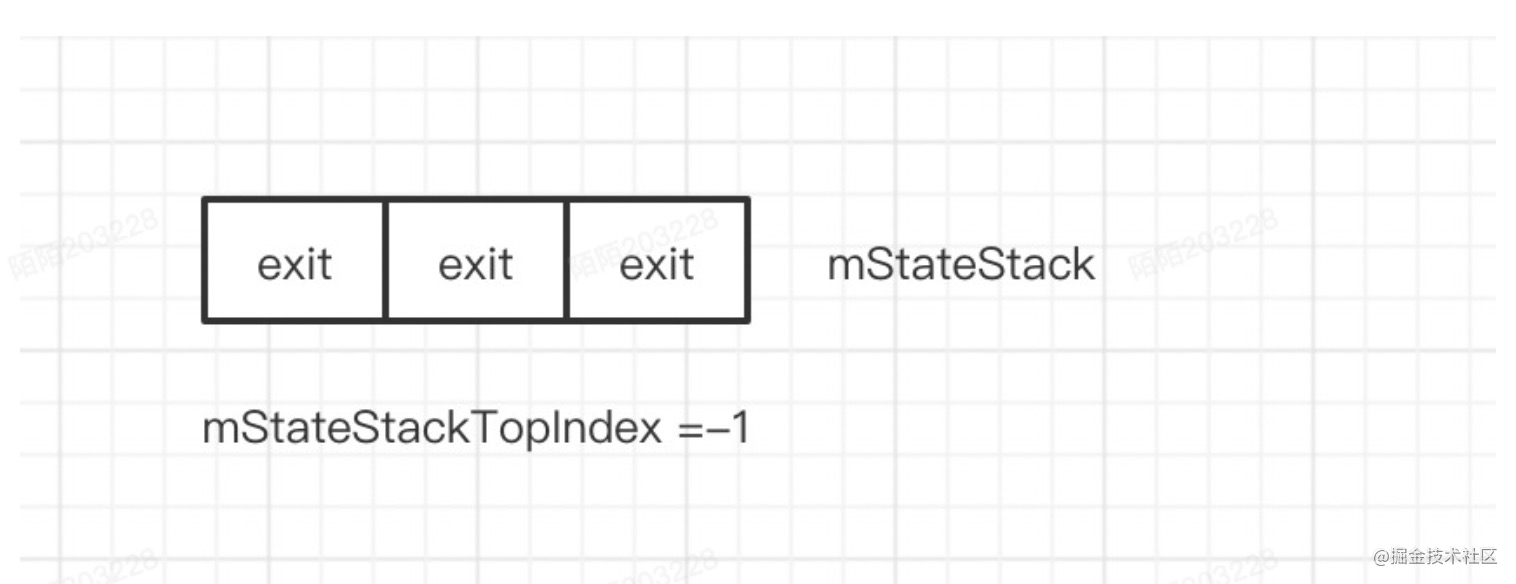
接下来调用moveTempStateStackToStateStack
private final int moveTempStateStackToStateStack() {
int startingIndex = mStateStackTopIndex + 1;
int i = mTempStateStackCount - 1;
int j = startingIndex;
while (i >= 0) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "moveTempStackToStateStack: i=" + i + ",j=" + j);
mStateStack[j] = mTempStateStack[i];
j += 1;
i -= 1;
}
mStateStackTopIndex = j - 1;
if (mDbg) {
Log.d(TAG, "moveTempStackToStateStack: X mStateStackTop="
+ mStateStackTopIndex + ",startingIndex=" + startingIndex
+ ",Top=" + mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex].state.getName());
}
return startingIndex;
}
这个就是把mTempStateStack翻转填充mStateStack,此时mStateStack状态为,此时返回值为0
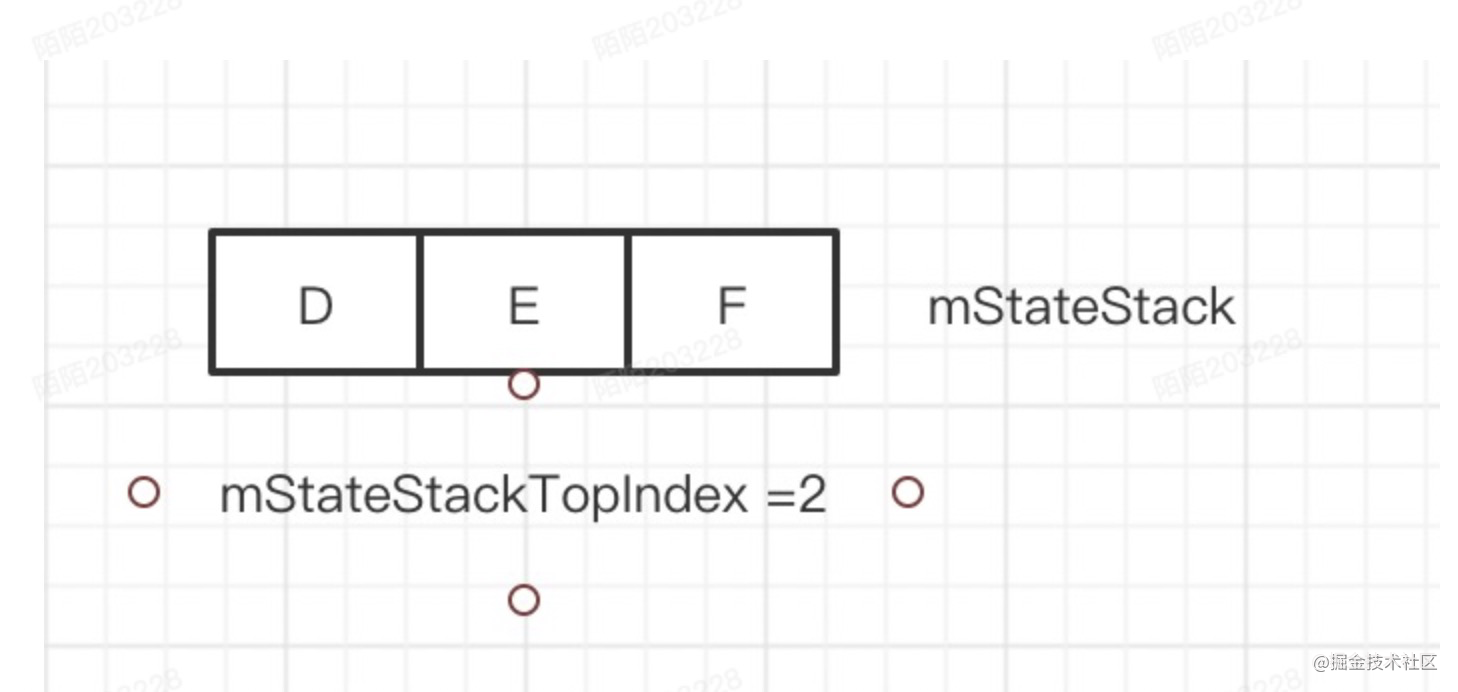
最后调用
private final void invokeEnterMethods(int stateStackEnteringIndex) {
for (int i = stateStackEnteringIndex; i <= mStateStackTopIndex; i++) {
if (mDbg) Log.d(TAG, "invokeEnterMethods: " + mStateStack[i].state.getName());
mStateStack[i].state.enter();
mStateStack[i].active = true;
}
}
把mStateStack中的状态激活,此时抓状态就装换完毕了,下次handle处理数据 StateInfo curStateInfo = mStateStack[mStateStackTopIndex]就是拿到的新的状态
这只是讨论其中一种情况切换到了状态F,如果切换到状态B呢?有些区差异,但基本差不多
使用
public class MyStateMachine extends StateMachine {
private static final String TAG = "mmm";
//设置状态改变事件
public static final int MSG_WAKEUP = 1; // 消息:醒
public static final int MSG_TIRED = 2; // 消息:困
public static final int MSG_HUNGRY = 3; // 消息:饿
private static final int MSG_HALTING = 4; // 状态机暂停消息
//创建状态
private State mBoringState = new BoringState();// 默认状态
private State mWorkState = new WorkState(); // 工作
private State mEatState = new EatState(); // 吃
private State mSleepState = new SleepState(); // 睡
/**
* 构造方法
*
* @param name
*/
MyStateMachine(String name) {
super(name);
//加入状态,初始化状态
addState(mBoringState, null);
addState(mSleepState, mBoringState);
addState(mWorkState, mBoringState);
addState(mEatState, mBoringState);
// sleep状态为初始状态
setInitialState(mSleepState);
}
/**
* @return 创建启动person 状态机
*/
public static MyStateMachine makePerson() {
MyStateMachine person = new MyStateMachine("Person");
person.start();
return person;
}
@Override
public void onHalting() {
synchronized (this) {
this.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 定义状态:无聊
*/
class BoringState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ enter Boring ############");
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ exit Boring ############");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
Log.e(TAG, "BoringState processMessage.....");
return true;
}
}
/**
* 定义状态:睡觉
*/
class SleepState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ enter Sleep ############");
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ exit Sleep ############");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
Log.e(TAG, "SleepState processMessage.....");
switch (msg.what) {
// 收到清醒信号
case MSG_WAKEUP:
Log.e(TAG, "SleepState MSG_WAKEUP");
// 进入工作状态
transitionTo(mWorkState);
//...
//...
//发送饿了信号...
sendMessage(obtainMessage(MSG_HUNGRY));
break;
case MSG_HALTING:
Log.e(TAG, "SleepState MSG_HALTING");
// 转化到暂停状态
transitionToHaltingState();
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* 定义状态:工作
*/
class WorkState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ enter Work ############");
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ exit Work ############");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
Log.e(TAG, "WorkState processMessage.....");
switch (msg.what) {
// 收到 饿了 信号
case MSG_HUNGRY:
Log.e(TAG, "WorkState MSG_HUNGRY");
// 吃饭状态
transitionTo(mEatState);
//...
//...
// 发送累了信号...
sendMessage(obtainMessage(MSG_TIRED));
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* 定义状态:吃
*/
class EatState extends State {
@Override
public void enter() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ enter Eat ############");
}
@Override
public void exit() {
Log.e(TAG, "############ exit Eat ############");
}
@Override
public boolean processMessage(Message msg) {
Log.e(TAG, "EatState processMessage.....");
switch (msg.what) {
// 收到 困了 信号
case MSG_TIRED:
Log.e(TAG, "EatState MSG_TIRED");
// 睡觉
transitionTo(mSleepState);
//...
//...
// 发出结束信号...
sendMessage(obtainMessage(MSG_HALTING));
break;
default:
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
调用
// 获取 状态机引用
MyStateMachine personStateMachine = MyStateMachine.makePerson();
// 初始状态为SleepState,发送消息MSG_WAKEUP
personStateMachine.sendMessage(MyStateMachine.MSG_WAKEUP);
日志
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ enter Boring ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ enter Sleep ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: SleepState processMessage.....
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: SleepState MSG_WAKEUP
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ exit Sleep ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ enter Work ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: WorkState processMessage.....
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: WorkState MSG_HUNGRY
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ exit Work ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ enter Eat ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: EatState processMessage.....
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: EatState MSG_TIRED
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ exit Eat ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ enter Sleep ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: SleepState processMessage.....
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: SleepState MSG_HALTING
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ exit Sleep ############
2021-08-12 18:20:03.137 6035-8981/com.example.myapplication E/mmm: ############ exit Boring ############
这里最重要的是要分清楚 状态和事件,首先触发某个事件,导致了状态的改变, 闹铃触发起床事件,导致状态的改变睡觉-->工作
这里首先把所有的状态都加入到了状态机,然后设置初始状态是为Sleep,然后就调用了start
所以开始就会把Sleep和其父节点加入状态栈中,然后调用enter,然后调用personStateMachine.sendMessage(MyStateMachine.MSG_WAKEUP);这里可以这样理解,sendMessage表示都动作,MyStateMachine.MSG_WAKEUP表示事件,然后SleepState接收事件情,触发状态的改变 transitionTo(mWorkState);
也就是说当前状态SleepState只接受接收事件MSG_WAKEUP,如果是其他事件,当前状态不接受,也就不会改变状态,比如当前状态时睡觉,触发事件吃饭,睡觉时不能吃饭,所以是个无效事件