目录
个人博客
www.tothefor.com
介绍一些在竞赛中会用到的集合(容器),和使用方法。具体一些的用法可见《JAVA基础学习-集合》
而本文是快速介绍和一些基本用法。最主要的还是要知道有这些东西,比赛时针对不同的场景用不同的集合(容器)。因为我从C++转过来的,所以对C++里面的容器使用比较了解。而本文不仅会把JAVA中特有的集合介绍一下,还会把C++中的容器如何在JAVA中使用也介绍一下。因为,C++中的一些容器确实很好用而且用的还挺多,但在JAVA中却很少。
1.JAVA
ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet、TreeMap、HashMap、LinkedHashMap 可见《JAVA基础学习-集合》
Map.Entry
一个Java中类似于C++中的Pair的容器。Map.Entry是Map的一个内部接口。配合Map使用。
主要的三个方法。
- K getKey():
- V getValue():
- V setValue(V value)
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedHashMap<String,Integer> lm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
lm.put("C",3);
lm.put("A",1);
lm.put("B",2);
lm.put("D",4);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> ent = lm.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = ent.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> mid = it.next();
System.out.println(mid.getKey());
System.out.println(mid.getValue());
}
}
//输出
C
3
A
1
B
2
D
4
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
LinkedHashMap<String,Integer> lm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
lm.put("C",3);
lm.put("A",1);
lm.put("B",2);
lm.put("D",4);
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> ent = lm.entrySet();
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = ent.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> mid = it.next();
System.out.println(mid.getKey());
System.out.println(mid.getValue());
mid.setValue(23);
}
System.out.println("修改后:");
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it2 = ent.iterator();
while(it2.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<String,Integer> mid = it2.next();
System.out.println(mid.getKey());
System.out.println(mid.getValue());
}
}
//输出
C
3
A
1
B
2
D
4
修改后:
C
23
A
23
B
23
D
23
2.C++
如何把C++中有的容器也用在JAVA中。需要注意的是,尽管C++中的容器在JAVA中也能使用,但是,并不是完全一样的,可能在JAVA中效率很低。这里只是说明在JAVA中也有,具体的使用情况根据实际而定。
2.1 Stack(栈)
Stack 类表示后进先出(LIFO)的对象堆栈。它通过五个操作对类 Vector 进行了扩展 ,允许将向量视为堆栈。它提供了通常的 push 和 pop 操作,以及取堆栈顶点的 peek 方法、测试堆栈是否为空的 empty 方法、在堆栈中查找项并确定到堆栈顶距离的 search 方法。
因为它继承自Vector,那么它的实现原理是以数组实现堆栈的。如果要以链表方式实现堆栈可以使用LinkedList!Stack只有下面几个方法!由于Stack继承了Vector ,它也有Vector的API方法!
| 返回值 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
boolean |
empty()测试此堆栈是否为空。 |
E |
peek()查看栈顶元素。 |
E |
pop()删除栈顶元素,并将该元素作为返回值返回。 |
E |
`push(E item)添加元素到堆栈的顶部。与addElement(item)效果完全相同。 |
int |
search(Object o)返回一个对象在此堆栈上的基于1的位置。 |
来自Vector的方法有:add, add, addAll, addAll, addElement, capacity, clear, clone, contains, containsAll, copyInto, elementAt, elements, ensureCapacity, equals, firstElement, forEach, get, hashCode, indexOf, indexOf, insertElementAt, isEmpty, iterator, lastElement, lastIndexOf, lastIndexOf, listIterator, listIterator, remove, remove, removeAll, removeAllElements, removeElement, removeElementAt, removeIf, removeRange, replaceAll, retainAll, set, setElementAt, setSize, size, sort, spliterator, subList, toArray, toArray, toString, trimToSize
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Stack<Integer> s = new Stack<Integer>();
System.out.println(s.empty()? "是空的":"不是空的");
System.out.println("现在Stack的大小为:"+s.size());
System.out.println("输入第一个元素:");
int a = sc.nextInt();
s.push(a);
System.out.println(s.empty()? "是空的":"不是空的");
System.out.println("现在Stack的大小为:"+s.size());
System.out.println("输入第二个元素:");
int b = sc.nextInt();
s.push(b);
System.out.println(s.empty()? "是空的":"不是空的");
System.out.println("现在Stack的大小为:"+s.size());
System.out.println("输入第三个元素:");
int c = sc.nextInt();
s.push(c);
System.out.println(s.empty()? "是空的":"不是空的");
System.out.println("现在Stack的大小为:"+s.size());
System.out.println("Stack中的元素有:");
while (!s.empty()){
System.out.println(s.peek());
System.out.println("删除了:"+s.pop()); //删除
}
}
//依次输入
7
13
23
//输出
是空的
现在Stack的大小为:0
输入第一个元素:
7
不是空的
现在Stack的大小为:1
输入第二个元素:
13
不是空的
现在Stack的大小为:2
输入第三个元素:
23
不是空的
现在Stack的大小为:3
Stack中的元素有:
23
删除了:23
13
删除了:13
7
删除了:7
Stack的用法还是挺简单的。
2.2 Vector(向量)
方法有点多。。。。帖张图吧。还有就是vector是线程安全的,所以效率低。
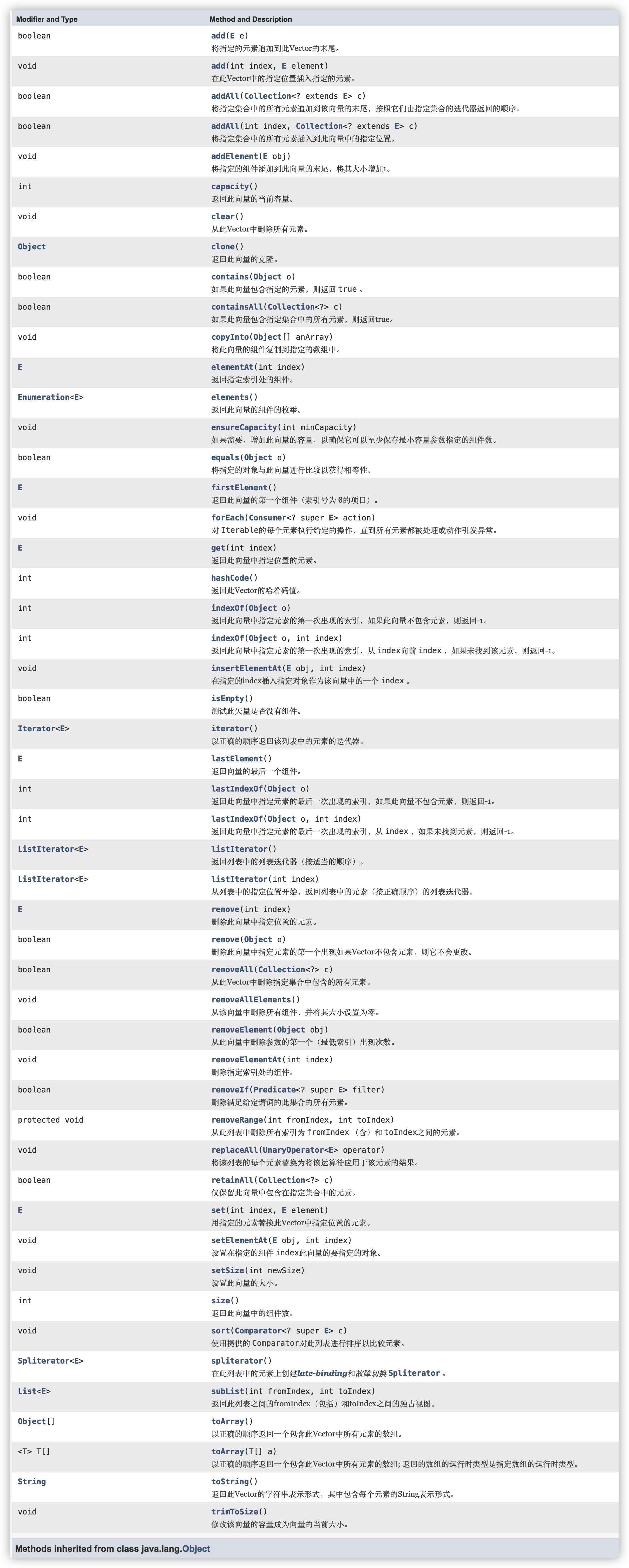
就演示几个常用的就行,其他的可自行了解。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Vector<String> vs = new Vector<>();
//添加
vs.add("aaaaaaaaa");
vs.add("bbbbbbbbb");
vs.add("cccc");
vs.add("1566165");
System.out.println("元素总共有:"+vs.size());
//for输出
System.out.println("for遍历输出:");
for (int i = 0; i < vs.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(vs.get(i));
}
System.out.println("================================");
System.out.println("迭代器遍历输出:");
Iterator<String> it = vs.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
System.out.println("================================");
System.out.println("Enumeration遍历输出:");
Enumeration<String> es = vs.elements();
while (es.hasMoreElements()){
System.out.println(es.nextElement());
}
System.out.println("==删除元素:========");
vs.remove("cccc"); //删除指定元素
System.out.println(vs.remove(0)); //删除指定索引元素
System.out.println("删除后元素总共有:"+vs.size());
// closeAll();
}
//输出
元素总共有:4
for遍历输出:
aaaaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbb
cccc
1566165
================================
迭代器遍历输出:
aaaaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbb
cccc
1566165
================================
Enumeration遍历输出:
aaaaaaaaa
bbbbbbbbb
cccc
1566165
==删除元素:========
aaaaaaaaa
删除后元素总共有:2
2.3 Queue(队列)
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//add()和remove()方法在失败的时候会抛出异常(不推荐)
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
queue.offer("a");
queue.offer("b");
queue.offer("c");
queue.offer("d");
queue.offer("e");
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("poll="+queue.poll()); //返回第一个元素,并在队列中删除
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("element="+queue.element()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("peek="+queue.peek()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
}
}
2.4 PriorityQueue(优先队列)
| 返回值 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e)将指定的元素插入到此优先级队列中。 |
void |
clear()从此优先级队列中删除所有元素。 |
Comparator<? super E> |
comparator()返回用于为了在这个队列中的元素,或比较null如果此队列根据所述排序natural ordering的元素。 |
boolean |
contains(Object o)如果此队列包含指定的元素,则返回 true 。 |
Iterator<E> |
iterator()返回此队列中的元素的迭代器。 |
boolean |
offer(E e)将指定的元素插入到此优先级队列中。 |
E |
peek()检索但不删除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。 |
E |
poll()检索并删除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。 |
boolean |
remove(Object o)从该队列中删除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。 |
int |
size()返回此集合中的元素数。 |
Spliterator<E> |
spliterator()在此队列中的元素上创建*late-binding和失败快速* Spliterator 。 |
Object[] |
toArray()返回一个包含此队列中所有元素的数组。 |
<T> T[] |
toArray(T[] a)返回一个包含此队列中所有元素的数组; 返回的数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 |
常用方法:
peek()//返回队首元素
poll()//返回队首元素,队首元素出队列
add()//添加元素
size()//返回队列元素个数
isEmpty()//判断队列是否为空,为空返回true,不空返回false
示例:
//自定义比较器,降序排列
static Comparator<Integer> cmp = new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer e1, Integer e2) {
return e2 - e1;
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
//不用比较器,默认升序排列
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.add(3);
q.add(2);
q.add(4);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
System.out.print(q.poll()+" ");
}
/**
* 输出结果
* 2 3 4
*/
//使用自定义比较器,降序排列
Queue<Integer> qq = new PriorityQueue<>(cmp);
qq.add(3);
qq.add(2);
qq.add(4);
while(!qq.isEmpty())
{
System.out.print(qq.poll()+" ");
}
/**
* 输出结果
* 4 3 2
*/
}
自定义类:
//矩形类
class Node{
public Node(int chang,int kuan)
{
this.chang=chang;
this.kuan=kuan;
}
int chang;
int kuan;
}
public class Test {
//自定义比较类,先比较长,长升序排列,若长相等再比较宽,宽降序
static Comparator<Node> cNode=new Comparator<Node>() {
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
if(o1.chang!=o2.chang)
return o1.chang-o2.chang;
else
return o2.kuan-o1.kuan;
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Node> q=new PriorityQueue<>(cNode);
Node n1=new Node(1, 2);
Node n2=new Node(2, 5);
Node n3=new Node(2, 3);
Node n4=new Node(1, 2);
q.add(n1);
q.add(n2);
q.add(n3);
Node n;
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
n=q.poll();
System.out.println("长: "+n.chang+" 宽:" +n.kuan);
}
/**
* 输出结果
* 长: 1 宽:2
* 长: 2 宽:5
* 长: 2 宽:3
*/
}
}
优先队列遍历。PriorityQueue的iterator()不保证以任何特定顺序遍历队列元素。若想按特定顺序遍历,先将队列转成数组,然后排序遍历
Queue<Integer> q = new PriorityQueue<>(cmp);
int[] nums= {
2,5,3,4,1,6};
for(int i:nums)
{
q.add(i);
}
Object[] nn=q.toArray();
Arrays.sort(nn);
for(int i=nn.length-1;i>=0;i--)
System.out.print((int)nn[i]+" ");
/**
* 输出结果
* 6 5 4 3 2 1
*/
比较器生降序说明
Comparator<Object> cmp = new Comparator<Object>() {
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
//升序
return o1-o2;
//降序
return o2-o1;
}
};
2.5 Pair
获取Key值:getKey()。
获取Value值:getValue()。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//单个
Pair<String,Integer> test = new Pair<>("qwer",234);
System.out.println(test.getKey());
System.out.println(test.getValue());
//数组
Pair<String,Integer>[] pair = new Pair[52];
pair[0] = new Pair<>("23",23);
pair[1] = new Pair<>("2323",2323);
pair[2] = new Pair<>("223343",2343);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
String s = pair[i].getKey();
System.out.println(s);
int t = pair[i].getValue();
System.out.println(t);
}
}
说明
offer,add 区别:
一些队列有大小限制,因此如果想在一个满的队列中加入一个新项,多出的项就会被拒绝。
这时新的 offer 方法就可以起作用了。它不是对调用 add() 方法抛出一个 unchecked 异常,而只是得到由 offer() 返回的 false。
poll,remove 区别:
remove() 和 poll() 方法都是从队列中删除第一个元素。remove() 的行为与 Collection 接口的版本相似, 但是新的 poll() 方法在用空集合调用时不是抛出异常,只是返回 null。因此新的方法更适合容易出现异常条件的情况。
peek,element区别:
element() 和 peek() 用于在队列的头部查询元素。与 remove() 方法类似,在队列为空时, element() 抛出一个异常,而 peek() 返回 null。