目录
3.LinkedHashSet和LinkedHashMap具体的方法
一.LinkedHashSet和LinkedHashMap
1.基本介绍
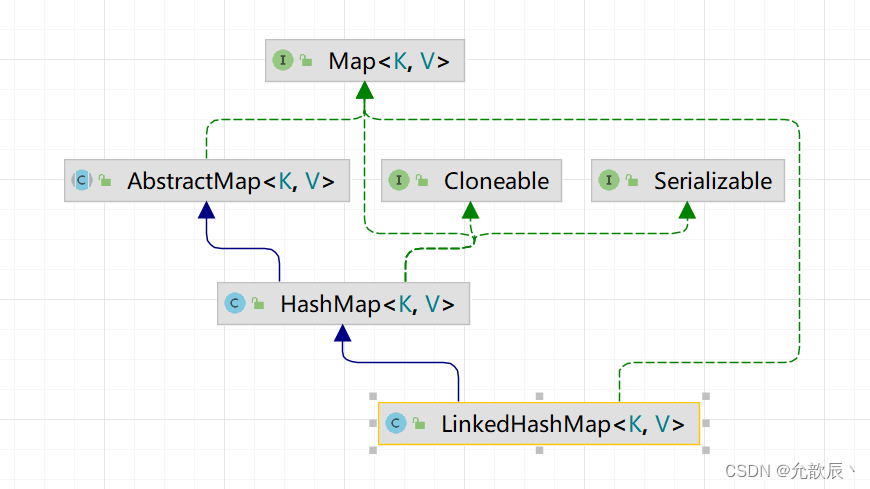
顾名思义,根据名字我们可以知道LinkedHastSet和LinkedHashMap底层是用链表实现的,具体是使用双向链表实现的,下面是继承树,LinkedHashMap继承了父类HashMap,因此HashMap中的方法,在LinkedHashMap中都是可以使用的.(LinkedHashSet一样)
2.与HashSet和HashMap的区别
我们都知道HashSet和HashMap是根据HashCode存储到具体位置,例如是求余7存储到具体的索引,那么当我们遍历时候,存储的顺序和添加的顺序是不一样的.例如如下代码执行的结果,toString打印出来的和添加的顺序不一样
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>(); set.add(1); set.add(5); set.add(4); set.add(3); System.out.println(set);//[1, 3, 4, 5]
而LinkedHashSet底层使用链表实现的,每次添加都是尾插法进行添加,所以添加的顺序一定是和遍历的顺序是一样的(这里采用迭代器遍历)
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set1 = new LinkedHashSet<>();
set1.add(1);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(4);
set1.add(3);
Iterator<Integer> iterator = set1.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");//1 5 4 3
}
3.LinkedHashSet和LinkedHashMap具体的方法
1.LinkedHashSet
具体就是以下方法,LinkedHashSet和HashSet一样,不保存值相同的元素
LinkedHashSet<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<>(); set.add(1); set.add(2); set.add(3); set.add(1); System.out.println(set);//[1, 2, 3] set.remove(1);//删除成功返回true,删除失败返回false System.out.println(set);//[2, 3] System.out.println(set.size());//2 System.out.println(set.isEmpty());//false System.out.println(set.contains(2));//true
2.LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> map=new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put(1,"1");
map.put(2,"2");
map.put(3,"3");
System.out.println(map);//{1=1, 2=2, 3=3}
map.remove(1);
System.out.println(map);//{2=2, 3=3}
System.out.println(map.size());//2
map.put(1,"10");
System.out.println(map);//{2=2, 3=3, 1=10}
System.out.println(map.containsKey(1));//true
System.out.println(map.containsValue("10"));//true
二.模拟代码实现LinkedHashMap
这里我们为了方便,就没有采用泛型来定义.用了HashMap来存储键和对应的Node结点,这样根据键就可以找到对应的Node在LinkedHashMap中的位置,并且添加的时候和遍历的顺序也是一致的,这是一种比较好理解的LinkedHashMap的实现方式.链表这里我们采用了双向链表的存储方式,结点存储key和value,并且结点的key和HashMap的key是一一对应的.
public class LinkedHashMap extends LinkedList {
//HashMap的键(key)和LinkedList的Node的键相互对应
HashMap<Integer, Node> map;
LinkedList list;
public LinkedHashMap() {
map = new HashMap<>();
list = new LinkedList();
}
public void addLast(int key, int val) {
Node x = new Node(key, val);
list.addLast(x);
map.put(key, x);
}
public void remove(int key) {
Node x = map.get(key);
list.remove(x);
map.remove(x);
}
public int size() {
return list.size();
}
public boolean containsKey(int key){
return map.containsKey(key);
}
}
class LinkedList {
class Node {
public int key, val;
public Node next, prev;
public Node(int key, int val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
//头尾虚拟节点
private Node head, tail;
//链表元素数
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
head = new Node(0, 0);
tail = new Node(0, 0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
size = 0;
}
public void addLast(Node x) {
x.prev = tail.prev;
x.next = tail;
tail.prev.next = x;
tail.prev = x;
size++;
}
public void remove(Node x) {
x.prev.next = x.next;
x.next.prev = x.prev;
size--;
}
public Node removeFirst() {
//空链表
if (head.next == tail) {
return null;
}
Node first = head.next;
remove(first);
return first;
}
public int size() {
return size;
}
}三.具体应用
具体在实现LRU缓存淘汰算法上有应用,只要就是应用的LinkedHashMap的存储的顺序和添加的顺序是一样的特性,我们对于不经常使用的数据进行淘汰处理,这个时候我们需要确保存储的顺序和添加的顺序保持一致性,也就是当内存满了之后,先添加的进行淘汰,具体的讲解明天进行博客的更新!!!!!!!!!