JDBC
JDBC的概念
1.jdbc的概念
JDBC ( Java DataBaseConnectivity java数据库连接)是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系型数据库提供统一访问,它是由一组用Java语言编写的类和接口组成的。
2.jdbc的本质
其实就是java官方提供的一套规范(接口)。用于帮助开发人员快速实现不同关系型数据库的连接!
JDBC快速入门
jdbc的快速入门步骤:
1.导入jar包
2.注册驱动
3.获取数据库连接
4.获取执行者对象
5.执行sql语句并返回结果
6.处理结果
7.释放资源
示例代码:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBC_index1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//MySQL5以后可直接省略
//获取数据库连接
Connection con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cadastre","root","XXXXXX");
//获取执行者对象
Statement stat=con.createStatement();
//执行sql语句并返回结果
String sql="select * from 网易云热评";
ResultSet re=stat.executeQuery(sql);
//处理结果
while (re.next()){
System.out.println(re.getString("userId")+"\t"+re.getString("nickname")+"\t"+re.getString("content"));
}
//释放资源
con.close();
}
}
JDBC功能详解
1、DriverManager驱动管理对象
(1)注册驱动:(mysql5以后可直接省略驱动)
1.注册给定的驱动程序: staticvoid registerDriver(Driver driver);2.写代码使用:Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”);
3.在com.mysql.jdbc.Driver类中存在静态代码块
(2)获取数据库连接:
1.获取数据库连接对象: static ConnectiongetConnection(Stringurl, String user,String password);2.返回值:Connection数据库连接对象
3.参数
url:指定连接的路径。语法: jdbc:mysql://ip地址(域名):端口号/数据库名称 user:用户名
password:密码
2、Connection数据库连接对象
1.获取执行者对象:
获取普通执行者对象: Statement createStatement0;
获取预编译执行者对象:PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql);2.管理事务
开启事务 : setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit);参数为false,则开启事务 提交事务:commit();
回滚事务: rollback();
3.释放资源
立即将数据库连接对象释放:void close();
3、Statement执行sql语句的对象
(1)执行DML语句: int executeUpdate(String sql);
返回值int :返回影响的行数。
参数sql:可以执行insert、update、delete语句。
(2) 执行DQL语句:ResultSet executeQuery(String sql);
返回值ResultSet:封装查询的结果。
参数sql:可以执行select语句。
(3)释放资源
立即将数据库连接对象释放:void close();
4、ResultSet结果集对象
1.判断结果集中是否还有数据: boolean next();
有数据返回true,并将索引向下移动一行。没有数据返回false。
2.获取结果集中的数据:XXX getXxx(“列名”);XXX代表数据类型(要获取某列数据,这一列的数据类型)。
例如: String getString(“name”);int getInt(" age");
3.释放资源
立即将结果集对象释放:void close();
JDBC案例
案例需求
使用JDBC完成对student表的CRUD操作
数据准备
1、数据库数据准备
-- 创建数据库
create DATABASE db14;
-- 使用数据库
use db14
-- 创建student表
CREATE TABLE student
(
id int PRIMARY KEY,
sname VARCHAR(20),
age int,
brithday date
);
-- 添加数据
INSERT into student VALUES(1,'张飞',23,'1999-08-11'),(2,'李四',23,'1998-08-11'),(3,'王五',23,'1997-08-11'),(4,'关羽',23,'1995-08-11');
2、创建student类
package Com.Stuclass;
import java.util.Date;
public class Student {
private Integer id;
private String sname;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public Student(Integer id, String sname, Integer age, Date birthday) {
this.id = id;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
}
功能实现
1、查询所有学生信息
public ArrayList<Student> findAll() {
ArrayList<Student> list=new ArrayList<>();
Connection con=null;
try {
con= DriverManager.getConnection(conName,name,password);
Statement statement = con.createStatement();
String sql="select * from student";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
Integer id=resultSet.getInt("id");
String sname=resultSet.getString("sname");
Integer age=resultSet.getInt("age");
Date birthday=resultSet.getDate("brithday");
Student s=new Student(id,sname,age,birthday);
list.add(s);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
2、通过ID查询学生信息
public Student findById(Integer id) {
Connection con=null;
Student s = null;
try{
con=DriverManager.getConnection(conName,name,password);
String sql="select * from student where id=?";
PreparedStatement pstate = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstate.setInt(1,id);
ResultSet resultSet = pstate.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
s=new Student(id,resultSet.getString("sname"),resultSet.getInt("age"),resultSet.getDate("brithday"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return s;
}
3、添加学生记录
public int insert(Integer id, String sname, Integer age, String birthday) {
Connection con=null;
int re=0;
Date date=new Date();//需要new一个Date对象
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); //设置日期格式 yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss这个是完整的
try {
date = dateFormat.parse(birthday);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
con= JDBCUtils.getConnect();
String sql="insert into student values(?,?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement p=con.prepareStatement(sql);
p.setInt(1,id);
p.setString(2,sname);
p.setInt(3,age);
p.setDate(4, new java.sql.Date(date.getTime()));
re = p.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return re;
}
4、修改学生信息
public int update(String name1,Integer age) {
Connection con=null;
int result=0;
String sql="update student " +
"set age=? " +
"where sname=?";
try {
con= JDBCUtils.getConnect();
PreparedStatement p = con.prepareStatement(sql);
p.setInt(1,age);
p.setString(2,name1);
result = p.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
5、删除学生记录
public int delete(Integer id) {
Connection con=null;
int result=0;
try {
con= JDBCUtils.getConnect();
String sql="delete from student where id=?";
PreparedStatement p = con.prepareStatement(sql);
p.setInt(1,id);
result = p.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
推荐使用工具类
配置信息:(在src目录下创建config.properties文件)
driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db14
username=root
password=XXXXXXx
工具类:
package Com.Stuclass.utils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/*
* JDBC工具类
* */
public class JDBCUtils {
// 1、构造方法私有
private JDBCUtils(){
}
// 2、声明所需要的配置变量
private static String driverClass;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
private static Connection con;
// 3、提供静态代码块,读取配置文件信息为变量赋值,注册驱动
static {
try {
// 赋值
InputStream is = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config.properties");
Properties pro=new Properties();
pro.load(is);
driverClass=pro.getProperty("driverClass");
url=pro.getProperty("url");
username=pro.getProperty("username");
password=pro.getProperty("password");
// 注册驱动
Class.forName(driverClass);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnect(){
try {
con= DriverManager.getConnection(url,username,password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
// 关闭连接
public static void close(Connection con, Statement state, ResultSet rs){
if (con!=null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (state!=null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Connection con, Statement state){
if (con!=null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (state!=null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
SQL注入攻击
利用SQL语句漏洞对系统进行攻击
例如:
按照正常道理来说,我们在密码处输入的所有内容,都应该认为是密码的组成
但是现在Statement对象在执行sql语句时,将密码的一部分内容当做查询条件来执行了
解决方式:
利用预编译SQL语句
JDBC事务管理
JDBC如何管理事务
管理事务的功能类:Connection
开启事务: setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit);参数为false,则开启事务。
提交事务:commit();
回滚事务:rollback();
数据库连接池
1.数据库连接的背景
数据库连接是一种关键的、有限的、昂贵的资源,这一点在多用户的网页应用程序中体现得尤为突出对数据库连接的管理能显著影响到整个应用程序的性能指标,数据库连接池正是针对这个问题提出来的
⒉.数据库连接池
数据库连接池负责分配、管理和释放数据库连接,它允许应用程序重复使用一个现有的数据库连接,而不是再重新建立一个。这项技术能明显提高对数据库操作的性能
自定义数据库连接池
1.DataSource接口概述
javax.sql.DataSource接口∶数据源(数据库连接池)。
Java官方提供的数据库连接池规范(接口)如果想完成数据库连接池技术,就必须实现DataSource接口
核心功能:获取数据库连接对象:Connection getConnection();
、
2.自定义数据库连接池
定义一个类,实现DataSource接口。
定义一个容器,用于保存多个Connection连接对象。
定义静态代码块,通过JDBC工具类获取10个连接保存到容器中。
重写getConnection方法,从容器中获取一个连接并返回。
定义getSize方法,用于获取容器的大小并返回。
准备:
上文中的JDBCutill工具类和相关配置文件
示例:
package JDBCplus.Demo1;
/*
* 自定义数据库连接池
* */
import JDBCplus.JDBCUtils;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
// 1、准备容器 注意必须是线程安全的
private static List<Connection> pool= Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
// 2、通过工具类获取10个连接对象
static {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Connection con= JDBCUtils.getConnect();
pool.add(con);
}
}
// 3、重写getConnection方法
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (pool.size()>0){
return pool.remove(0);
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接池已空");
}
}
// 4、定义getSize方法获取连接池大小
public int getSize(){
return pool.size();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
}
使用测试:
package JDBCplus.Demo1;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Test {
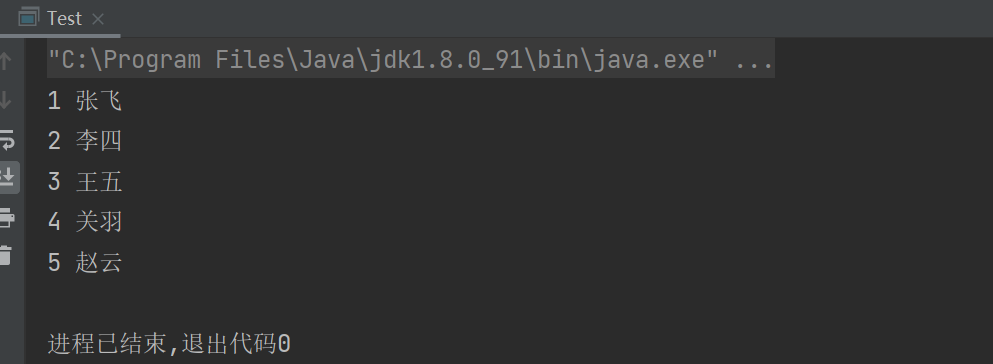
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
Connection con=myDataSource.getConnection();
String sql="select * from student";
Statement statement = con.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt("id")+" "+resultSet.getString("sname"));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
con.close();
}
}
归还连接
归还数据库连接的方式:
继承方式
装饰设计模式
适配器设计模式
动态代理方式
归还连接-继承方式
1.继承方式归还数据库连接的思想。
通过打印连接对象,发现DriverManager获取的连接实现类是JDBC4Connection那我们就可以自定义一个类,继承JDBC4Connection这个类,重写close()方法完成连接对象的归还。
2.继承方式归还数据库连接的实现步骤。
1定义一个类,继承JDBC4Connection。
2定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的成员变量。
3通过有参构造方法完成对成员变量的赋值。
4重写close方法,将连接对象添加到池中。
3.继承方式归还数据库连接存在的问题。
通过查看JDBC工具类获取连接的方法发现∶我们虽然自定义了一个子类,完成了归还连接的操作。但是DriverManager获取的还是JDBC4Connection这个对象,并不是我们的子类对象,而我们又不能整体去修改驱动包中类的功能,所继承这种方式行不通!心
(此处我的MySQL包中未找到JDBC4Connection类不能展示)
归还连接-装饰设计模式
1.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接的思想。
我们可以自定义一个类,实现Connection接口。
这样就具备了和JDBC4Connection相同的行为了重写close()方法,完成连接的归还。其余的功能还调用mysql驱动包实现类原有的方法即可。
2.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接的实现步骤。
1、定义一个类,实现Connection接口
2、定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的成员变量
3、通过有参构造方法完成对成员变量的赋值
4、重写close()方法,将连接对象添加到池中
5、剩余方法,只需要调用mysql驱动包的连接对象完成即可
6、在自定义连接池中,将获取的连接对象通过自定义连接对象进行包装
3.装饰设计模式归还数据库连接存在的问题。
实现Connection接口后,有大量的方法需要在自定义类中进行重写
示例代码:
package JDBCplus.Demo2;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
public class MyConnection2 implements Connection {
// 定义连接对象和连接池对象
private Connection con;
private List<Connection> pool;
// 构造方法赋值
public MyConnection2(Connection con,List<Connection> pool){
this.con=con;
this.pool=pool;
}
// 重写close方法
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.add(con);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement();
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql);
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.nativeSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return con.getAutoCommit();
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
con.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return con.isClosed();
}
@Override
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return con.getMetaData();
}
@Override
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
con.setReadOnly(false);
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return con.isReadOnly();
}
@Override
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
con.setCatalog(catalog);
}
@Override
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return con.getCatalog();
}
@Override
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
con.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
@Override
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return con.getTransactionIsolation();
}
@Override
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return con.getWarnings();
}
@Override
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
con.clearWarnings();
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return con.getTypeMap();
}
@Override
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
con.setTypeMap(map);
}
@Override
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
con.setHoldability(holdability);
}
@Override
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return con.getHoldability();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint(name);
}
@Override
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);
}
@Override
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createClob();
}
@Override
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return con.createBlob();
}
@Override
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createNClob();
}
@Override
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return con.createSQLXML();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return con.isValid(timeout);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(name,value);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(properties);
}
@Override
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo(name);
}
@Override
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo();
}
@Override
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);
}
@Override
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);
}
@Override
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
con.setSchema(schema);
}
@Override
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return con.getSchema();
}
@Override
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
con.abort(executor);
}
@Override
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);
}
@Override
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return con.getNetworkTimeout();
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
}
更改MyDataSouce(数据库连接池方法):
// 3、重写getConnection方法
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (pool.size()>0){
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
MyConnection2 myCon=new MyConnection2(con,pool);
return myCon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接池已空");
}
}
测试代码:
package JDBCplus.Demo1;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Test {
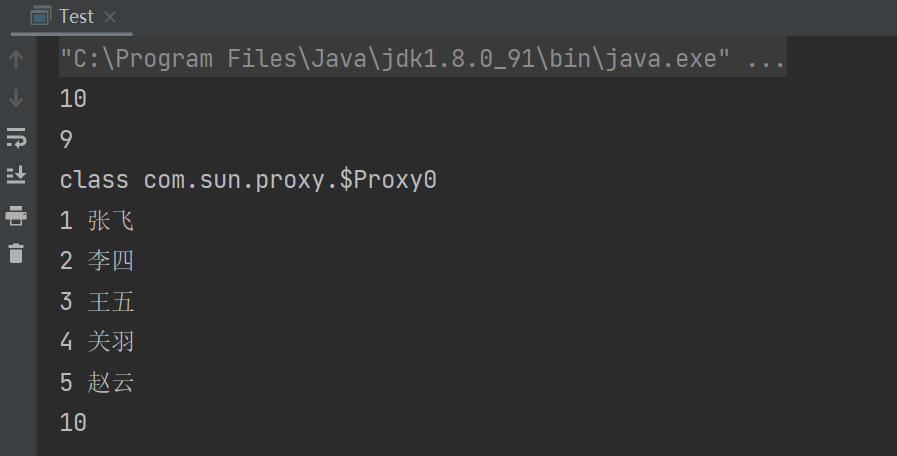
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
System.out.println(myDataSource.getSize());
Connection con=myDataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(myDataSource.getSize());
System.out.println(con.getClass());
String sql="select * from student";
Statement statement = con.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt("id")+" "+resultSet.getString("sname"));
}
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
con.close();
System.out.println(myDataSource.getSize());
}
}
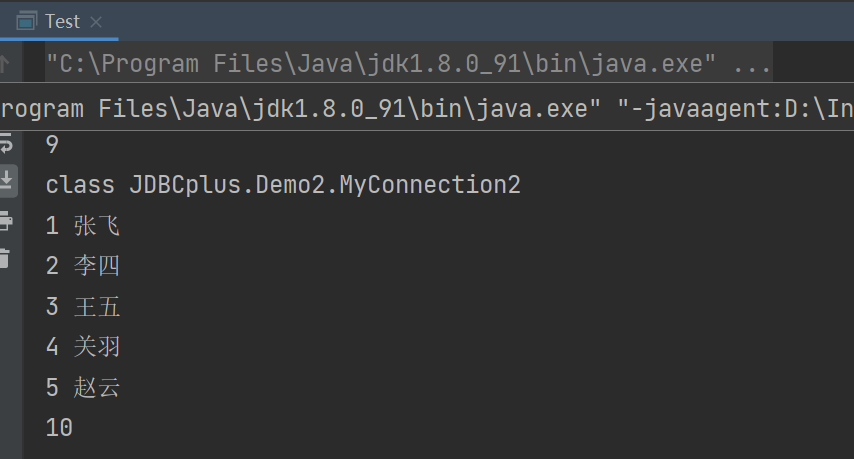
发现父类为自定义类,使用后连接池大小为10
归还连接-适配器设计模式
1.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接的思想。
我们可以提供一个适配器类,实现Connection接口,将所有方法进行实现(除了close方法
自定义连接类只需要继承这个适配器类,重写需要改进的close方法即可
2.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接的实现步骤。
1定义一个适配器类,实现Connection接口。
2定义Connection连接对象的成员变量。
3通过有参构造方法完成对成员变量的赋值。
4重写所有方法(除了close ),调用mysq驱动包的连接对象完成即可。
5定义一个连接类,继承适配器类。
6定义Connection连接对象和连接池容器对象的成员变量,并通过有参构造进行赋值。
7重写close()方法,完成归还连接。
8在自定义连接池中,将获取的连接对象通过自定义连接对象进行包装。
3.适配器设计模式归还数据库连接存在的问题。
自定义连接类虽然很简洁了,但适配器类还是我们自己编写的,也比较的麻烦
示例代码:
适配器类:(重写除close外的所有方法,抽象类)
package JDBCplus.Dome3;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.Executor;
/*
* 适配器类
* */
public abstract class MyAdapter implements Connection{
private Connection con;
public MyAdapter(Connection con){
this.con=con;
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement();
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql);
}
@Override
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
return con.nativeSQL(sql);
}
@Override
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
con.setAutoCommit(false);
}
@Override
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
return con.getAutoCommit();
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
con.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
return con.isClosed();
}
@Override
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
return con.getMetaData();
}
@Override
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
con.setReadOnly(false);
}
@Override
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
return con.isReadOnly();
}
@Override
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
con.setCatalog(catalog);
}
@Override
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
return con.getCatalog();
}
@Override
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
con.setTransactionIsolation(level);
}
@Override
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
return con.getTransactionIsolation();
}
@Override
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
return con.getWarnings();
}
@Override
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
con.clearWarnings();
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
return con.getTypeMap();
}
@Override
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
con.setTypeMap(map);
}
@Override
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
con.setHoldability(holdability);
}
@Override
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
return con.getHoldability();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint();
}
@Override
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.setSavepoint(name);
}
@Override
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.rollback();
}
@Override
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
con.releaseSavepoint(savepoint);
}
@Override
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.createStatement(resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency);
}
@Override
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareCall(sql,resultSetType,resultSetConcurrency,resultSetHoldability);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,autoGeneratedKeys);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnIndexes);
}
@Override
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames) throws SQLException {
return con.prepareStatement(sql,columnNames);
}
@Override
public Clob createClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createClob();
}
@Override
public Blob createBlob() throws SQLException {
return con.createBlob();
}
@Override
public NClob createNClob() throws SQLException {
return con.createNClob();
}
@Override
public SQLXML createSQLXML() throws SQLException {
return con.createSQLXML();
}
@Override
public boolean isValid(int timeout) throws SQLException {
return con.isValid(timeout);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(String name, String value) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(name,value);
}
@Override
public void setClientInfo(Properties properties) throws SQLClientInfoException {
con.setClientInfo(properties);
}
@Override
public String getClientInfo(String name) throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo(name);
}
@Override
public Properties getClientInfo() throws SQLException {
return con.getClientInfo();
}
@Override
public Array createArrayOf(String typeName, Object[] elements) throws SQLException {
return con.createArrayOf(typeName,elements);
}
@Override
public Struct createStruct(String typeName, Object[] attributes) throws SQLException {
return con.createStruct(typeName,attributes);
}
@Override
public void setSchema(String schema) throws SQLException {
con.setSchema(schema);
}
@Override
public String getSchema() throws SQLException {
return con.getSchema();
}
@Override
public void abort(Executor executor) throws SQLException {
con.abort(executor);
}
@Override
public void setNetworkTimeout(Executor executor, int milliseconds) throws SQLException {
con.setNetworkTimeout(executor,milliseconds);
}
@Override
public int getNetworkTimeout() throws SQLException {
return con.getNetworkTimeout();
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.unwrap(iface);
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return con.isWrapperFor(iface);
}
}
自定义连接类:
package JDBCplus.Dome3;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
/*
* 自定义连接类
* */
public class MyConnection3 extends MyAdapter {
// 定义连接对象和连接池对象
private Connection con;
private List<Connection> pool;
// 构造方法赋值
public MyConnection3(Connection con,List<Connection> pool) {
super(con);
this.con=con;
this.pool=pool;
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
pool.add(con);
}
}
数据库连接池更改:
// 3、重写getConnection方法
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (pool.size()>0){
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
MyConnection3 myCon=new MyConnection3(con,pool);
return myCon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接池已空");
}
}
测试代码:
(同装饰设计模式)
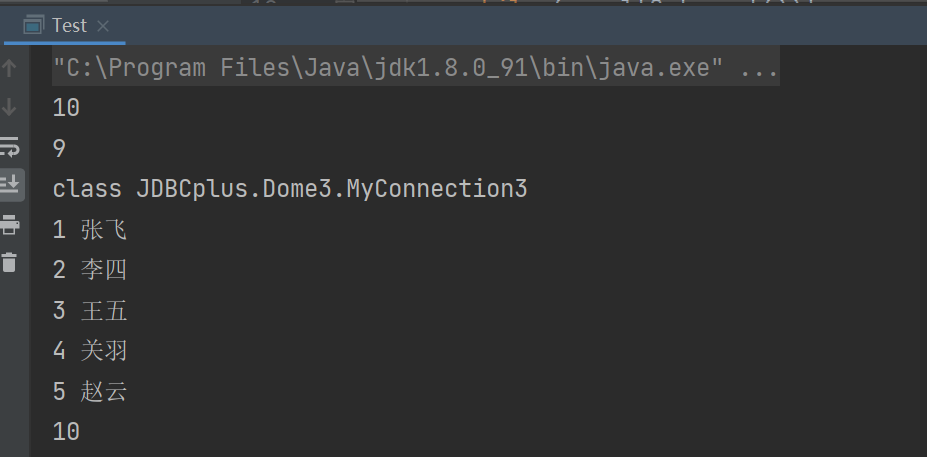
目标到达
动态代理
动态代理:
在不改变目标对象方法的情况下对方法进行增强
组成:
被代理对象︰真实的对象
代理对象︰内存中的一个对象
要求:
代理对象必须和被代理对象实现相同的接口
示例:
student类:
package proxy;
public class Student implements StudentInterface{
@Override
public void eat(String name){
System.out.println("学生吃"+name);
}
@Override
public void study(){
System.out.println("在家自学");
}
}
StudentInterface接口:
package proxy;
public interface StudentInterface {
public void eat(String name);
public void study();
}
测试:
package proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
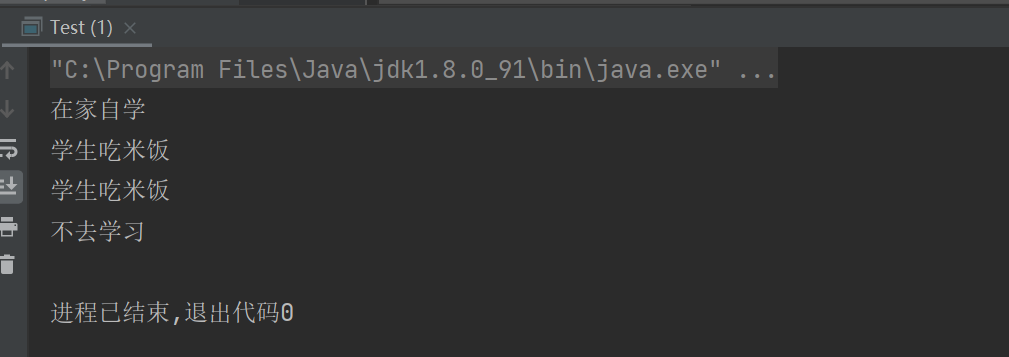
student.study();
student.eat("米饭");
/*
* 要求不改动Student的代码,更改study方法的输出内容
* */
//参数一:类加载器,参数二:接口类型class数组,参数三:代理规则
StudentInterface proxy= (StudentInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(student.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{
StudentInterface.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
/*
* 执行student类中所有的方法都会经过invoke方法
* 对method方法判断,修改想要的方法
* */
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if(method.getName().equals("study")){
System.out.println("不去学习");
return null;
}else {
return method.invoke(student,args);
}
}
});
proxy.eat("米饭");
proxy.study();
}
}
运行结果:
成功修改
动态代理归还数据库连接:
1.动态代理方式归还数据库连接的思想。
我们可以通过Proxy来完成对Connection实现类对象的代理
代理过程中判断如果执行的是close方法,就将连接归还池中。
如果是其他方法则调用连接对象原来的功能即可
2.动态代理方式归还数据库连接的实现步骤。
定义一个类,实现DataSource接口
定义一个容器,用于保存多个Connection连接对象
定义静态代码块,通过JDBC工具类获取10个连接保存到容器中
重写getConnection方法,从容器中获取一个连接
通过 Proxy代理,如果是close方法,就将连接归还池中。如果是其他方法却则调用原有功能
定义getSize方法,用于获取容器的大小并返回
实现重写MyDataSource中的getConnection方法(使用动态代理方式实现)
// 3、重写getConnection方法 使用动态代理方式实现
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (pool.size()>0){
Connection con = pool.remove(0);
Connection myCon = (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(con.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{
Connection.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (method.getName().equals("close")){
pool.add(con);
return null;
}else {
return method.invoke(con,args);
}
}
});
return myCon;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("连接池已空");
}
}
使用上文中测试代码:
开源数据库连接池
C3P0数据库连接池
1.C3PO数据库连接池的使用步骤。
导入jar包。
导入配置文件到src目录下。
创建C3PO连接池对象。
获取数据库连接进行使用。
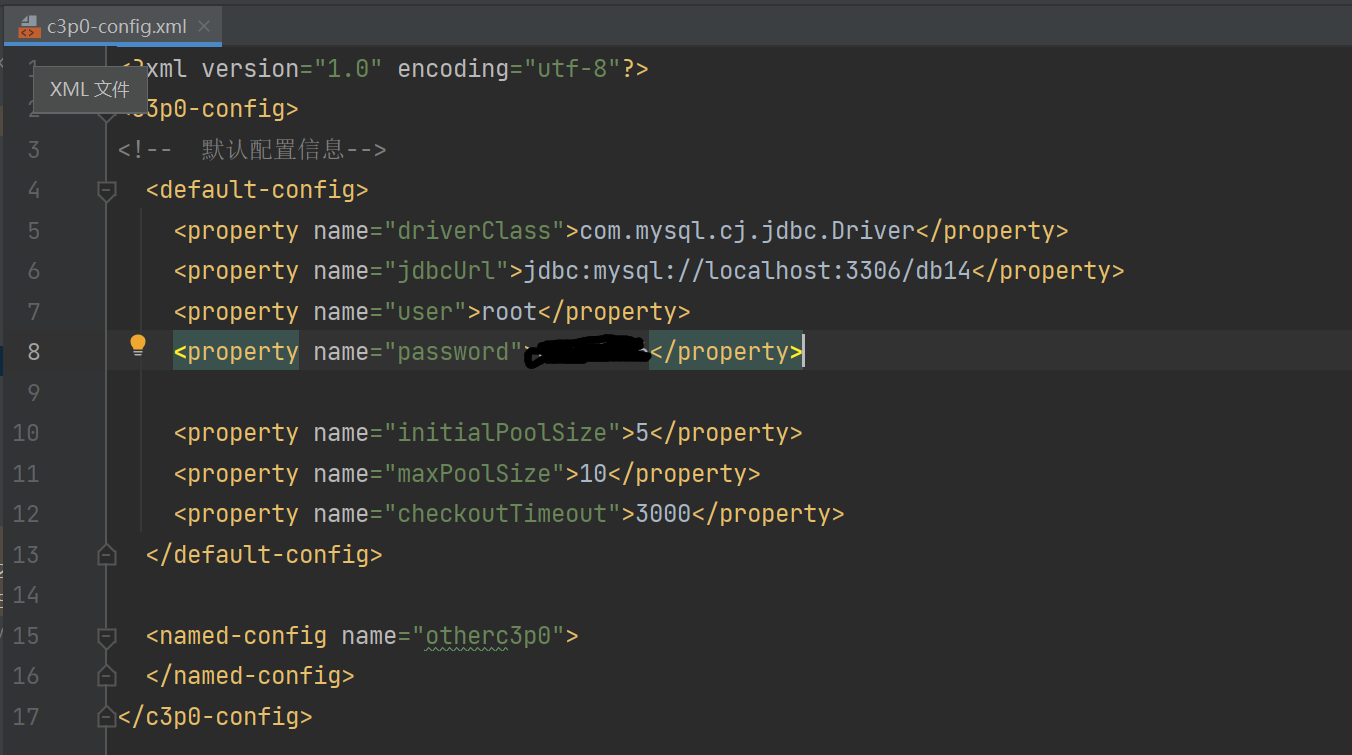
注意:C3PO的配置文件会自动加载,但是必须叫c3p0-config.xml或 c3pO-config.properties
下载jar包:
官网:https://sourceforge.net/projects/c3p0/files/latest/download
别人百度网盘:百度网盘下载链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1o9cBkMVb_kZmAksZjjoZYg 密码:c7pr
导入jar包:
导入配置文件到src目录:
使用示例:
package C3P0;
import com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
// 1、创建c3p0数据库连接池
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
// 2、通过连接池获取数据库连接
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 3、执行数据库操作
String sql="select * from student";
PreparedStatement p = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet re = p.executeQuery();
while (re.next()){
System.out.println(re.getInt("id")+"\t"+re.getString("sname"));
}
}
}
Druid数据库连接池
1、介绍
Druid(德鲁伊)是阿里巴巴开发的号称为监控而生的数据库连接池,Druid是目前最好的数据库连接池。在功能、性能、扩展性方面,都超过其他数据库连接池,同时加入了日志监控,可以很好的监控DB池连接和SQL的执行情况。Druid已经在阿里巴巴部署了超过600个应用,经过一年多生产环境大规模部署的严苛考验。
1.Druid数据库连接池的使用步骤:
导入jar包。
编写配置文件,放在src目录下。
通过Properties集合加载配置文件。
通过Druid连接池工厂类获取数据库连接池对象。
获取数据库连接进行使用。
注意:Druid不会自动加载配置文件,需要我们手动加载,但是文件的名称可以自定义。
下载jar包:
别人的百度网盘::https://pan.baidu.com/s/1U9v5c_DindqXva92JeRVJQ 密码:nquq
导入jar包:

编写配置文件:
driverClassName=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db14
username=root
password=xxxxxx
initialSize=5
maxActive=10
maxWait=3000
示例代码:
package Druid;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.Properties;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取配置文件的流对象
InputStream is = test1.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
// 通过properties集合,加载配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(is);
// 通过Druid连接池工厂类获取连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
// 连接池中获取连接对象
Connection con = dataSource.getConnection();
// 执行数据库操作
String sql="select * from student";
PreparedStatement p = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet re = p.executeQuery();
while (re.next()){
System.out.println(re.getInt("id")+"\t"+re.getString("sname"));
}
}
}
基于Druid数据库连接池创建的工具类
代码:
package Druid;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
public class DruidUtils {
// 私有化构造方法
private DruidUtils(){
}
// 声明数据源变量
private static DataSource dataSource;
// 静态代码块完成配置文件加载和获取数据库连接对象
static {
InputStream is = DruidUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(is);
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection con=null;
try {
con = dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return con;
}
// 获取数据库连接池
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
return dataSource;
}
// 关闭连接
public static void close(Connection con, Statement state, ResultSet rs){
if (con!=null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (state!=null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(Connection con, Statement state){
if (con!=null){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (state!=null){
try {
state.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
使用示例:
package Druid;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
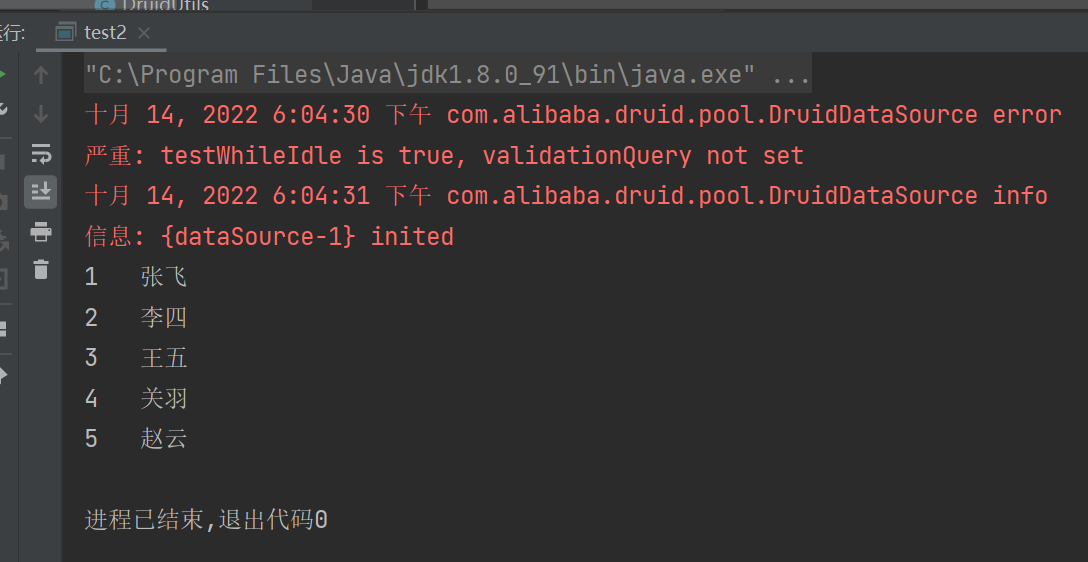
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection con=DruidUtils.getConnection();
String sql="select * from student";
PreparedStatement p = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet re = p.executeQuery();
while (re.next()){
System.out.println(re.getInt("id")+"\t"+re.getString("sname"));
}
}
}