学习
目标:
- Shell 脚本入门
学习内容:
- Shell 脚本入门
- 脚本格式
脚本以#!/bin/bash 开头(指定解析器)
2.第一个 Shell 脚本:helloworld.sh
touch helloworld.shvim helloworld.sh在 helloworld.sh 中输入如下内容
#!/bin/bash
echo "helloworld"3.脚本的常用执行方式
第一种:采用 bash 或 sh+脚本的相对路径或绝对路径(不用赋予脚本+x 权限)
sh+脚本的相对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ sh ./helloworld.sh
Helloworld
sh+脚本的绝对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ sh /home/atguigu/shells/helloworld.sh
helloworld
bash+脚本的相对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ bash ./helloworld.sh
Helloworld
bash+脚本的绝对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ bash /home/atguigu/shells/helloworld.sh
Helloworld
第二种:采用输入脚本的绝对路径或相对路径执行脚本(必须具有可执行权限+x)
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ chmod +x helloworld.sh
相对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ ./helloworld.sh
Helloworld
绝对路径
[atguigu@hadoop101 shells]$ /home/atguigu/shells/helloworld.sh
Helloworld
注意:第一种执行方法,本质是 bash 解析器帮你执行脚本,所以脚本本身不需要执行权限。第二种执行方法,本质是脚本需要自己执行,所以需要执行权限。
第三种:在脚本的路径前加上“.”或者 source
(noetic) jjm2@ubuntu:~$ source hello.sh
hello world
(noetic) jjm2@ubuntu:~$ . hello.sh
hello world
几种方法的区别

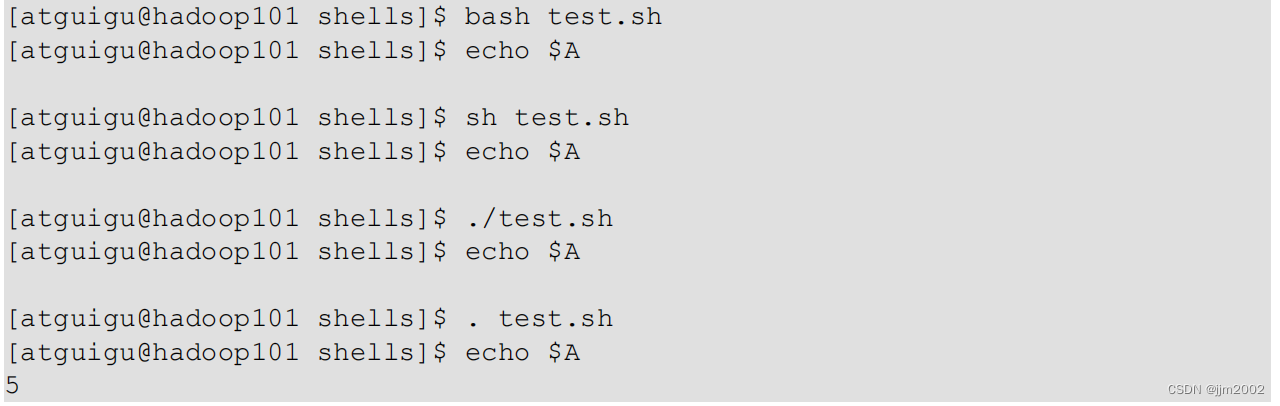
原因:
前两种方式都是在当前 shell 中打开一个子 shell 来执行脚本内容,当脚本内容结束,则子 shell 关闭,回到父 shell 中。第三种,也就是使用在脚本路径前加“.”或者 source 的方式,可以使脚本内容在当前shell 里执行,而无需打开子 shell!这也是为什么我们每次要修改完/etc/profile 文件以后,需要 source 一下的原因。开子 shell 与不开子 shell 的区别就在于,环境变量的继承关系,如在子 shell 中设置的当前变量,父 shell 是不可见的。