CLASStorch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None
一、参数说明:

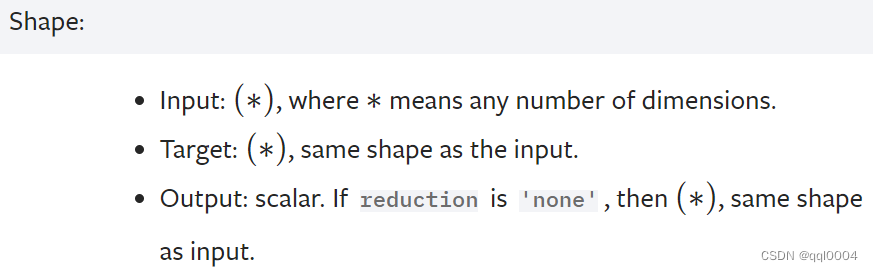
二、输入logits和label和输出loss的shape:
三、说明
这个loss将一个Sigmoid层和BCELoss结合在一个类里。这个版本比使用一个普通的Sigmoid后接一个BCELoss更数值稳定。
二分类unreduced的loss可以被描述为:
,
其中N是batch size。x_n是第n个样本的logits。
如果reduction是'mean',the sum of the output will be divided by the number of elements in the output;如果reduction是'sum',the output will be summed。如果reduction是none的话,loss输出的大小与input和label shape相同,都是[batch_size, #class]。
pos_weight指定每个类的正样本的权重,其shape与input shape和label shape相同,都是[batch_size, #class]。For example, if a dataset contains 100 positive and 300 negative examples of a single class, then pos_weight for the class should be equal to 300/100=3. The loss would act as if the dataset contains 3×100=300 positive examples.
在多标签分类里,loss可以被描述为:
,
其中c是类别,p_c is the weight of the positive answer for the class c。p_c > 1 increases the recall, p_c < 1increases the precision.
四、例子:
target = torch.ones([10, 64], dtype=torch.float32) # 64 classes, batch size = 10
output = torch.full([10, 64], 1.5) # A prediction (logit)
pos_weight = torch.ones([64]) # All weights are equal to 1
criterion = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=pos_weight)
criterion(output, target) # -log(sigmoid(1.5))参考: