0 函数入口地址
如果在程序中定义了一个函数,在编译时会把函数的源代码转换为可执行代码并分配一段存储空间。这段内存空间有一个起始地址,也称为函数的入口地址。函数名代表函数的起始地址。调用函数时,从函数名得到函数的起始地址,并执行函数代码。摘自《C程序设计(第五版)》-谭浩强,P265页。
1 通过函数入口地址调用函数的例子
#include "stdio.h"
void test(int num)
{
printf("\n Using test function %d OK! \n", num);
}
int add(int a,int b)
{
int c;
c = a+b;
printf("\n Count of the a && b is :%d \n",c);
return c;
}
int main()
{
int *addr;
int *addr1;
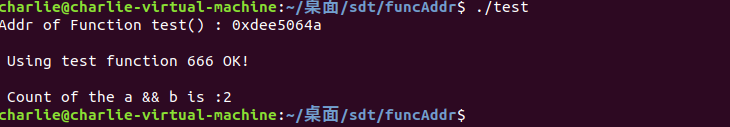
printf("Addr of Function test() : 0x%x\n",test);
addr = test;
((void(*)(int))addr)(666);
addr1 = add;
((int(*)(int,int))addr1)(1,1);
return 0;
}((void(*)(int))addr)(666);
(void(*)(int)) : 表示带有一个int型参数,无返回值的函数指针,确定了addr的函数类型;
addr : 由上述代码(addr = test;)可知,为test()函数的入口地址;
666 :指传入的参数
运行结果如下图所示: