定义于头文件 <ios>
| class ios_base; |
类 ios_base 是作为所有 I/O 流类的基类工作的多用途类。它维护数种数据:
1) 状态信息:流状态标志;
2) 控制信息:控制输入和输出序列格式化和感染的本地环境的标志;
3) 私有存储:允许 long 和 void* 成员的有下标可扩展数据结构,它可以实现为二个任意长度的数组,或二元素结构体的单个数组,或另一容器;
4) 回调:从 imbue() 、 copyfmt() 和 ~ios_base() 调用的任意数量用户定义函数。
典型实现保有对应下列 fmtflags 、 iostate 、 openmode 及 seekdir 所有值的成员常量,维护当前精度、宽度、格式化标志、异常掩码、缓冲区错误状态、保有回调的可调大小容器、当前感染的 locale 、私有存储的成员变量及 xalloc() 所用的静态整数变量。
成员函数
构造对象
std::ios_base::ios_base| private: |
(C++11 前) |
| public: |
(C++11 起) |
| protected: |
(2) |
1) 复制构造函数被删除:流不可复制
2) 默认构造函数受保护:只有导出类可构造 std::ios_base 。构造后内部状态未定义。导出类必须在首次使用或析构函数前调用 basic_ios::init() 完成初始化;否则行为未定义。
注意
同样的情况应用于 I/O 层级中的下个类 std::basic_ios 的构造函数。进一步导出的类( std::istream 与 std::ostream )始终以具体的 streambuffer 构造,并可能多于一次调用 basic_ios::init() ,以完成其虚基类的初始化。
析构对象
std::ios_base::~ios_base| virtual ~ios_base(); |
销毁 ios_base 对象。
在任何成员函数会产出未定义结果前,调用 register_callback() 传递 erase_event 为参数注册的回调函数。
不进行 rdbuf 上的操作,不销毁它。
格式化
参数
| flags | - | 新格式化设置。它能是下列内容的组合:
|
管理格式标志
std::ios_base::flags| fmtflags flags() const; |
(1) | |
| fmtflags flags( fmtflags flags ); |
(2) |
管理格式化标志。
1) 返回当前格式化设置。
2) 以给定者替换当前设置。
返回值
调用函数前的格式化标志
设置特定格式标志
std::ios_base::setf| fmtflags setf( fmtflags flags ); |
(1) | |
| fmtflags setf( fmtflags flags, fmtflags mask ); |
(2) |
设置格式化标志以指定设置。
1) 设置 flags 所标识的格式化标志。等效地进行下列操作: fl = fl | flags ,其中 fl 定义内部格式化标志的状态。
2) 清除 mask 下的格式化标志,并设置被清除的标志为 flags 所指定者。等效地进行下列操作: fl = (fl & ~mask) | (flags & mask) ,其中 fl 定义格式化标志的内部状态。
清除特定格式的标志
std::ios_base::unsetf| void unsetf( fmtflags flags ); |
反设置 flags 所表示的格式化标志。
返回值
(无)
管理浮点操作的精度
std::ios_base::precision| streamsize precision() const; |
(1) | |
| streamsize precision( streamsize new_precision ); |
(2) |
管理 std::num_put::do_put 所进行的浮点输出精度(即生成多少数位)。
1) 返回当前精度。
2) 设置精度为给定值。返回先前的精度。
std::basic_ios::init 所建立的默认精度为 6 。
参数
| new_precision | - | 新的精度设置 |
返回值
调用函数前的精度
管理域的宽度
std::ios_base::width| streamsize width() const; |
(1) | |
| streamsize width( streamsize new_width ); |
(2) |
管理某些输出操作时生成的最小字符数,和某些输出操作时生成的最大字符数。
1) 返回当前域宽。
2) 设置域宽为给定值。返回先前的位宽。
参数
| new_width | - | 设置的新域宽 |
返回值
调用函数前的域宽
注意
一些 I/O 函数在返回前调用 width(0) ,见 std::setw (这导致此域仅在下次 I/O 函数,而不再任何后继 I/O 时有效)。
此修改器在输入和输出上拥有的准确效果在单独的 I/O 函数之间有别,效果单独描述于每个 operator<< 和 operator>> 重载的页面。
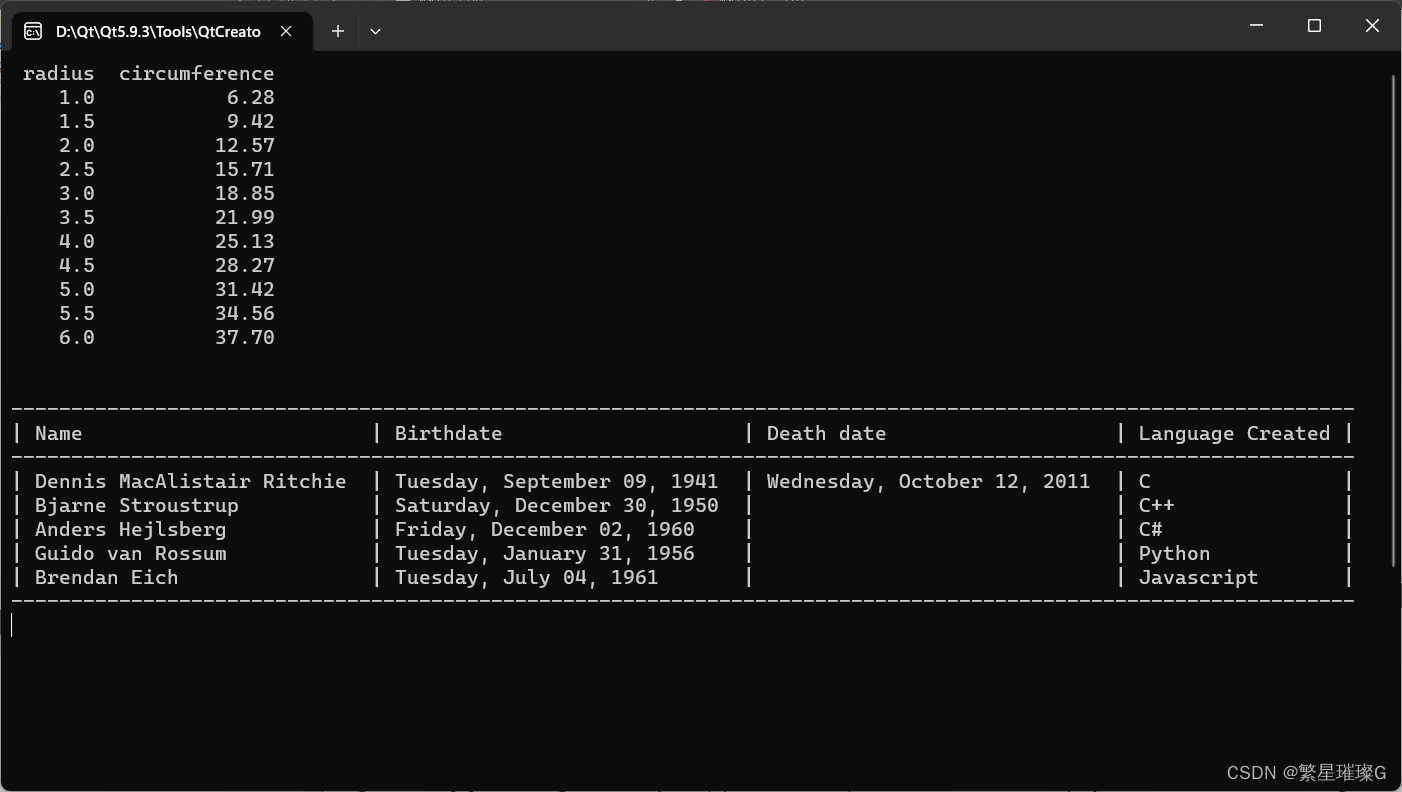
调用示例
#include <array>
#include <tuple>
#include <ctime>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.1415926535;
int main()
{
const int WIDTH = 15;
std::cout.setf(std::ios::right); // 等价: cout << right;
std::cout << std::setw(WIDTH / 2) << "radius"
<< std::setw(WIDTH) << "circumference" << std::endl;
std::cout.setf(std::ios::fixed);
for (double radius = 1; radius <= 6; radius += 0.5)
{
std::cout << std::setprecision(1) << std::setw(WIDTH / 2)
<< radius
<< std::setprecision(2) << std::setw(WIDTH)
<< (2 * PI * radius) << std::endl;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
auto str_time = [](int year, int mon, int day)
{
constexpr std::array<const char*, 7> week_day{ {
"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"
} };
std::tm tm{};
tm.tm_year = year - 1900;
tm.tm_mon = mon - 1;
tm.tm_mday = day;
day += mon < 3 ? year-- : year - 2;
tm.tm_wday = (23 * mon / 9 + day + 4 + year / 4 - year / 100 + year / 400) % 7;
std::ostringstream out;
out << week_day[tm.tm_wday] << ", " << std::put_time(&tm, "%B %d, %Y");
return out.str();
};
constexpr int column_size = 4;
using table_t = std::array<std::string, column_size>;
table_t headers{ { "Name", "Birthdate", "Death date", "Language Created" } };
std::array<table_t, 5> data{ {
{ { "Dennis MacAlistair Ritchie", str_time(1941, 9, 9), str_time(2011, 10, 12), "C" } },
{ { "Bjarne Stroustrup", str_time(1950, 12, 30), "", "C++" } },
{ { "Anders Hejlsberg", str_time(1960, 12, 2), "", "C#" } },
{ { "Guido van Rossum", str_time(1956, 1, 31), "", "Python" } },
{ { "Brendan Eich", str_time(1961, 7, 4), "", "Javascript" } }
} };
constexpr int name_wid = 30;
constexpr int birth_wid = 30;
constexpr int death_wid = 30;
constexpr int lang_wid = 18;
auto print_line = [](table_t const & tbl)
{
const std::string &Name = tbl[0];
const std::string &Birthdate = tbl[1];
const std::string &DeathDate = tbl[2];
const std::string &LanguageCreated = tbl[3];
std::cout.width(name_wid);
std::cout << ("| " + Name) << '|';
std::cout.width(birth_wid);
std::cout << (' ' + Birthdate) << '|';
std::cout.width(death_wid);
std::cout << (' ' + DeathDate) << '|';
std::cout.width(lang_wid);
std::cout << (' ' + LanguageCreated) << '|';
std::cout << '\n';
};
constexpr int total_wid = name_wid + birth_wid + death_wid + lang_wid + column_size;
auto print_break = []
{
std::cout.width(total_wid);
std::cout.fill('-');
std::cout << '-' << std::endl;
std::cout.fill(' ');
};
std::cout.setf(std::ios::left, std::ios::adjustfield);
print_break();
print_line(headers);
print_break();
for (auto const &entry : data)
{
print_line(entry);
}
print_break();
return 0;
}输出