概述
本文记录工作中使用Spring Boot + ElasticSearch的实战,Spring Boot版本:2.1.6.RELEASE。
基础
Spring Boot已是Java开发标配,使用SB提供的starter,简单高效。
配置
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
增加配置文件:
spring:
data:
elasticsearch:
cluster-nodes: 100.200.33.203:9300,100.200.33.204:9300,100.200.33.205:9300
cluster-name: elasticsearch6
repositories:
enabled: true
定义实体类:
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
@Data
@Document(indexName="symptom-inquiry", type="symptom", createIndex = false)
public class SymptomEntity {
/**
* 根据key由指定hash算法生成
*/
@Id
private Long id;
private String key;
// 省略其他字段定义
}
主键Id生成算法util工具类:
import com.google.common.base.Charsets;
import com.google.common.hash.HashCode;
import com.google.common.hash.HashFunction;
import com.google.common.hash.Hasher;
import com.google.common.hash.Hashing;
@Slf4j
public class HashUtils {
/**
* 针对 SymptomEntity key 计算hash值
*/
public static Long getHashCode(String key) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(key)) {
return 0L;
}
/*
* 使用 MURMUR3_128 hash算法计算hash值
*/
HashFunction function = Hashing.murmur3_128();
Hasher hasher = function.newHasher();
HashCode code = hasher.putString(key, Charsets.UTF_8).hash();
log.info("目标 key = {}, 生成ID = {}", key, code.asLong());
return code.asLong();
}
}
基于Repository提供一个空实现的查询接口类:
import org.springframework.data.domain.Page;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.ElasticsearchRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
@Configuration
public interface SymptomSearchRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<SymptomEntity, Long> {
}
根据业务需要,上述接口里可以新增自定义查询方法,满足命名规范即可。如,findByFieldname,Filedname是SymptomEntity实体类里面定义的字段,也是ES文档的字段:
Page<SymptomEntity> findByKey(String key, Pageable pageable);
Optional<SymptomEntity> findByDescription(String description);
使用:
@Resource
private SymptomSearchRepository symptomSearchRepository;
@Test
public void test() {
// 基础使用
symptomSearchRepository.saveAll();
symptomSearchRepository.save();
symptomSearchRepository.findAll();
symptomSearchRepository.findById(1L);
// 进阶使用, 拼接组装ES SQL
BoolQueryBuilder allBoolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
BoolQueryBuilder bodyTagBoolQueryBuilder = this.setBodyTagBoolQueryBuilder(Sets.newHashSet("手", "胳膊"));
BoolQueryBuilder sexBoolQueryBuilder = this.setSexBoolQueryBuilder(Sex.MALE);
allBoolQueryBuilder.should(bodyTagBoolQueryBuilder);
allBoolQueryBuilder.must(sexBoolQueryBuilder);
symptomSearchRepository.search(allBoolQueryBuilder);
}
private BoolQueryBuilder setSexBoolQueryBuilder(Sex sex) {
BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
String notSex = Sex.getNotSex(sex);
boolQueryBuilder.mustNot(QueryBuilders.matchPhraseQuery("sex", notSex));
return boolQueryBuilder;
}
private BoolQueryBuilder setBodyTagBoolQueryBuilder(Set<String> allBodyTags) {
BoolQueryBuilder boolQueryBuilder = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
/*
* 部位匹配逻辑 封装 bodyTagBoolQueryBuilder
*/
for (String bodyTag : allBodyTags) {
QueryBuilder queryBuilderSearchCondition = QueryBuilders.termQuery("bodyTags", bodyTag);
boolQueryBuilder.should(queryBuilderSearchCondition);
}
return boolQueryBuilder;
}
上述API封装得到的ES SQL如下:
{
"bool" : {
"must" : [
{
"bool" : {
"must_not" : [
{
"match_phrase" : {
"sex" : {
"query" : "FEMALE",
"slop" : 0,
"zero_terms_query" : "NONE",
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
],
"should" : [
{
"bool" : {
"should" : [
{
"term" : {
"bodyTags" : {
"value" : "手",
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
},
{
"term" : {
"bodyTags" : {
"value" : "胳膊",
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
],
"adjust_pure_negative" : true,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
kibana + ES 使用
Dev-Tools
上面拼接的SQL,可以在ES可视化平台,执行并查看数据。
ES可视化客户端工具,首选一般就是Kibana。Dev-Tools,提供自动补全提示功能,支持手写SQL语法,适合有要求的开发者。

常用的语法:
- 查询
POST symptom-inquiry/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"commonName": "腹痛"
}
}
}
- 删除:以主键Id删除
POST symptom-inquiry/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match": {
"_id": "2193474183642781887"
}
}
}
- 新增
PUT symptom-inquiry-stg/symptom/<_id>
{
"_id": "111",
"commonName": "aaa",
"key": "find:ss"
}
Discover
除了上面的Dev-Tools方式,还提供如下简单点点点操作的Discover
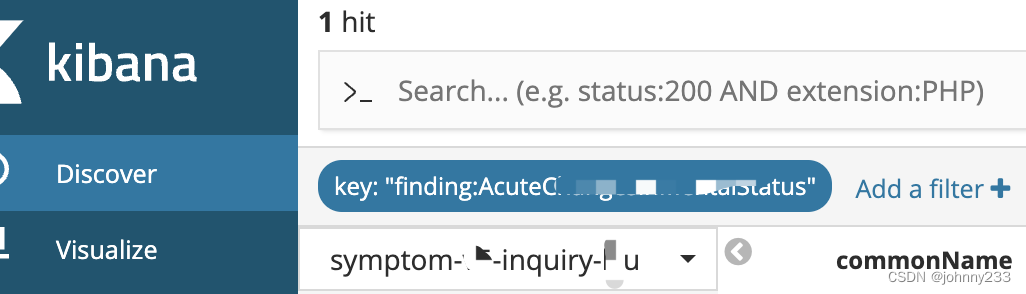
配置2
除了上面这种使用spring-data-jpa提供的封装好的
数据源配置类的另一种方式:
@Configuration
public class EsConfig {
@Bean(name = "stgHigh", destroyMethod = "close")
public RestHighLevelClient stgHigh() {
final CredentialsProvider provider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
provider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials("", ""));
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("100.199.222.111", 9200),
new HttpHost("100.199.222.112", 9200),
new HttpHost("100.199.222.113", 9200));
builder.setHttpClientConfigCallback(inner -> inner.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(provider));
return new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
}
}
使用上面的,测试程序如下:
@Autowired
@Qualifier("stgHigh")
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
@Test
public void test() {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("symptom-inquiry");
searchRequest.source().size(1500);
SearchResponse stgResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
JSONObject stgJson = (JSONObject) JSON.parse(stgResponse.toString());
JSONObject stgHits = (JSONObject) stgJson.get("hits");
Integer total = stgHits.getInteger("total");
JSONArray stgArray = stgHits.getJSONArray("hits");
for (int i = 0; i < total; i++) {
JSONObject item = (JSONObject) stgArray.get(i);
SymptomEntity stgEntity = JSON.parseObject(item.getString("_source"), SymptomEntity.class);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(stgEntity.getKey()) || StringUtils.isEmpty(stgEntity.getCommonName())) {
log.info("symptomEntity {}", JsonUtil.beanToJson(item));
continue;
}
}
}
多数据配置
如下代码
@Configuration
public class EsConfig {
@Primary
@Bean(name = "prod", destroyMethod = "close")
public RestClient prod() {
final CredentialsProvider provider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
provider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials("es7", "root"));
RestClientBuilder clientBuilder = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("170.188.116.203", 9200),
new HttpHost("170.188.117.204", 9200),
new HttpHost("170.188.118.205", 9200));
// 根据需求配置身份验证
clientBuilder.setHttpClientConfigCallback(builder -> builder.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(provider));
return clientBuilder.build();
}
@Bean(name = "stg", destroyMethod = "close")
public RestClient stg() {
final CredentialsProvider provider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
provider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials("es6", "root"));
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("100.119.222.11", 9200),
new HttpHost("100.119.222.12", 9200),
new HttpHost("100.119.222.13", 9200));
builder.setHttpClientConfigCallback(inner -> inner.setDefaultCredentialsProvider(provider));
return builder.build();
}
}
使用上面配置好的两个ES数据源,从stg和prod两个数据源取数:
@Component
public class queryFromStgAndProdService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("prod")
private RestClient prodClient;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("stg")
private RestClient stgClient;
}