异常首先从调用堆栈的顶部抛出,如果没有被捕获,它会向下传递到前一个方法。如果在那里没有被捕获,异常会再次向下传递到前一个方法,依此类推,直到它们被捕获或者达到调用堆栈的最底部。这被称为异常传播。
异常传播示例
TestExceptionPropagation1.java
class TestExceptionPropagation1{void m(){int data=50/0;}void n(){m();}void p(){try{n();}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("exception handled");}}public static void main(String args[]){TestExceptionPropagation1 obj=new TestExceptionPropagation1();obj.p();System.out.println("normal flow...");}}
输出:
exception handlednormal flow...
在上面的示例中,异常在m()方法中发生,但没有被处理,所以它向前传播到前一个n()方法,也没有被处理,然后又传播到p()方法,其中异常被处理。
异常可以在调用堆栈中的任何方法中处理,无论是在main()方法、p()方法、n()方法还是m()方法中。
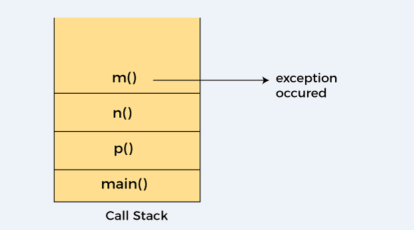
异常传播示例
TestExceptionPropagation1.java
class TestExceptionPropagation2{void m(){throw new java.io.IOException("device error");//检查异常}void n(){m();}void p(){try{n();}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("exception handeled");}}public static void main(String args[]){TestExceptionPropagation2 obj=new TestExceptionPropagation2();obj.p();System.out.println("normal flow");}}
输出:
Compile Time Error