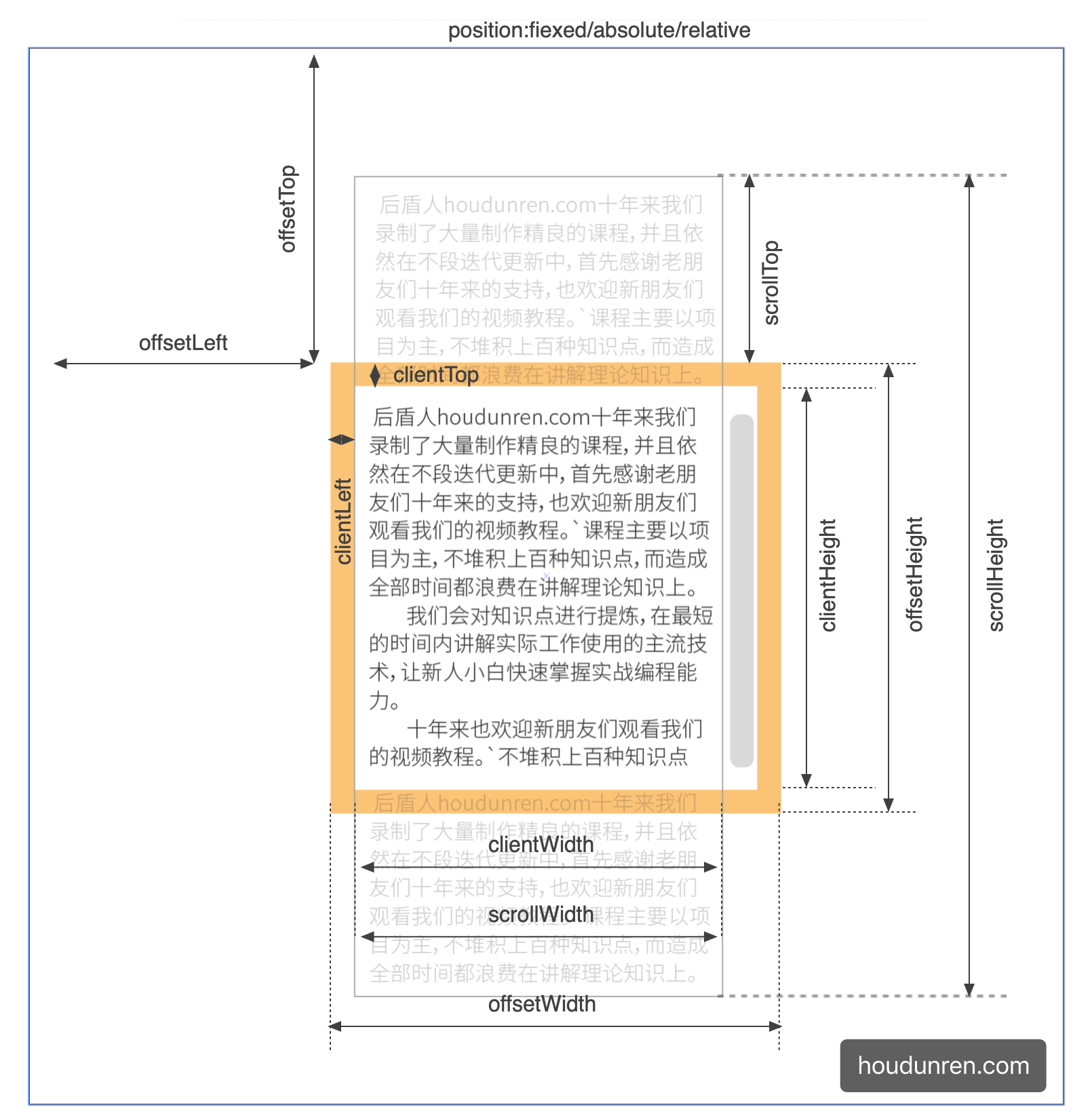
一、尺寸
1.视窗尺寸
document.documentElement.clientWidth:视窗宽度document.documentElement.clientHeight:视窗高度
2.各种尺寸
举例:<div id="gao"></div>
前提:var a = document.getElementById('gao')
| 内容 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| a.offsetWidth | a元素宽度(包含内容和padding值和border值) |
| a.offsetHeight | a元素高度(包含内容和padding值和border值) |
| a.offsetLeft | a元素盒子边距距离父元素边界值(左边) |
| a.offsetTop | a元素盒子边距距离父元素边界值(上边) |
| 内容 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| a.clientWidth | a元素宽度(包含内容和padding值) |
| a.clientHeight | a元素高度(包含内容和padding值) |
| a.clientLeft | a元素(包含内容和padding值)距离外部边界值(左边)(一般就是border值) |
| a.clientTop | a元素(包含内容和padding值)距离外部边界值(上边)(一般就是border值) |
| 内容 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| a.scrollWidth | a元素宽度(包含内容和padding值和溢出值(例如子元素尺寸超出父元素)) |
| a.scrollHeight | a元素高度(包含内容和padding值和溢出值(例如子元素尺寸超出父元素) |
| document.documentElement.scrollLeft | 滑动条距离视窗左边的距离 |
| document.documentElement.scrollTop | 滑动条距离视窗顶部的距离 |
二、滑动
1.连续滑动
解释:配合setInterval使用,能够每次向下滑行一点,一直滑动
格式:element.scrollBy()//其会在每次的基础上再向下滑动一次,其相当于“相对定位”
参数:behavior:smooth 为平滑滚动
<style>
body {
height: 1500px;
}
</style>
<script>
setInterval(() => {
document.documentElement.scrollBy({
top: 10, behavior: 'smooth' })//还可以设置left值
}, 100)
</script>
2.一次滑动
解释:一次性滑动目标位置
格式:element.scrollTo()//其一次滑倒设定的值的位置,其相当于“绝对定位”
参数:behavior:smooth 为平滑滚动
<style>
body {
height: 1500px;
}
</style>
<script>
setTimeout(() => {
document.documentElement.scroll({
top: 200, behavior: 'smooth' })//还可以设置left值
}, 1500)
</script>
3.顶部或底部滑动
解释:element.scrollIntoView()//其只能设置block值,end表示结尾,start表示开始
参数:behavior:smooth 为平滑滚动
<style>
body {
height: 1500px;
}
</style>
<style>
body {
height: 1500px;
}
</style>
<button onclick="a()">000</button>
<script>
function a(){
document.documentElement.scrollIntoView({
block: 'end', behavior: 'smooth' })
}
</script>