在Java8中,Function接口是一个函数接口。
源码
package java.util.function;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 函数接口:表示接受一个实参并产生结果的函数。
* 函数方法 {@link #apply(Object)}.
* @param <T> 函数输入的类型
* @param <R> 函数结果的类型
* @since 1.8
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
/**
* 应用函数
* @param t the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
R apply(T t);
/**
* 可以让多个`Function`函数组合使用
*/
default <V> Function<V, R> compose(Function<? super V, ? extends T> before) {
Objects.requireNonNull(before);
return (V v) -> apply(before.apply(v));
}
/**
* 可以让多个`Function`函数组合使用
*/
default <V> Function<T, V> andThen(Function<? super R, ? extends V> after) {
Objects.requireNonNull(after);
return (T t) -> after.apply(apply(t));
}
static <T> Function<T, T> identity() {
return t -> t;
}
}
apply
ex: 传递一个字符串,打印一下 & 返回处理后的字符串
public class Java8Function {
@Test
public void test_apply() throws Exception {
// 传递一个字符串,打印一下 & 返回处理后的字符串
Function<String, String> helloFunction = str -> {
System.out.println(str);
return "hello: " + str;
};
String result = helloFunction.apply("zhengqingya");
System.out.println(result);
}
}

compose/andThen
多个Function函数组合使用
tips: 执行顺序差异
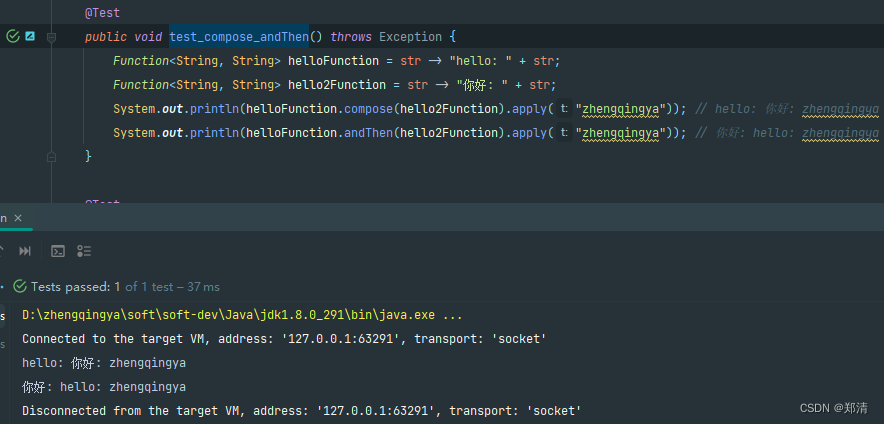
public class Java8Function {
@Test
public void test_compose_andThen() throws Exception {
Function<String, String> helloFunction = str -> "hello: " + str;
Function<String, String> hello2Function = str -> "你好: " + str;
System.out.println(helloFunction.compose(hello2Function).apply("zhengqingya")); // hello: 你好: zhengqingya
System.out.println(helloFunction.andThen(hello2Function).apply("zhengqingya")); // 你好: hello: zhengqingya
}
}
作为方法参数传入
将函数接口作为方法参数传入,可以解决只有部分差异的相同业务代码中的硬编码问题,让代码更灵活通用。
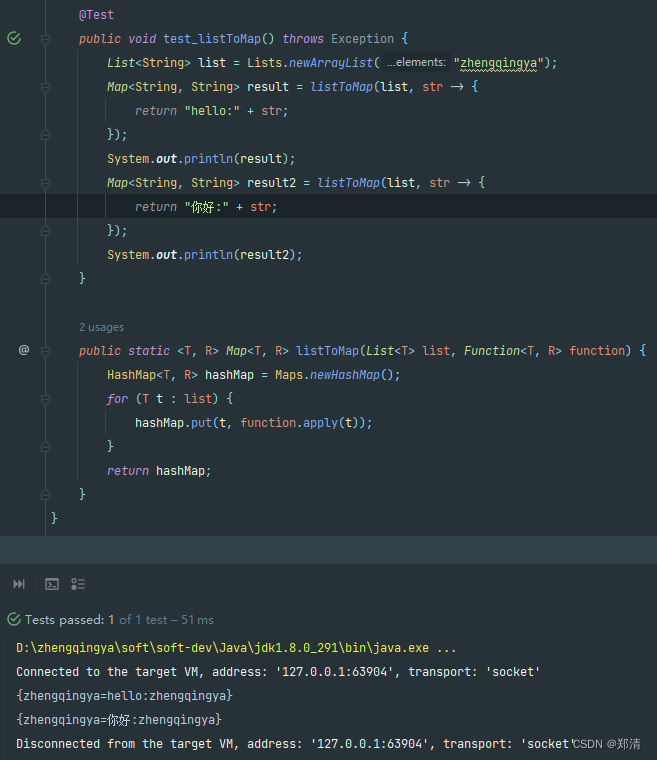
ex: 将list转成map。通过传入不同的处理方式实现不同的结果。
public class Java8Function {
@Test
public void test_listToMap() throws Exception {
List<String> list = Lists.newArrayList("zhengqingya");
Map<String, String> result = listToMap(list, str -> {
return "hello:" + str;
});
System.out.println(result);
Map<String, String> result2 = listToMap(list, str -> {
return "你好:" + str;
});
System.out.println(result2);
}
public static <T, R> Map<T, R> listToMap(List<T> list, Function<T, R> function) {
HashMap<T, R> hashMap = Maps.newHashMap();
for (T t : list) {
hashMap.put(t, function.apply(t));
}
return hashMap;
}
}