上一次谈到Naive approach的缺点,在这篇论文里,作者提出一个DP-Mapping的概念,以及两种数据结构
the ancestry tree和the map,并且使粒子滤波的计算复杂度与迭代次数无关
今天来分析一下这些数据结构,先来看the ancestry tree:
1, The tree itself is rooted with an initial particle, of which all other particles are progeny
2, Each particle maintains a pointer to its parent and is assigned a unique numerical ID
3, Each particle maintains a list of grid squares that it has updated
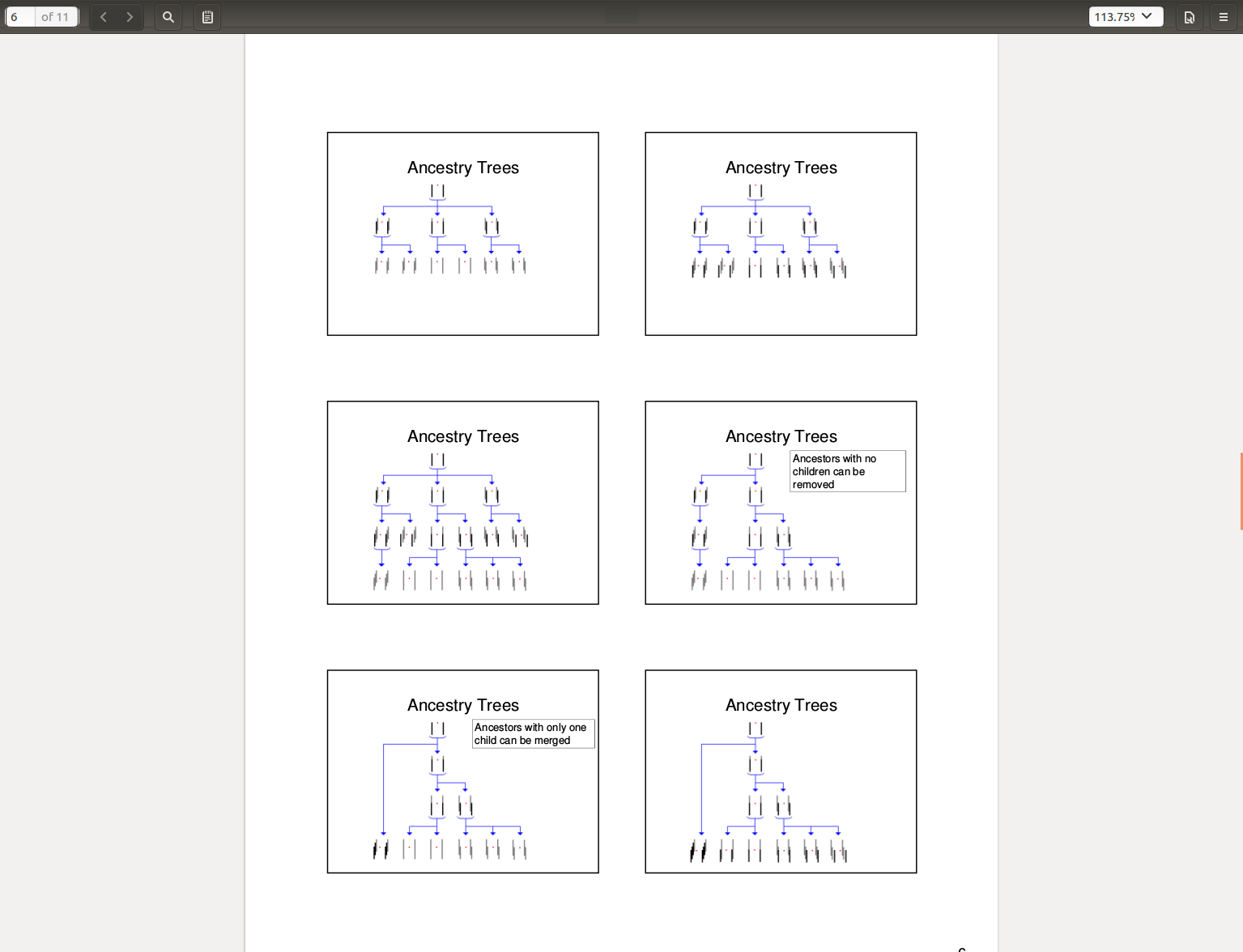
Ancestry tree的特点:
The tree has bounded size regardless of the number of iterations of the particle filter
维护Ancestry tree过程 (maintain the ancestry tree):
概括描述:
We maintain a bounded size tree by pruning away unnecessary nodes
具体措施:
1, note that certain particles may not have children and can simply be removed from the tree
2, we can recursively prune away dead branches of the tree
剪枝的结果:
the only particle which are stored in our ancestry tree are exactly those particles which are ancestors of the
current generation of particles
PS:从句有一点复杂,慢慢理解
可想而知,这样的剪枝会产生一个结果:
If a particle has only one child in our ancestry tree, we can essentially remove it, by collapsing that branch of
the tree
剪枝操作可以得到minimal ancestry tree,它有一个良好的性质:
Independent of the number of iterations of particle filtering, a minimal ancestry tree of P particles
1. has exactly P leaves
2. has branching factor of at least 2, and
3. has depth no more than P
ancestry tree的数据结构就介绍到这里,至于它怎样运用在SLAM过程,后面章节会介绍
我这里画一个草图,
哈哈,下次来分析Map representation
这是官方ppt的讲解图: