文章目录
前言
链表和顺序表都是线性表,都是数据结构中重要的部分,今天来看的单链表是很多高级结构的子部分,所以学好单链表有助于我们后期的提升。
一、链表和顺序表的区别
我们知道顺序表在内存上的存储方式: 是在内存中连续存放的。
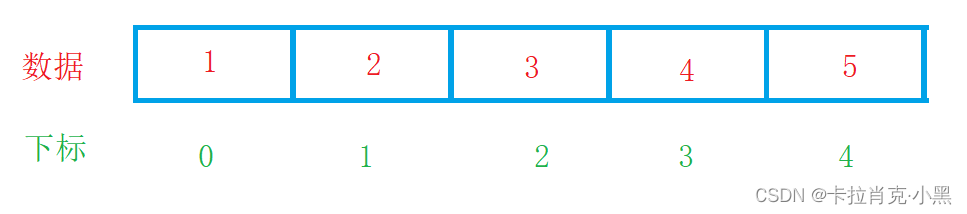
从内存分布可以看出,顺序表的随机访问性强,有下标就可以知道我们的数据,但是缺点也很明显,插入删除时要保证空间连续,就要进行移动,造成插入删除不便,且数组还要考虑是否要扩容等情况。
链表在空间上的存储方式:随机存储。
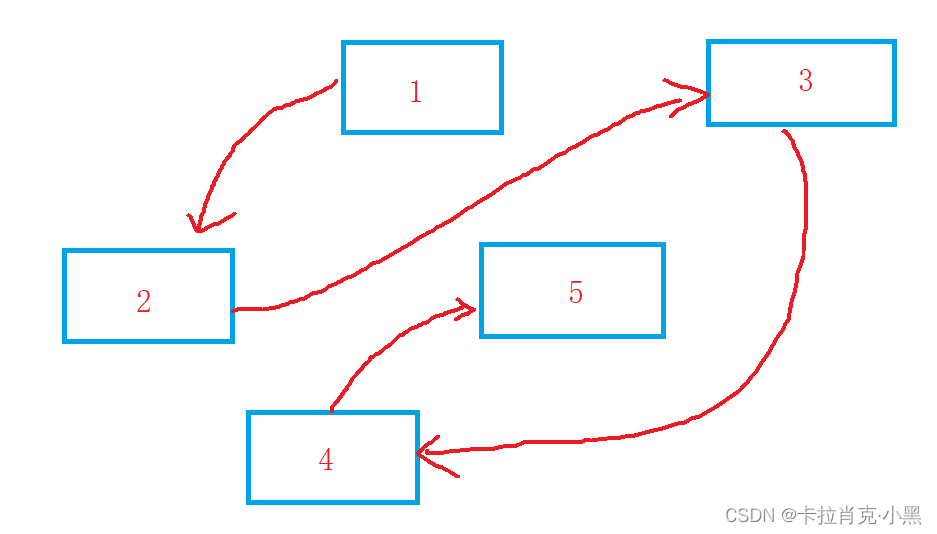
从内存可以看出:链表在空间上的随机存储,由上一个节点通过指针指向下一个节点。这样的好处是插入删除不在需要移动数据,只需要改变指针就可以了,但也失去了随机访问,造成了访问不便。
和顺序表的对比:
顺序表的优点:物理空间连续,支持下标随机访问。
顺序表的缺点:空间不够需要扩容,扩容有一定的性能消耗,也会存在一定的空间浪费。且头部或中间的插入删除效率低下。
顺序表的优点:按需申请空间。头部和中间插入不需要移动数据。
顺序表的缺点:数据的随机访问性差。
二、什么是单链表
有一个或多个存放数据的结构体成员,还有一个指向下一个节点的指针。
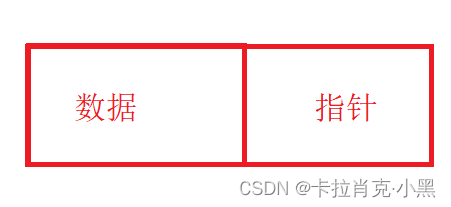
数据:用来存储我们使用的数据。
指针:用来存储下一个节点的地址。
单链表分类
单链表分为四种:带头不循环单链表,带头循环单链表,不带头循环单链表和不带头不循环单链表。
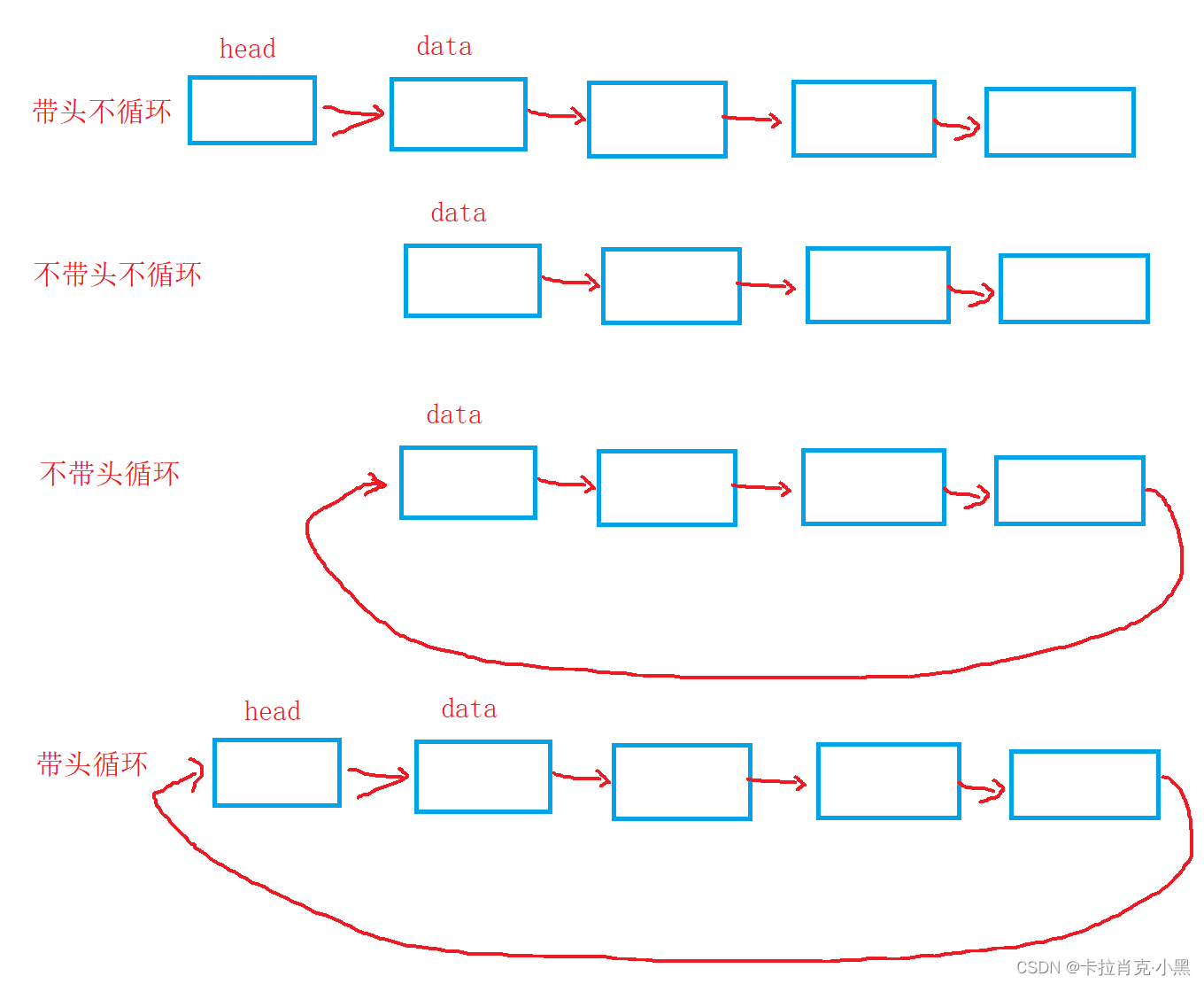
带头中的头节点不存储有效的数据。
单链表的结构
不管带不带头,是否是循环非循环,单链表的结构是一样的。
struct SListNode
{
SLTDateType data;//SLTDateType数据类型
struct SListNode* next;//指向下一个结构体的指针
}
三、带头不循环单链表
下面我们来实现一下带头不循环单链表吧
1.单链表的结构体
typedef int SLTDateType;
typedef struct SListNode SListNode;
struct SListNode
{
SLTDateType data;//SLTDateType数据类型
struct SListNode* next;//指向下一个结构体的指针
};
这里我们用的数据类型为整形的数据。
2.带头不循环单链表的初始化和销毁
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)// 动态申请一个节点
{
SListNode* pos = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//动态开辟一个空间
pos->data = x;//给结构体的数据域赋值
pos->next = NULL;//把指向下一个节点的地址置空
}
SListNode* Initialization()//初始带头节点的单链表
{
SListNode* pHead = BuySListNode(0);
return pHead;
}
void SListDestroy(SListNode* pHead)//单链表的销毁
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
while (pHead->next != NULL)//如果头节点的下一个位置不为空,则证明没有到链表结尾
{
SListNode* pos = pHead->next;//创建一个指向头节点下一个位置的指针
pHead->next = pos->next;//把头节点的下一个位置指向要删除的位置的下一个
free(pos);//释放要删除的位置
}
}
在这里我们单独创建了一个函数,这个函数用来开辟节点,方便我们后面插入时的节点开辟。
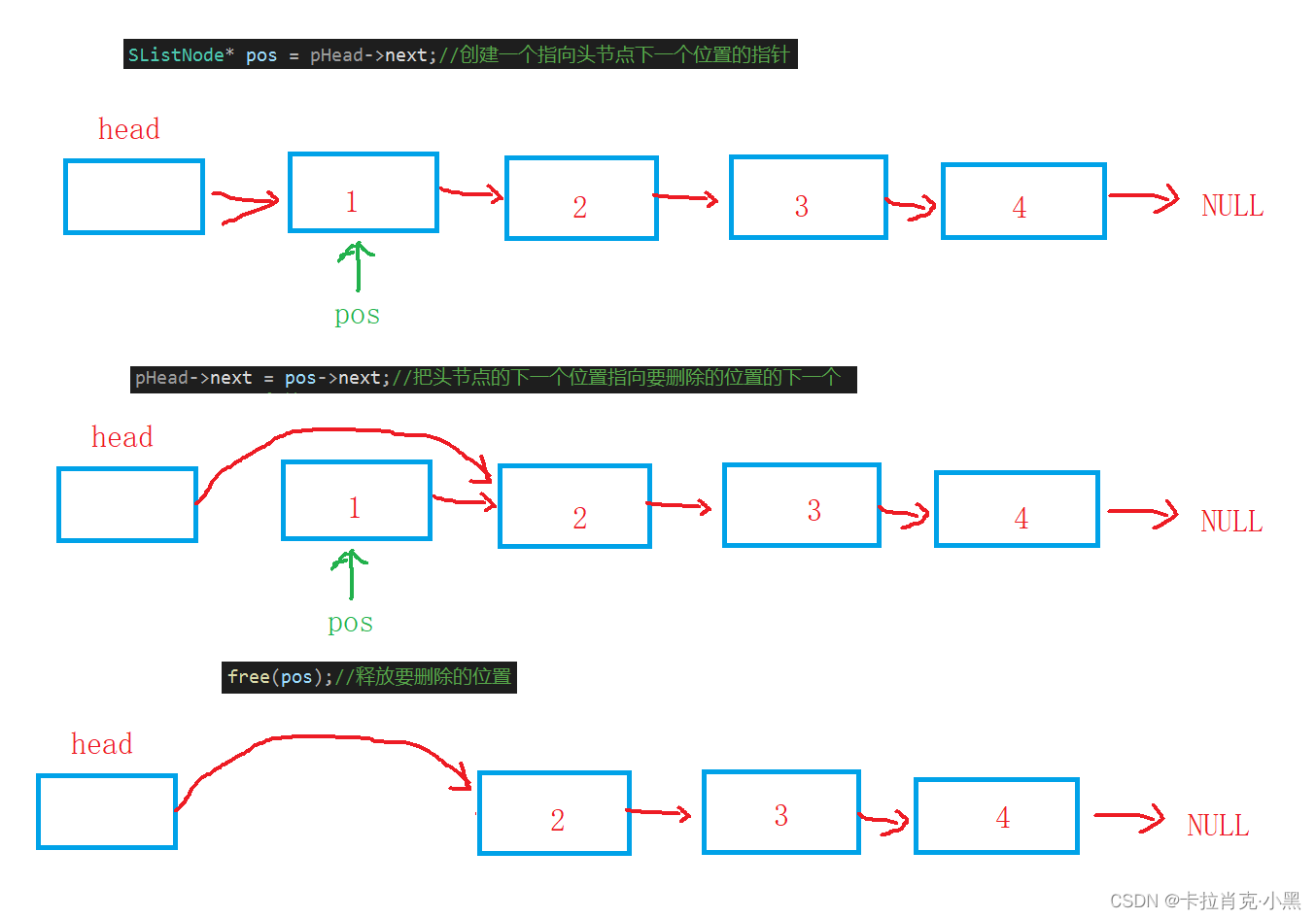
我们创建的头节点需要在销毁函数外释放。
3.带头不循环单链表的头插,尾插和打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* pHead)// 单链表打印
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = pHead->next;//创建一个指向头节点下一个位置的指针
while (pos != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", pos->data);
pos = pos->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
void SListPushBack(SListNode* pHead, SLTDateType x)//单链表尾插
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = BuySListNode(x);
SListNode* inse = pHead;
while (inse->next != NULL)
{
inse = inse->next;//让元素向后移动
}
inse->next = pos;//把节点连接到最后的节点上。
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode* pHead, SLTDateType x)//单链表的头插
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = BuySListNode(x);
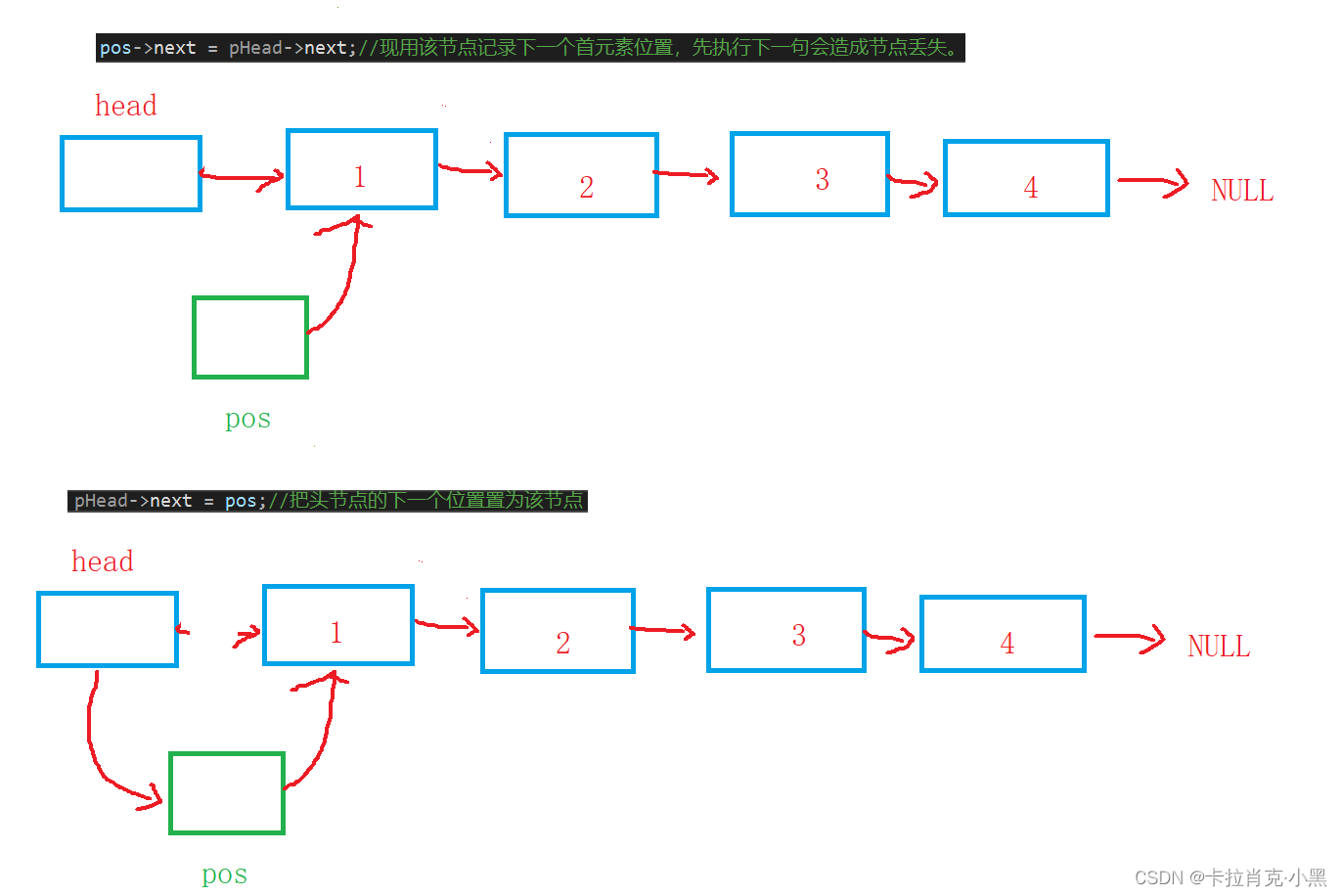
pos->next = pHead->next;//现用该节点记录下一个首元素位置,先执行下一句会造成节点丢失。
pHead->next = pos;//把头节点的下一个位置置为该节点
}
测试函数:
void test1()
{
SListNode* pHead = Initialization();
SListPushBack(pHead, 1);
SListPushBack(pHead, 2);
SListPushBack(pHead, 3);
SListPushBack(pHead, 4);
SListPushBack(pHead, 5);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(pHead);
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
void test2()
{
SListNode* pHead = Initialization();
SListPushFront(pHead, 1);
SListPushFront(pHead, 2);
SListPushFront(pHead, 3);
SListPushFront(pHead, 4);
SListPushFront(pHead, 5);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(pHead);
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
int main()
{
test1();//单链表尾插
test2();//单链表的头插
return 0;
}

注意:我们插入时如果不额外创建一个变量,那么进行插入时就要考虑顺序问题,不然会造成指针丢失。
4.带头不循环单链表的头删和尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode* pHead)// 单链表的尾删
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
assert(pHead->next);//对头节点的下一个位置进行判断,如果为空,则证明没有元素
SListNode* pos = pHead;//用于保存要删除节点的上一个位置
SListNode* del = pHead->next;//用于保存要删除节点的位置
while (del->next != NULL)
{
pos = pos->next;
del = del->next;//让元素向后移动
}
free(del);
pos->next = NULL;//把要删除节点的上一个位置的下一个节点置空
}
void SListPopFront(SListNode* pHead)// 单链表头删
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
assert(pHead->next);//对头节点的下一个位置进行判断,如果为空,则证明没有元素
SListNode* del = pHead->next;//用于保存要删除节点的位置
pHead->next = del->next;
free(del);
}
测试函数:
void test3()
{
SListNode* pHead = Initialization();
SListPushBack(pHead, 1);
SListPushBack(pHead, 2);
SListPushBack(pHead, 3);
SListPushBack(pHead, 4);
SListPushBack(pHead, 5);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopBack(pHead);// 单链表的尾删
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopFront(pHead);// 单链表头删
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopBack(pHead);// 单链表的尾删
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopFront(pHead);// 单链表头删
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(pHead);
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
int main()
{
//test1();//单链表尾插
//test2();//单链表的头插
test3();//单链表的头删和尾删
return 0;
}

注意:我们不仅要判断传入的头节点是否正确,还要看传入的头节点下一个位置是否为NULL,当为空时证明没有节点,无法删除。
5.带头不循环单链表的查找,指定位置的插入和删除
SListNode* SListFind(SListNode* pHead, SLTDateType x)// 单链表查找
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = pHead->next;
while (pos != NULL)
{
if (pos->data == x)
{
return pos;//找打了该数据,返回这个结构体
}
pos = pos->next;
}
return NULL;//代表未找到
}
void SListInsertAfter(SListNode* pos, SLTDateType x)// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
{
assert(pos);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* inse = BuySListNode(x);
inse->next = pos->next;
pos->next = inse;
}
void SListEraseAfter(SListNode* pos)// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
{
assert(pos);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* del = pos->next;
pos->next = del->next;
free(del);
}
测试函数:
void test4()
{
SListNode* pHead = Initialization();
SListPushBack(pHead, 1);
SListPushBack(pHead, 2);
SListPushBack(pHead, 3);
SListPushBack(pHead, 4);
SListPushBack(pHead, 5);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListInsertAfter(SListFind(pHead, 3), 30);// 单链表在pos位置之后插入x
SListPrint(pHead);
SListEraseAfter(SListFind(pHead, 3));// 单链表删除pos位置之后的值
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(pHead);
free(pHead);
pHead = NULL;
}
int main()
{
//test1();//单链表尾插
//test2();//单链表的头插
//test3();//单链表的头删和尾删
test4();//单链表的查找,指定位置的插入和删除
return 0;
}

这里的实现思路和插入删除一样,只需要注意顺序就可以了。
四、不带头循环单链表
下面我们加一点难度来实现一下不带头循环单链表吧。
1.单链表的结构体
typedef struct STU SLTDateType;
typedef struct SListNode SListNode;
struct STU
{
char name[10];//姓名
int score;//分数
};
struct SListNode
{
SLTDateType data;//SLTDateType数据类型
struct SListNode* next;//指向下一个结构体的指针
};
这里我们用的数据类型为自定义类型的结构体。
2.不带头循环单链表的申请销毁
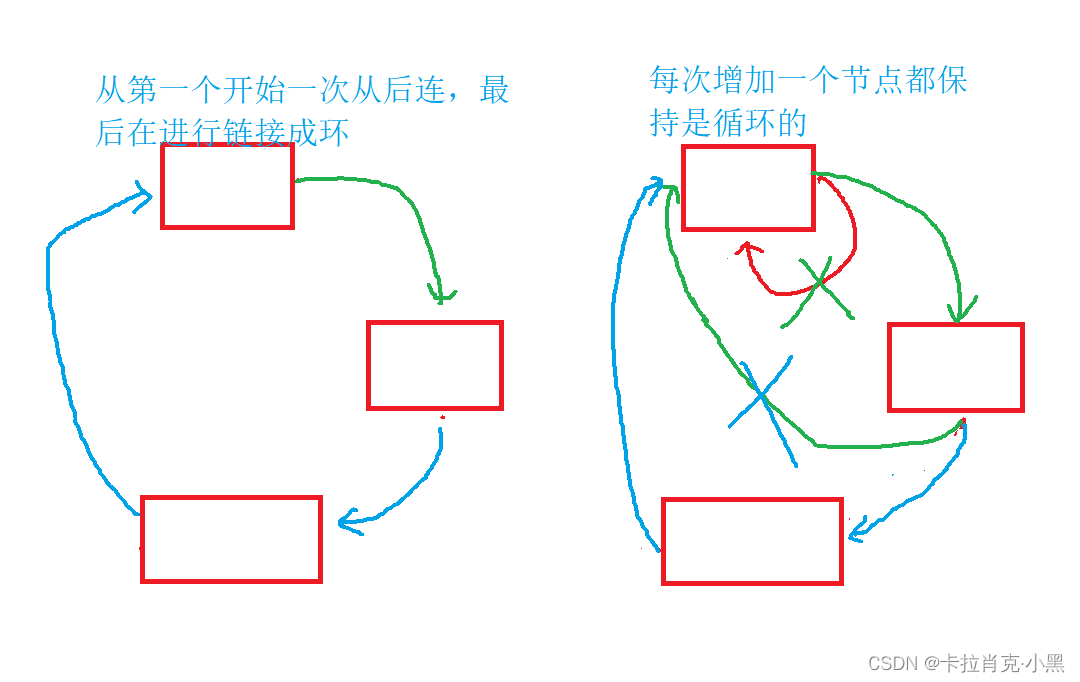
上面是我们的两种思路:第一种是错的,我们要用第二种,因为第二种随时都保持着我们的模型的完整。
SListNode* BuySListNode(SLTDateType x)// 动态申请一个节点
{
SListNode* pos = (SListNode*)malloc(sizeof(SListNode));//动态开辟一个空间
pos->data = x;//给结构体的数据域赋值
pos->next = pos;//即使是一个节点也保持链表是循环的
}
SListNode* Initialization()//初始带头节点的单链表
{
SListNode* pHead = BuySListNode(0);
return pHead;
}
void SListDestroy(SListNode* pHead)//单链表的销毁
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
while (pHead->next != NULL)//如果头节点的下一个位置不为空,则证明没有到链表结尾
{
SListNode* pos = pHead->next;//创建一个指向头节点下一个位置的指针
pHead->next = pos->next;//把头节点的下一个位置指向要删除的位置的下一个
free(pos);//释放要删除的位置
}
}
注意:我们要时刻保持结构的完整性,即使是一个节点也保持链表是循环的。维持模型的完整性至关重要,它关乎着我们的思路是否会不经意之间出错!!!
3.带头不循环单链表的头插,尾插和打印
void SListPrint(SListNode* pHead)// 单链表打印
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = pHead;//我们头节点也存储的有效数据
while (pos->next != pHead)
{
printf("姓名:%s 分数:%2d --> ", pos->data.name, pos->data.score);
pos = pos->next;
}
//此时少打印最后一名的数据
printf("姓名:%s 分数:%2d --> ", pos->data.name, pos->data.score);
printf("\n");
}
void SListPushBack(SListNode** pHead, SLTDateType x)//单链表尾插
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pHead == NULL)
{
*pHead = pos;
(*pHead)->next = (*pHead);
return;
}
SListNode* inse = *pHead;
while (inse->next != *pHead)
{
inse = inse->next;//让元素向后移动
}
inse->next = pos;//把节点连接到最后的节点上。
pos->next = *pHead;
}
void SListPushFront(SListNode** pHead, SLTDateType x)//单链表的头插
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
SListNode* pos = BuySListNode(x);
if (*pHead == NULL)
{
*pHead = pos;
(*pHead)->next = (*pHead);
return;
}
SListNode* inse = *pHead;
while (inse->next != *pHead)//找到最后的节点
{
inse = inse->next;//让元素向后移动
}
inse->next = pos;//让最后的节点的下一个指向新的头节点
pos->next = *pHead;//把新头节点的下一个位置置为旧头节点
*pHead = pos;//更新头节点
}
测试函数:
void test5()
{
SListNode* pHead = NULL;
SLTDateType stu;
int i = 5;
while (i--)//插入5个数据
{
snprintf(stu.name, 10, "stu%2d", i);//和strcpy函数功能相似,这里我们换一个函数
stu.score = rand() % 100;//用来产生随机数
SListPushBack(&pHead, stu);//尾插
}
SListPrint(pHead);
//ListPopBack(SListNode * pHead)
SListDestroy(&pHead);
}
void test6()
{
SListNode* pHead = NULL;
SLTDateType stu;
int i = 5;
while (i--)
{
snprintf(stu.name, 10, "stu%2d", i);
stu.score = rand() % 100;
SListPushFront(&pHead, stu);//头插
}
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(&pHead);
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time());//用来产生随机数
test5();
test6();
return 0;
}
注意:我们插入时一定要保持链表是循环的。
4.带头不循环单链表的头删和尾删
void SListPopBack(SListNode** pHead)// 单链表的尾删
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
assert(*pHead);//进行断言,保证有元素
SListNode* pos = NULL;//用于保存要删除节点的上一个位置
SListNode* del = *pHead;
while (del->next != *pHead)
{
pos = del;
del = del->next;//让元素向后移动
}
free(del);
if (pos == NULL)//证明只有一个元素
{
*pHead = NULL;
}
pos->next = *pHead;//把要删除节点的上一个位置的下一个节点置空
}
void SListPopFront(SListNode** pHead)// 单链表头删
{
assert(pHead);//进行断言,判断传入的地址是否和法
assert(*pHead);//进行断言,保证有元素
SListNode* pos = *pHead;//用来存储最后节点的位置
while (pos->next != *pHead)
{
pos = pos->next;//让元素向后移动
}
pos->next = (*pHead)->next;//断开和旧节点的循环,和新节点连成环
free(*pHead);//释放就旧节点
*pHead = pos->next;//更新头节点
}
测试函数:
void test5()
{
SListNode* pHead = NULL;
SLTDateType stu;
int i = 5;
while (i--)//插入5个数据
{
snprintf(stu.name, 10, "stu%2d", i);//和strcpy函数功能相似,这里我们换一个函数
stu.score = rand() % 100;//用来产生随机数
SListPushBack(&pHead, stu);//尾插
}
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopBack(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopBack(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopBack(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(&pHead);
}
void test6()
{
SListNode* pHead = NULL;
SLTDateType stu;
int i = 5;
while (i--)
{
snprintf(stu.name, 10, "stu%2d", i);
stu.score = rand() % 100;
SListPushFront(&pHead, stu);//头插
}
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopFront(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopFront(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListPopFront(&pHead);
SListPrint(pHead);
SListDestroy(&pHead);
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned)time());//用来产生随机数
test5();
test6();
return 0;
}
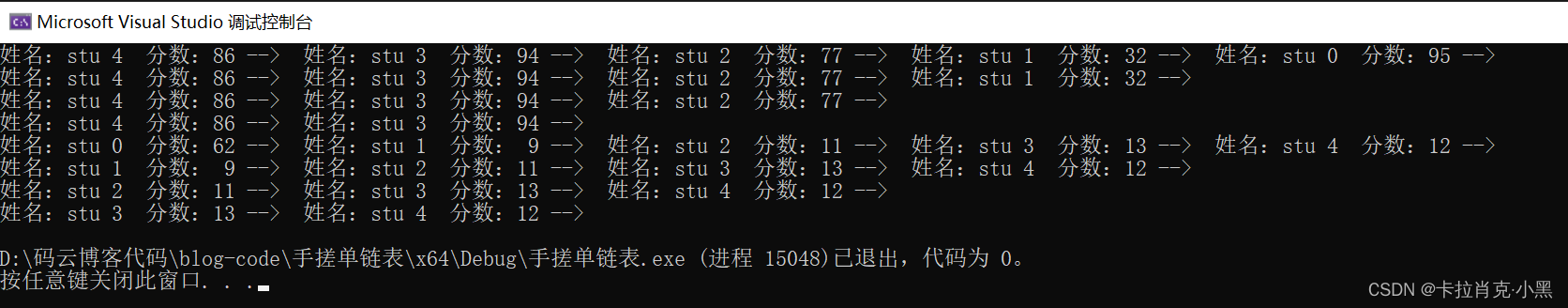
注意:我们头删尾删是都要保持链表是循环的,要注意更新头节点的位置,否则造成野指针问题。
其他的思路和上面很像,这里就不演示了。
五、插入比较有无头节点的区别
下面我们通过一道题来看一下有头和无头的区别吧:oj练习链接
题目描述:
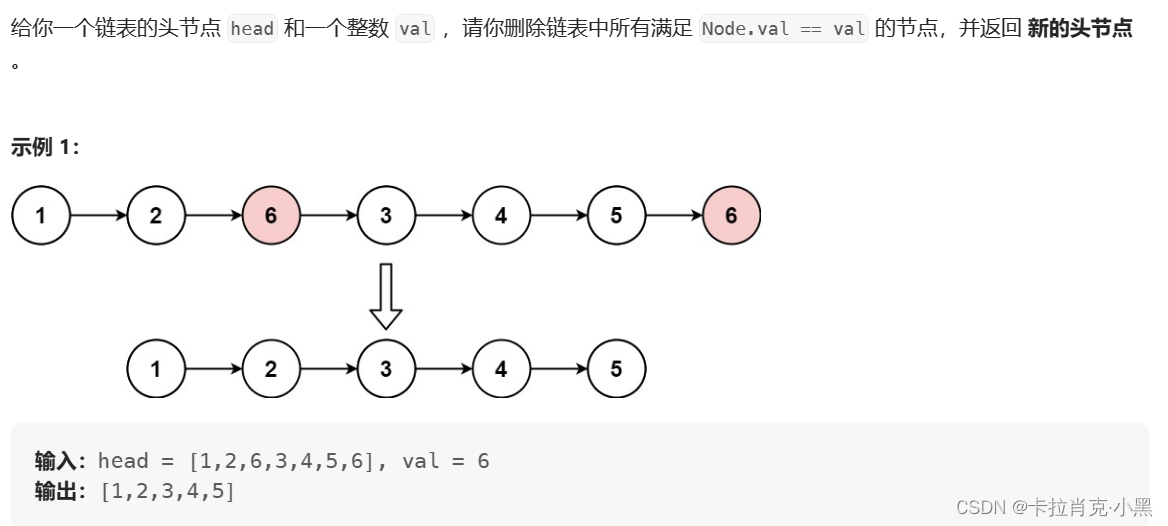
1.有头节点
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* first = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));//创建一个头节点
first->next = head;//指向题目所给的链表
struct ListNode* del = head;//要删除的元素
struct ListNode* pos = first;//要删除元素的上一个
while(del != NULL)
{
if(del->val == val)//如果为要删除的元素,则进行删除
{
pos->next = del->next;
free(del);
del = pos->next;
}
else
{
//如果del不是需要删除的节点,则更新pos,del
pos = pos->next;
del = del->next;
}
}
head = first->next;//更新题目所传入头节点
free(first);//释放我们创建的头节点
first = NULL;
return head;
}
2.无头节点
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head == NULL)//判断传入的链表是否为空
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* del = head;
struct ListNode* pos = NULL;
while(del)
{
if(del->val == val)//如果当前节点是需要删除的节点
{
struct ListNode* next = del->next;//首先保存下一个节点
//如果删除的为头节点,更新头节点
//否则让当前节点的前趋节点链接next节点
if(pos == NULL)
{
head = del->next;
}
else
{
pos->next = del->next;
}
free(del);
del = next;
}
else
{
pos = del;
del = del->next;
}
}
return head;
}
从上面的对比我们还是可以发现头节点的好处,当然,不是有头节点一定好,要根据具体问题具体分析。
六、注意事项
1.我们要时刻保持模型的完整性。
2.我们可以创建一个临时变量来存储头节点,用临时变量进行移动修改。目的是为了保证头节点位置固定,且不需要额外返回。
3.当我们对无头链表进行修改时,要传二级指针,尤其是修改第一个节点,不传二级指针无法修改,因为形参的改变无法影响实参。
4.只有逻辑正确结果才可能正确。