剪枝
复杂的回溯问题通常包含一个或多个约束条件,约束条件通常可用于“剪枝”。
!!! question “例题三”
在二叉树中搜索所有值为 $7$ 的节点,请返回根节点到这些节点的路径,**并要求路径中不包含值为 $3$ 的节点**。
为了满足以上约束条件,我们需要添加剪枝操作:在搜索过程中,若遇到值为 3 3 3 的节点,则提前返回,停止继续搜索。
=== “Python”
```python title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.py"
[class]{}-[func]{pre_order}
```
=== “C++”
```cpp title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.cpp"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “Java”
```java title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.java"
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_compact}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “C#”
```csharp title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.cs"
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_compact}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “Go”
```go title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.go"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrderIII}
```
=== “Swift”
```swift title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.swift"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “JS”
```javascript title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.js"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “TS”
```typescript title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.ts"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “Dart”
```dart title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.dart"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “Rust”
```rust title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.rs"
[class]{}-[func]{pre_order}
```
=== “C”
```c title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.c"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
=== “Zig”
```zig title="preorder_traversal_iii_compact.zig"
[class]{}-[func]{preOrder}
```
剪枝是一个非常形象的名词。如下图所示,在搜索过程中,我们“剪掉”了不满足约束条件的搜索分支,避免许多无意义的尝试,从而提高了搜索效率。

框架代码
接下来,我们尝试将回溯的“尝试、回退、剪枝”的主体框架提炼出来,提升代码的通用性。
在以下框架代码中,state 表示问题的当前状态,choices 表示当前状态下可以做出的选择。
=== “Python”
```python title=""
def backtrack(state: State, choices: list[choice], res: list[state]):
"""回溯算法框架"""
# 判断是否为解
if is_solution(state):
# 记录解
record_solution(state, res)
# 停止继续搜索
return
# 遍历所有选择
for choice in choices:
# 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if is_valid(state, choice):
# 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
make_choice(state, choice)
backtrack(state, choices, res)
# 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undo_choice(state, choice)
```
=== “C++”
```cpp title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
void backtrack(State *state, vector<Choice *> &choices, vector<State *> &res) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (Choice choice : choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “Java”
```java title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
void backtrack(State state, List<Choice> choices, List<State> res) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (Choice choice : choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “C#”
```csharp title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
void backtrack(State state, List<Choice> choices, List<State> res) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
foreach (Choice choice in choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “Go”
```go title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
func backtrack(state *State, choices []Choice, res *[]State) {
// 判断是否为解
if isSolution(state) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res)
// 停止继续搜索
return
}
// 遍历所有选择
for _, choice := range choices {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if isValid(state, choice) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice)
backtrack(state, choices, res)
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice)
}
}
}
```
=== “Swift”
```swift title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
func backtrack(state: inout State, choices: [Choice], res: inout [State]) {
// 判断是否为解
if isSolution(state: state) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state: state, res: &res)
// 停止继续搜索
return
}
// 遍历所有选择
for choice in choices {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if isValid(state: state, choice: choice) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state: &state, choice: choice)
backtrack(state: &state, choices: choices, res: &res)
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state: &state, choice: choice)
}
}
}
```
=== “JS”
```javascript title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
function backtrack(state, choices, res) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (let choice of choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “TS”
```typescript title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
function backtrack(state: State, choices: Choice[], res: State[]): void {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (let choice of choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “Dart”
```dart title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
void backtrack(State state, List<Choice>, List<State> res) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (Choice choice in choices) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, choice)) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, choice);
backtrack(state, choices, res);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, choice);
}
}
}
```
=== “Rust”
```rust title=""
```
=== “C”
```c title=""
/* 回溯算法框架 */
void backtrack(State *state, Choice *choices, int numChoices, State *res, int numRes) {
// 判断是否为解
if (isSolution(state)) {
// 记录解
recordSolution(state, res, numRes);
// 停止继续搜索
return;
}
// 遍历所有选择
for (int i = 0; i < numChoices; i++) {
// 剪枝:判断选择是否合法
if (isValid(state, &choices[i])) {
// 尝试:做出选择,更新状态
makeChoice(state, &choices[i]);
backtrack(state, choices, numChoices, res, numRes);
// 回退:撤销选择,恢复到之前的状态
undoChoice(state, &choices[i]);
}
}
}
```
=== “Zig”
```zig title=""
```
接下来,我们基于框架代码来解决例题三。状态 state 为节点遍历路径,选择 choices 为当前节点的左子节点和右子节点,结果 res 是路径列表。
=== “Python”
```python title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.py"
[class]{}-[func]{is_solution}
[class]{}-[func]{record_solution}
[class]{}-[func]{is_valid}
[class]{}-[func]{make_choice}
[class]{}-[func]{undo_choice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “C++”
```cpp title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.cpp"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “Java”
```java title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.java"
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “C#”
```csharp title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.cs"
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{preorder_traversal_iii_template}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “Go”
```go title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.go"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrackIII}
```
=== “Swift”
```swift title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.swift"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “JS”
```javascript title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.js"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “TS”
```typescript title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.ts"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “Dart”
```dart title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.dart"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “Rust”
```rust title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.rs"
[class]{}-[func]{is_solution}
[class]{}-[func]{record_solution}
[class]{}-[func]{is_valid}
[class]{}-[func]{make_choice}
[class]{}-[func]{undo_choice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “C”
```c title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.c"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
=== “Zig”
```zig title="preorder_traversal_iii_template.zig"
[class]{}-[func]{isSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{recordSolution}
[class]{}-[func]{isValid}
[class]{}-[func]{makeChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{undoChoice}
[class]{}-[func]{backtrack}
```
根据题意,我们在找到值为 7 7 7 的节点后应该继续搜索,因此需要将记录解之后的 return 语句删除。下图对比了保留或删除 return 语句的搜索过程。
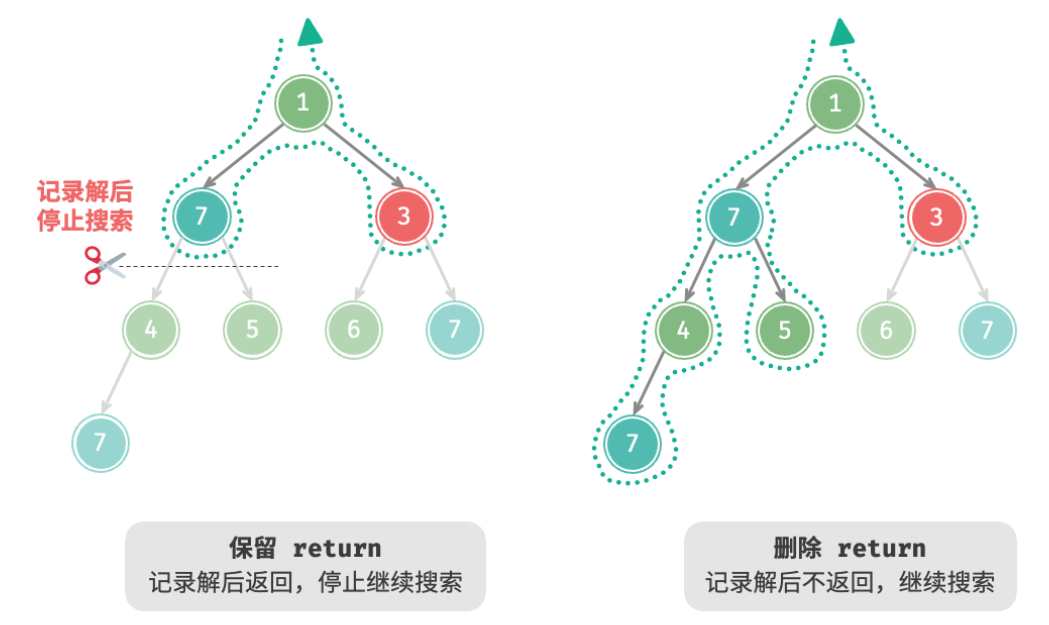
相比基于前序遍历的代码实现,基于回溯算法框架的代码实现虽然显得啰嗦,但通用性更好。实际上,许多回溯问题都可以在该框架下解决。我们只需根据具体问题来定义 state 和 choices ,并实现框架中的各个方法即可。
常用术语
为了更清晰地分析算法问题,我们总结一下回溯算法中常用术语的含义,并对照例题三给出对应示例。
表 常见的回溯算法术语
| 名词 | 定义 | 例题三 |
|---|---|---|
| 解 Solution | 解是满足问题特定条件的答案,可能有一个或多个 | 根节点到节点 7 7 7 的满足约束条件的所有路径 |
| 约束条件 Constraint | 约束条件是问题中限制解的可行性的条件,通常用于剪枝 | 路径中不包含节点 3 3 3 |
| 状态 State | 状态表示问题在某一时刻的情况,包括已经做出的选择 | 当前已访问的节点路径,即 path 节点列表 |
| 尝试 Attempt | 尝试是根据可用选择来探索解空间的过程,包括做出选择,更新状态,检查是否为解 | 递归访问左(右)子节点,将节点添加进 path ,判断节点的值是否为 7 7 7 |
| 回退 Backtracking | 回退指遇到不满足约束条件的状态时,撤销前面做出的选择,回到上一个状态 | 当越过叶结点、结束结点访问、遇到值为 3 3 3 的节点时终止搜索,函数返回 |
| 剪枝 Pruning | 剪枝是根据问题特性和约束条件避免无意义的搜索路径的方法,可提高搜索效率 | 当遇到值为 3 3 3 的节点时,则终止继续搜索 |
!!! tip
问题、解、状态等概念是通用的,在分治、回溯、动态规划、贪心等算法中都有涉及。
优势与局限性
回溯算法本质上是一种深度优先搜索算法,它尝试所有可能的解决方案直到找到满足条件的解。这种方法的优势在于它能够找到所有可能的解决方案,而且在合理的剪枝操作下,具有很高的效率。
然而,在处理大规模或者复杂问题时,回溯算法的运行效率可能难以接受。
- 时间:回溯算法通常需要遍历状态空间的所有可能,时间复杂度可以达到指数阶或阶乘阶。
- 空间:在递归调用中需要保存当前的状态(例如路径、用于剪枝的辅助变量等),当深度很大时,空间需求可能会变得很大。
即便如此,回溯算法仍然是某些搜索问题和约束满足问题的最佳解决方案。对于这些问题,由于无法预测哪些选择可生成有效的解,因此我们必须对所有可能的选择进行遍历。在这种情况下,关键是如何进行效率优化,常见的效率优化方法有两种。
- 剪枝:避免搜索那些肯定不会产生解的路径,从而节省时间和空间。
- 启发式搜索:在搜索过程中引入一些策略或者估计值,从而优先搜索最有可能产生有效解的路径。
回溯典型例题
回溯算法可用于解决许多搜索问题、约束满足问题和组合优化问题。
搜索问题:这类问题的目标是找到满足特定条件的解决方案。
- 全排列问题:给定一个集合,求出其所有可能的排列组合。
- 子集和问题:给定一个集合和一个目标和,找到集合中所有和为目标和的子集。
- 汉诺塔问题:给定三个柱子和一系列大小不同的圆盘,要求将所有圆盘从一个柱子移动到另一个柱子,每次只能移动一个圆盘,且不能将大圆盘放在小圆盘上。
约束满足问题:这类问题的目标是找到满足所有约束条件的解。
- n n n 皇后:在 n × n n \times n n×n 的棋盘上放置 n n n 个皇后,使得它们互不攻击。
- 数独:在 9 × 9 9 \times 9 9×9 的网格中填入数字 1 1 1 ~ 9 9 9 ,使得每行、每列和每个 3 × 3 3 \times 3 3×3 子网格中的数字不重复。
- 图着色问题:给定一个无向图,用最少的颜色给图的每个顶点着色,使得相邻顶点颜色不同。
组合优化问题:这类问题的目标是在一个组合空间中找到满足某些条件的最优解。
- 0-1 背包问题:给定一组物品和一个背包,每个物品有一定的价值和重量,要求在背包容量限制内,选择物品使得总价值最大。
- 旅行商问题:在一个图中,从一个点出发,访问所有其他点恰好一次后返回起点,求最短路径。
- 最大团问题:给定一个无向图,找到最大的完全子图,即子图中的任意两个顶点之间都有边相连。
请注意,对于许多组合优化问题,回溯都不是最优解决方案。
- 0-1 背包问题通常使用动态规划解决,以达到更高的时间效率。
- 旅行商是一个著名的 NP-Hard 问题,常用解法有遗传算法和蚁群算法等。
- 最大团问题是图论中的一个经典问题,可用贪心等启发式算法来解决。