文章作者:里海
来源网站:王牌飞行员_里海_里海NX二次开发3000例,里海BlockUI专栏,C\C++-CSDN博客
目录
1.介绍
Pugixml是轻量级、简单、快速的 XML 解析器。Pugixml库仅由pugixml.cpp、pugixml.hpp和pugiconfig.hpp三个文件组成,非常容易使用。解析速度快,支持XPath表达式。
2.Pugixml库
官网下载地址::pugixml.org - Home

3.配置Visual Studio开发环境
1. 创建项目并将“src"目录设置到“附加包含目录”:

2. 添加文件
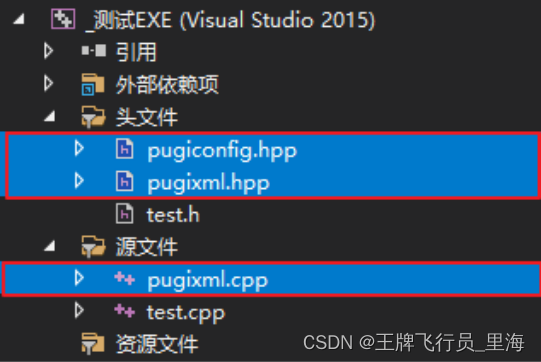
3. 代码中包含头文件pugiconfig.hpp和pugixml.hpp头文件
#include <Windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <pugiconfig.hpp> //包含头文件
#include <pugixml.hpp> //包含头文件
int main()
{
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}4.节点
树的根是文档本身,对应于C++类型
xml_document。文档子节点,对应于C++类型xml_node。节点有不同的类型,对应于C++类型的xml_attribute
5.常见的节点类型
- 文档节点 (
node_document) - 这是树的根,由多个子节点组成。此节点对应于xml_document类;请注意,它是xml_document的xml_node子类,因此整个节点接口也可用。- 元素/标记节点 (
node_element) - 这是最常见的节点类型,表示 XML 元素。元素节点具有名称、属性集合和子节点集合(两者都可能为空)。该属性是一个简单的名称/值对。- 纯字符数据节点 (
node_pcdata) 表示 XML 中的纯文本。PCDATA 节点具有值,但没有名称或子节点/属性。请注意,纯字符数据不是元素节点的一部分,而是具有自己的节点;例如,一个元素节点可以有多个子 PCDATA 节点。
6.命名空间pugi
所有 pugixml 类和函数都位于命名空间中
pugi;您必须使用显式名称限定(即pugi::xml_node),或者通过指令(即using pugi::xml_node;或using namespace pugi;)访问using相关符号。
7.xml_document装载整个XML文档结构
xml_document 是整个文档结构的所有者;销毁文档会销毁整棵树。xml_document 界面由加载功能、保存功能和整个 xml_node 界面组成,允许进行文档检查和/或修改。
8.xml_node文档节点
xml_node 是文档节点的句柄;它可以指向文档中的任何节点,包括文档本身。所有类型的节点都有一个通用接口。请注意,这只是 xml_node 实际节点的句柄,而不是节点本身 - 您可以有多个 xml_node 句柄指向同一基础对象。销毁 xml_node 句柄不会破坏节点,也不会将其从树中删除。
xml_node 有一个特殊的类型值,称为空节点或空节点。它不对应于任何文档中的任何节点,因此类似于空指针。但是,所有操作都是在空节点上定义的;通常,操作不执行任何操作,并返回空节点/属性或空字符串作为其结果。这对于链接调用很有用;即,您可以像这样获取节点的祖父级: node.parent().parent() ;如果节点是空节点或没有父节点,则第一次 parent() 调用返回空节点;然后,第二次 parent() 调用也会返回 null 节点,因此您不必两次检查错误。可以通过隐式布尔转换来测试句柄是否为 null: if (node) { … } 或 if (!node) { … } 。
9.xml_attribute 属性
xml_attribute 是 XML 属性的句柄;它具有与 相同的 xml_node 语义,即可以有多个 xml_attribute 句柄指向相同的底层对象,并且有一个特殊的 null 属性值,该值传播到函数结果。
10.例子
例1.生成xml文件

#include <Windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <pugiconfig.hpp> //包含头文件
#include <pugixml.hpp> //包含头文件
using namespace std;
using namespace pugi;
int main()
{
// 创建一个XML文档对象
xml_document doc;
// 添加根节点
xml_node root = doc.append_child("fruits");
// 添加子节点
xml_node apple = root.append_child("fruit");
apple.append_attribute("name").set_value("苹果");
apple.append_attribute("color").set_value("红色");
apple.append_attribute("taste").set_value("甜");
xml_node banana = root.append_child("fruit");
banana.append_attribute("name").set_value("香蕉");
banana.append_attribute("color").set_value("黄色");
banana.append_attribute("taste").set_value("甜");
// 将XML内容写入文件
ofstream file("fruits.xml");
doc.save(file);
file.close();
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}例2.读xml文件并解析

#include <Windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <pugiconfig.hpp> //包含头文件
#include <pugixml.hpp> //包含头文件
using namespace std;
using namespace pugi;
int main()
{
// 打开XML文件
ifstream file("fruits.xml");
// 加载XML文档
xml_document doc;
doc.load(file);
// 获取根节点
xml_node root = doc.child("fruits");
// 遍历子节点
for (xml_node fruit = root.first_child(); fruit; fruit = fruit.next_sibling()) {
// 获取属性值
string name = fruit.attribute("name").as_string();
string color = fruit.attribute("color").as_string();
string taste = fruit.attribute("taste").as_string();
// 输出属性值
cout << "Name: " << name << endl;
cout << "Color: " << color << endl;
cout << "Taste: " << taste << endl;
}
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}例3.修改xml文件
目的:将苹果修改为青色、不甜

#include <Windows.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <pugiconfig.hpp> //包含头文件
#include <pugixml.hpp> //包含头文件
using namespace std;
using namespace pugi;
int main()
{
// 打开XML文件
ifstream file("fruits.xml");
// 加载XML文档
xml_document doc;
doc.load(file);
// 获取根节点
xml_node root = doc.child("fruits");
// 遍历子节点
for (xml_node fruit = root.first_child(); fruit; fruit = fruit.next_sibling()) {
// 获取属性值
string name = fruit.attribute("name").as_string();
// 如果该子节点表示的是苹果
if (name == "苹果") {
// 修改属性值
fruit.attribute("color").set_value("青色");
fruit.attribute("taste").set_value("不甜");
break; // 只修改第一个匹配的节点,退出循环
}
}
// 将修改后的XML内容写入文件
ofstream outfile("fruits.xml");
doc.save(outfile);
outfile.close();
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}![]()