- /*
- * Copyright(c) 2017,烟台大学计算机学院
- * All rights reserved.
- * 文件名称:cpp1.
- * 作 者:张翠平
- * 完成日期:2017 年 9 月 2 日
- * 版 本 号:v1.0
- *
- * 问题描述:设计一个函数,产生一个至少5万条记录的数据集合。在同一数据集上,用直接插入排序、冒泡排序、快速排序、直接选择排序、堆排序、归并排序、基数排序等算法进行排序,记录所需要的时间,经过对比,得到对复杂度不同的各种算法在运行时间方面的感性认识。
- * 输入描述:
- * 程序输出:各种排序所需时间
- */
- sort.h
-
#ifndef SORT_H_INCLUDED #define SORT_H_INCLUDED #define MaxSize 50000 //最多的数据,取5万,只测试快速算法,可以往大调整 //下面的符号常量和结构体针对基数排序 #define Radix 10 //基数的取值 #define Digits 10 //关键字位数 typedef int KeyType; //定义关键字类型 typedef char InfoType[10]; typedef struct //记录类型 { KeyType key; //关键字项 InfoType data; //其他数据项,类型为InfoType } RecType; //排序的记录类型定义 typedef struct node { KeyType data; //记录的关键字,同算法讲解中有差别 struct node *next; } RadixRecType; void InsertSort(RecType R[],int n); //直接插入排序 void ShellSort(RecType R[],int n); //希尔排序算法 void BubbleSort(RecType R[],int n); //冒泡排序 void QuickSort(RecType R[],int n); //快速排序 void SelectSort(RecType R[],int n); //直接选择排序 void HeapSort(RecType R[],int n); //堆排序 void MergeSort(RecType R[],int n); //归并排序 //下面函数支持基数排序 void CreateLink(RadixRecType *&p,RecType R[],int n); //创建基数排序用的链表 void DestoryLink(RadixRecType *&p); //释放基数排序用的链表 void RadixSort(RadixRecType *&p); //基数排序 #endif // SORT_H_INCLUDED -
sort.cpp -
#include "sort.h" #include <malloc.h> //1. 对R[0..n-1]按递增有序进行直接插入排序 void InsertSort(RecType R[],int n) { int i,j; RecType tmp; for (i=1; i<n; i++) { tmp=R[i]; j=i-1; //从右向左在有序区R[0..i-1]中找R[i]的插入位置 while (j>=0 && tmp.key<R[j].key) { R[j+1]=R[j]; //将关键字大于R[i].key的记录后移 j--; } R[j+1]=tmp; //在j+1处插入R[i] } } //2. 希尔排序算法 void ShellSort(RecType R[],int n) { int i,j,gap; RecType tmp; gap=n/2; //增量置初值 while (gap>0) { for (i=gap; i<n; i++) //对所有相隔gap位置的所有元素组进行排序 { tmp=R[i]; j=i-gap; while (j>=0 && tmp.key<R[j].key)//对相隔gap位置的元素组进行排序 { R[j+gap]=R[j]; j=j-gap; } R[j+gap]=tmp; j=j-gap; } gap=gap/2; //减小增量 } } //3. 冒泡排序 void BubbleSort(RecType R[],int n) { int i,j,exchange; RecType tmp; for (i=0; i<n-1; i++) { exchange=0; for (j=n-1; j>i; j--) //比较,找出最小关键字的记录 if (R[j].key<R[j-1].key) { tmp=R[j]; //R[j]与R[j-1]进行交换,将最小关键字记录前移 R[j]=R[j-1]; R[j-1]=tmp; exchange=1; } if (exchange==0) //没有交换,即结束算法 return; } } //4. 对R[s]至R[t]的元素进行快速排序 void QuickSortR(RecType R[],int s,int t) { int i=s,j=t; RecType tmp; if (s<t) //区间内至少存在两个元素的情况 { tmp=R[s]; //用区间的第1个记录作为基准 while (i!=j) //从区间两端交替向中间扫描,直至i=j为止 { while (j>i && R[j].key>=tmp.key) j--; //从右向左扫描,找第1个小于tmp.key的R[j] R[i]=R[j]; //找到这样的R[j],R[i]"R[j]交换 while (i<j && R[i].key<=tmp.key) i++; //从左向右扫描,找第1个大于tmp.key的记录R[i] R[j]=R[i]; //找到这样的R[i],R[i]"R[j]交换 } R[i]=tmp; QuickSortR(R,s,i-1); //对左区间递归排序 QuickSortR(R,i+1,t); //对右区间递归排序 } } //4. 快速排序辅助函数,对外同其他算法统一接口,内部调用递归的快速排序 void QuickSort(RecType R[],int n) { QuickSortR(R, 0, n-1); } //5. 直接选择排序 void SelectSort(RecType R[],int n) { int i,j,k; RecType temp; for (i=0; i<n-1; i++) //做第i趟排序 { k=i; for (j=i+1; j<n; j++) //在当前无序区R[i..n-1]中选key最小的R[k] if (R[j].key<R[k].key) k=j; //k记下目前找到的最小关键字所在的位置 if (k!=i) //交换R[i]和R[k] { temp=R[i]; R[i]=R[k]; R[k]=temp; } } } //6. 堆排序辅助之——调整堆 void sift(RecType R[],int low,int high) { int i=low,j=2*i; //R[j]是R[i]的左孩子 RecType temp=R[i]; while (j<=high) { if (j<high && R[j].key<R[j+1].key) //若右孩子较大,把j指向右孩子 j++; //变为2i+1 if (temp.key<R[j].key) { R[i]=R[j]; //将R[j]调整到双亲结点位置上 i=j; //修改i和j值,以便继续向下筛选 j=2*i; } else break; //筛选结束 } R[i]=temp; //被筛选结点的值放入最终位置 } //6. 堆排序 void HeapSort(RecType R[],int n) { int i; RecType temp; for (i=n/2; i>=1; i--) //循环建立初始堆 sift(R,i,n); for (i=n; i>=2; i--) //进行n-1次循环,完成推排序 { temp=R[1]; //将第一个元素同当前区间内R[1]对换 R[1]=R[i]; R[i]=temp; sift(R,1,i-1); //筛选R[1]结点,得到i-1个结点的堆 } } //7.归并排序辅助1——合并有序表 void Merge(RecType R[],int low,int mid,int high) { RecType *R1; int i=low,j=mid+1,k=0; //k是R1的下标,i、j分别为第1、2段的下标 R1=(RecType *)malloc((high-low+1)*sizeof(RecType)); //动态分配空间 while (i<=mid && j<=high) //在第1段和第2段均未扫描完时循环 if (R[i].key<=R[j].key) //将第1段中的记录放入R1中 { R1[k]=R[i]; i++; k++; } else //将第2段中的记录放入R1中 { R1[k]=R[j]; j++; k++; } while (i<=mid) //将第1段余下部分复制到R1 { R1[k]=R[i]; i++; k++; } while (j<=high) //将第2段余下部分复制到R1 { R1[k]=R[j]; j++; k++; } for (k=0,i=low; i<=high; k++,i++) //将R1复制回R中 R[i]=R1[k]; } //7. 归并排序辅助2——一趟归并 void MergePass(RecType R[],int length,int n) //对整个数序进行一趟归并 { int i; for (i=0; i+2*length-1<n; i=i+2*length) //归并length长的两相邻子表 Merge(R,i,i+length-1,i+2*length-1); if (i+length-1<n) //余下两个子表,后者长度小于length Merge(R,i,i+length-1,n-1); //归并这两个子表 } //7. 归并排序 void MergeSort(RecType R[],int n) //自底向上的二路归并算法 { int length; for (length=1; length<n; length=2*length) //进行log2n趟归并 MergePass(R,length,n); } //以下基数排序,为了统一测试有改造 //8. 基数排序的辅助函数,创建基数排序用的链表 void CreateLink(RadixRecType *&p,RecType R[],int n) //采用后插法产生链表 { int i; RadixRecType *s,*t; for (i=0; i<n; i++) { s=(RadixRecType *)malloc(sizeof(RadixRecType)); s->data = R[i].key; if (i==0) { p=s; t=s; } else { t->next=s; t=s; } } t->next=NULL; } //8. 基数排序的辅助函数,释放基数排序用的链表 void DestoryLink(RadixRecType *&p) { RadixRecType *q; while(p!=NULL) { q=p->next; free(p); p=q; } return; } //8. 实现基数排序:*p为待排序序列链表指针,基数R和关键字位数D已经作为符号常量定义好 void RadixSort(RadixRecType *&p) { RadixRecType *head[Radix],*tail[Radix],*t; //定义各链队的首尾指针 int i,j,k; unsigned int d1, d2=1; //用于分离出第i位数字,见下面的注释 for (i=1; i<=Digits; i++) //从低位到高位循环 { //分离出倒数第i位数字,先通过对d1=10^i取余,得到其后i位,再通过整除d2=10^(i-1)得到第i位 //例如,分离出倒数第1位,即个位数,先对d1=10取余,再整除d2=1 //再例如,分离出倒数第2位,即十位数,先对d1=100取余,再整除d2=10 //循环之前,d2已经初始化为1,在这一层循环末增加10倍 //下面根据d2,得到d1的值 d1=d2*10; for (j=0; j<Radix; j++) //初始化各链队首、尾指针 head[j]=tail[j]=NULL; while (p!=NULL) //对于原链表中每个结点循环 { k=(p->data%d1)/d2; //分离出第i位数字k if (head[k]==NULL) //进行分配 { head[k]=p; tail[k]=p; } else { tail[k]->next=p; tail[k]=p; } p=p->next; //取下一个待排序的元素 } p=NULL; //重新用p来收集所有结点 for (j=0; j<Radix; j++) //对于每一个链队循环 if (head[j]!=NULL) //进行收集 { if (p==NULL) { p=head[j]; t=tail[j]; } else { t->next=head[j]; t=tail[j]; } } t->next=NULL; //最后一个结点的next域置NULL //下面更新用于分离出第i位数字的d2 d2*=10; } }
-
main.cpp -
#include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include "sort.h" void GetLargeData(RecType *&R, int n) { srand(time(0)); R=(RecType*)malloc(sizeof(RecType)*n); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) R[i].key= rand(); //产生0~RAND_MAX间的数 printf("生成了%d条记录\n", n); } //调用某一排序算法完成排序,返回排序用时 long Sort(RecType *&R, int n, void f(RecType*, int)) { int i; long beginTime, endTime; RecType *R1=(RecType*)malloc(sizeof(RecType)*n); for (i=0;i<n;i++) R1[i]=R[i]; beginTime = time(0); f(R1,n); endTime = time(0); free(R1); return endTime-beginTime; } //调用基数排序算法完成排序,返回排序用时 long Sort1(RecType *&R, int n) { long beginTime, endTime; RadixRecType *p; CreateLink(p,R,n); beginTime = time(0); RadixSort(p); endTime = time(0); DestoryLink(p); return endTime-beginTime; } int main() { RecType *R; int n = MaxSize; //测试中, MaxSize取50W GetLargeData(R, n); printf("各种排序花费时间:\n"); printf(" 直接插入排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, InsertSort)); printf(" 希尔排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, ShellSort)); printf(" 冒泡排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, BubbleSort)); printf(" 快速排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, QuickSort)); printf(" 直接选择排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, SelectSort)); printf(" 堆排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, HeapSort)); printf(" 归并排序:%ld\n", Sort(R, n, MergeSort)); printf(" 基数排序:%ld\n", Sort1(R, n)); free(R); return 0; }
运行结果:
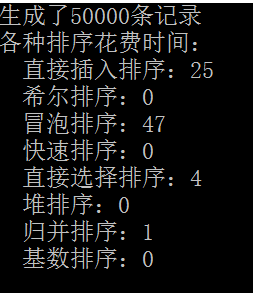
知识点总结和心得体会:
通过对各种算法排序的验证结果,来更好的体会算法的复杂度。