Hibernate的一对一关联关系
我们以Company与Address类为例,介绍映射一对一关联关系的方法。
一对一的关联方法有两种
-按照外键映射:两个表任意一个表定义一个外键,来关联另一个表。
-按照主键映射:一个表的主键同时作为外键,和另一个表的主键保持一致。
按照外键映射
我们先创建实体类
public class Company {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
public class Address {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Company company;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Company getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(Company company) {
this.company = company;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
我们配置映射文件,我们在Company这一方设置外键来关联Address
有外键的一方要使用<many-to-one>元素来配置。
Company.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Company" table="company">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--column指定外键,unique指定外键唯一约束,设为true,就可以表达Company和Address对象之间的一对一关联-->
<many-to-one name="address" class="com.cad.domain.Address" column="aid" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Address.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Address" table="address">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--property-ref属性指定通过从Company的address属性来查找自己-->
<one-to-one name="Company" class="com.cad.domain.Company" property-ref="address"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
我们操作一下
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
Company c=new Company();
c.setName("百度");
Address a=new Address();
a.setName("深圳");
c.setAddress(a);
a.setCompany(c);
session.save(a);
session.save(c);
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
默认情况下,一对一关联采用迫切左外连接检索策略。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
按照主键映射
实体类不变,我们编写一下配置文件
address的表的id字段既是主键又是外键.
编写配置文件
Company.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Company" table="company">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<one-to-one name="address" class="com.cad.domain.Address" ></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Address.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Address" table="address">
<id name="id" column="id">
<!--必须使用foreign标识符生成策略,还要指定哪个对象共享OID-->
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">company</param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--constrained属性设为true,说明主键同时作为外键-->
<one-to-one name="company" class="com.cad.domain.Company" constrained="true"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Hibernate的二级缓存
二级缓存简介
二级缓存是一个可插拔的缓存插件,由SessionFactory管理,是进程范围的缓存。
二级缓存有可能出现并发问题,因此需要采用适当的并发访问策略。
该策略为缓存中的数据提供了事务隔离级别。。
Hibernate还提供了查询缓存,依赖于二级缓存。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
二级缓存中存放什么?
符合以下条件的数据适合存放在二级缓存中
-很少被修改的数据
-不是很重要的数据,允许偶然出现的并发问题
-参考数据(指供应用程序参考的常量数据)
以下数据不适合存放到二级缓存中
-经常被修改的数据
-财务数据,绝对不允许出现并发文日
-与其他应用共享的数据
二级缓存中缓存的并不是对象,而是对象的散装数据。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
常用二级缓存插件
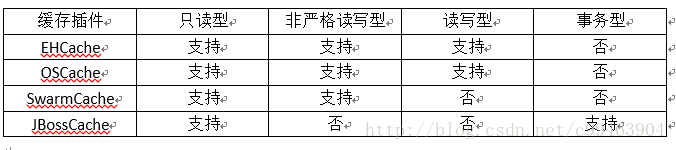
二级缓存是可配置的插件,Hibernate允许选用以下的缓存插件
-EHCache:可作为进程范围内的缓存。存放数据的物理介质可以是硬盘或者内存,支持hibernate的查询缓存。
-OSCache:可作为进程范围内的缓存,存放数据的物理介质可以是硬盘或者内存,支持hibernate的查询缓存,提供了丰富的缓存数据过期策略。
-SwarmCache:可作为集群范围内的缓存,不支持Hibernate的查询缓存。
-JBossCache:可作为集群范围内的缓存,支持事务并发访问策略。支持Hibernate的查询缓存。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
二级缓存的事务隔离级别
transactional(事务型):
仅在受管理的环境中适用
提供Repeatable Read事务隔离级别
适用经常被读,很少修改的数据
可以防止脏读和不可重复读的并发问题
缓存支持事务,发生异常的时候,缓存也能够回滚
read-write(读写型);
提供Read Committed事务隔离级别
在非集群的环境中适用
适用经常被读,很少修改的数据
可以防止脏读
更新缓存的时候会锁定缓存中的数据
nonstrict-read-write(非严格读写型):
适用极少被修改,偶尔允许脏读的数据(两个事务同时修改数据的情况很少见)
不保证缓存和数据库中数据的一致性
为缓存数据设置很短的过期时间,从而尽量避免脏读
不锁定缓存中的数据
read-only(只读型):
适用从来不会被修改的数据(如参考数据)
在此模式下,如果对数据进行更新操作,会有异常
事务隔离级别低,并发性能高
在集群环境中也能完美运作
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
为了把这些第三方缓存插件集成到Hibernate中,Hibernate提供了org.hibernate.cache.CacheProvider接口
它是缓存插件与Hibernate之间的适配器。Hibernate为以上四个缓存插件提供了内置的适配器实现类。
如果需要使用其他的缓存插件,只需要为这个插件提供实现了接口的类即可。
使用二级缓存
配置二级缓存
1.打开二级缓存
2.选择需要使用的二级缓存的持久化类,设置二级缓存的并发访问策略。
3.选择合适的缓存插件,配置缓存插件的配置文件。
我们演示使用EHCache插件
(1)先导包,Hibernate包中已经为我们准备好了 将hibernate-release-5.1.7.Final\lib\optional\ehcache目录下的jar包导入
(2)在hibernate.cfg.xml中配置使用二级缓存
配置使用二级缓存
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
(3)配置使用EHcache的实现类
配置文件中的类名为org.hibernate.cache.internal.EhCacheRegionFactory,但是出错。把internal去掉就行了
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Hibernate允许配置类和集合上设置二级缓存。还可以设置查询缓存
(一)在类上设置二级缓存
在hibernate.cfg.xml的<mapping>元素后面配置
<!--usage设置隔离级别,class设置哪个类-->
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Customer"/>
(2)我们测试一下是否对象存到了二级缓存
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象,打印select语句
Customer c1=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
//清除一级缓存
session.clear();
//再获取对象,没有打印select语句,说明对象存放在了二级缓存中
Customer c2=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
(二) 在集合上设置二级缓存区
要把集合中的对象也给设置二级缓存区。
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Customer"/>
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Order"/>
<!--collection设置对象中的集合-->
<collection-cache usage="read-only" collection="com.cad.domain.Customer.orders"/>
我们测试一下
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
//打印select语句
Customer c1=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
for(com.cad.domain.Order o:c1.getOrders()){
System.out.println(o.getName());
}
//清空缓冲区
session.clear();
//再查找,不打印,说明集合中的对象都被放到了二级缓存中
Customer c2=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
for(com.cad.domain.Order o:c2.getOrders()){
System.out.println(o.getName());
}
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
Hibernate也学的差不多,很多方面增删改查等虽然方便,但是配置文件却依然繁琐沉重,可能这就是人们现在都用Mybatis的原因吧,不过学习学习也是蛮好的。
想过一段时间出去闯闯,试试找工作,心理紧张兴奋慌乱恐惧,开始有了考研的想法,但随即一想,如果考研是为了躲避就业,那还是提早面对这个挑战。
等我把想拿的都拿到,再写篇励志的心得给你看。
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/markdown_views-ea0013b516.css">
</div>
Hibernate的一对一关联关系
我们以Company与Address类为例,介绍映射一对一关联关系的方法。
一对一的关联方法有两种
-按照外键映射:两个表任意一个表定义一个外键,来关联另一个表。
-按照主键映射:一个表的主键同时作为外键,和另一个表的主键保持一致。
按照外键映射
我们先创建实体类
public class Company {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Address address;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
public class Address {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Company company;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Company getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(Company company) {
this.company = company;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
我们配置映射文件,我们在Company这一方设置外键来关联Address
有外键的一方要使用<many-to-one>元素来配置。
Company.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Company" table="company">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--column指定外键,unique指定外键唯一约束,设为true,就可以表达Company和Address对象之间的一对一关联-->
<many-to-one name="address" class="com.cad.domain.Address" column="aid" unique="true"></many-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Address.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Address" table="address">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--property-ref属性指定通过从Company的address属性来查找自己-->
<one-to-one name="Company" class="com.cad.domain.Company" property-ref="address"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
我们操作一下
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
Company c=new Company();
c.setName("百度");
Address a=new Address();
a.setName("深圳");
c.setAddress(a);
a.setCompany(c);
session.save(a);
session.save(c);
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
默认情况下,一对一关联采用迫切左外连接检索策略。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
按照主键映射
实体类不变,我们编写一下配置文件
address的表的id字段既是主键又是外键.
编写配置文件
Company.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Company" table="company">
<id name="id" column="id">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<one-to-one name="address" class="com.cad.domain.Address" ></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
Address.hbm.xml
<hibernate-mapping >
<class name="com.cad.domain.Address" table="address">
<id name="id" column="id">
<!--必须使用foreign标识符生成策略,还要指定哪个对象共享OID-->
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">company</param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="name"></property>
<!--constrained属性设为true,说明主键同时作为外键-->
<one-to-one name="company" class="com.cad.domain.Company" constrained="true"></one-to-one>
</class>
</hibernate-mapping>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
Hibernate的二级缓存
二级缓存简介
二级缓存是一个可插拔的缓存插件,由SessionFactory管理,是进程范围的缓存。
二级缓存有可能出现并发问题,因此需要采用适当的并发访问策略。
该策略为缓存中的数据提供了事务隔离级别。。
Hibernate还提供了查询缓存,依赖于二级缓存。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
二级缓存中存放什么?
符合以下条件的数据适合存放在二级缓存中
-很少被修改的数据
-不是很重要的数据,允许偶然出现的并发问题
-参考数据(指供应用程序参考的常量数据)
以下数据不适合存放到二级缓存中
-经常被修改的数据
-财务数据,绝对不允许出现并发文日
-与其他应用共享的数据
二级缓存中缓存的并不是对象,而是对象的散装数据。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
常用二级缓存插件
二级缓存是可配置的插件,Hibernate允许选用以下的缓存插件
-EHCache:可作为进程范围内的缓存。存放数据的物理介质可以是硬盘或者内存,支持hibernate的查询缓存。
-OSCache:可作为进程范围内的缓存,存放数据的物理介质可以是硬盘或者内存,支持hibernate的查询缓存,提供了丰富的缓存数据过期策略。
-SwarmCache:可作为集群范围内的缓存,不支持Hibernate的查询缓存。
-JBossCache:可作为集群范围内的缓存,支持事务并发访问策略。支持Hibernate的查询缓存。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
二级缓存的事务隔离级别
transactional(事务型):
仅在受管理的环境中适用
提供Repeatable Read事务隔离级别
适用经常被读,很少修改的数据
可以防止脏读和不可重复读的并发问题
缓存支持事务,发生异常的时候,缓存也能够回滚
read-write(读写型);
提供Read Committed事务隔离级别
在非集群的环境中适用
适用经常被读,很少修改的数据
可以防止脏读
更新缓存的时候会锁定缓存中的数据
nonstrict-read-write(非严格读写型):
适用极少被修改,偶尔允许脏读的数据(两个事务同时修改数据的情况很少见)
不保证缓存和数据库中数据的一致性
为缓存数据设置很短的过期时间,从而尽量避免脏读
不锁定缓存中的数据
read-only(只读型):
适用从来不会被修改的数据(如参考数据)
在此模式下,如果对数据进行更新操作,会有异常
事务隔离级别低,并发性能高
在集群环境中也能完美运作
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23

为了把这些第三方缓存插件集成到Hibernate中,Hibernate提供了org.hibernate.cache.CacheProvider接口
它是缓存插件与Hibernate之间的适配器。Hibernate为以上四个缓存插件提供了内置的适配器实现类。
如果需要使用其他的缓存插件,只需要为这个插件提供实现了接口的类即可。
使用二级缓存
配置二级缓存
1.打开二级缓存
2.选择需要使用的二级缓存的持久化类,设置二级缓存的并发访问策略。
3.选择合适的缓存插件,配置缓存插件的配置文件。
我们演示使用EHCache插件
(1)先导包,Hibernate包中已经为我们准备好了 将hibernate-release-5.1.7.Final\lib\optional\ehcache目录下的jar包导入
(2)在hibernate.cfg.xml中配置使用二级缓存
配置使用二级缓存
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property>
(3)配置使用EHcache的实现类
配置文件中的类名为org.hibernate.cache.internal.EhCacheRegionFactory,但是出错。把internal去掉就行了
<property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
Hibernate允许配置类和集合上设置二级缓存。还可以设置查询缓存
(一)在类上设置二级缓存
在hibernate.cfg.xml的<mapping>元素后面配置
<!--usage设置隔离级别,class设置哪个类-->
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Customer"/>
(2)我们测试一下是否对象存到了二级缓存
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象,打印select语句
Customer c1=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
//清除一级缓存
session.clear();
//再获取对象,没有打印select语句,说明对象存放在了二级缓存中
Customer c2=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
(二) 在集合上设置二级缓存区
要把集合中的对象也给设置二级缓存区。
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Customer"/>
<class-cache usage="read-only" class="com.cad.domain.Order"/>
<!--collection设置对象中的集合-->
<collection-cache usage="read-only" collection="com.cad.domain.Customer.orders"/>
我们测试一下
public class Demo {
private Session session;
@Test
public void test() {
//读取配置文件
Configuration conf=new Configuration().configure();
//根据配置创建factory
SessionFactory sessionfactory=conf.buildSessionFactory();
session = sessionfactory.openSession();
Transaction ts=session.beginTransaction();
//打印select语句
Customer c1=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
for(com.cad.domain.Order o:c1.getOrders()){
System.out.println(o.getName());
}
//清空缓冲区
session.clear();
//再查找,不打印,说明集合中的对象都被放到了二级缓存中
Customer c2=session.get(Customer.class, 7);
for(com.cad.domain.Order o:c2.getOrders()){
System.out.println(o.getName());
}
ts.commit();
session.close();
sessionfactory.close();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
Hibernate也学的差不多,很多方面增删改查等虽然方便,但是配置文件却依然繁琐沉重,可能这就是人们现在都用Mybatis的原因吧,不过学习学习也是蛮好的。
想过一段时间出去闯闯,试试找工作,心理紧张兴奋慌乱恐惧,开始有了考研的想法,但随即一想,如果考研是为了躲避就业,那还是提早面对这个挑战。
等我把想拿的都拿到,再写篇励志的心得给你看。
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/markdown_views-ea0013b516.css">
</div>