1、被调用的3个时机:
(1)直接初始化或拷贝初始化;
(2)将一个对象作为一个实参传递,形参采用非指针或非引用的对象进行接收时;
(3)函数的返回值是一个非指针或者非对象被接收时。
2、举例说明:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test{
private:
int a;
int b;
static int count;
public:
Test(int i, int j): a(i), b(j){}
void print();
Test(Test &t);
void fun(Test t);
Test fun1();
};
int Test::count = 1;
void Test::print(){
cout<<"a = "<<a<<" b = "<<b<<endl;
}
Test::Test(Test & t){
cout<<"第"<<count++<<"次拷贝构造函数被调用! "<<endl;
this->a = t.a;
this->b = t.b;
}
void Test::fun(Test t){ // 关于情形2 需要注意的是:形参不能是引用或者不能是指针的对象
cout<<"a = "<<t.a<<" b = "<<t.b<<endl;
}
Test Test::fun1(){ // 关于情形3 需要注意的是:返回类型不能是引用或者不能是指针的对象
this->a = this ->a ++;
this->b = this->b ++;
return *this;
}
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
Test t(1,2);
// 调用拷贝构造函数 情形1
Test t1(t);
// 调用拷贝构造函数 情形2
t1.fun(t);
t.print();
// 调用拷贝构造函数 情形3
Test t3 = t1.fun1(); // 注意这种情况不会调用重载赋值操作符 Test t; t = t1这种情况的赋值运算符是会被重载的
t3.print();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
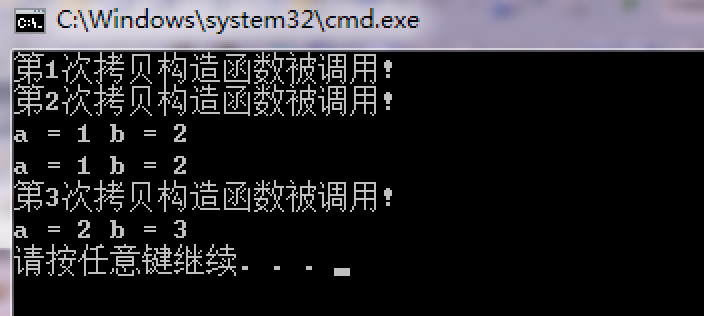
输出结果: