Admiral
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 153428/153428 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1013 Accepted Submission(s): 399
Problem Description
Suppose that you are an admiral of a famous naval troop. Our naval forces have got 21 battleships. There are 6 types of battleships.
First, we have got one flagship in which the admiral must be and it is denoted by number 0. Others are denoted by number from 1 to 5, each of them has 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ships of its kind. So, we have got 21 battleships in total and we must take a giant battle against the enemy. Hence, the correct strategy of how to arrange each type of battleships is very important to us.
The shape of the battlefield is like the picture that is shown below.
To simplify the problem, we consider all battleships have the same rectangular shape.
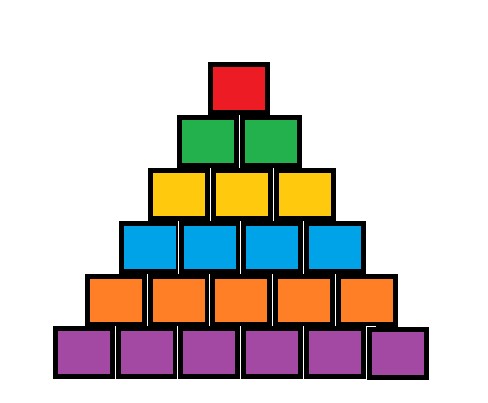
Fortunately, we have already known the optimal state of battleships.
As you can see, the battlefield consists of 6 rows. And we have 6 types of battleship, so the optimal state is that all the battleships denoted by number i are located at the i-th row. Hence, each type of battleship corresponds to different color.
You are given the initial state of battlefield as input. You can change the state of battlefield by changing the position of flagship with adjacent battleship.
Two battleships are considered adjacent if and only if they are not in the same row and share parts of their edges. For example, if we denote the cell which is at i-th row and j-th position from the left as (i,j), then the cell (2,1) is adjacent to the cells (1,0), (1,1), (3,1), (3,2).
Your task is to change the position of the battleships minimum times so as to reach the optimal state.
Note: All the coordinates are 0-base indexed.
Input
The first line of input contains an integer T (1 <= T <= 10), the number of test cases.
Each test case consists of 6 lines. The i-th line of each test case contains i integers, denoting the type of battleships at i-th row of battlefield, from left to right.
Output
For each test case, if you can’t reach the goal in no more than 20 moves, you must output “too difficult” in one line. Otherwise, you must output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
1 1 2 0 2 1 2 3 3 3 3 4 4 4 4 4 5 5 5 5 5 5
Sample Output
3
Source
2017 Multi-University Training Contest - Team 10
Recommend
liuyiding
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6171
题意:给你一个三角形,只有0那点可以移动,需要多少步才能移动到第一行一个0,第二行两个1...
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int x = 231;
int mv[][2] = {1,0,-1,0,-1,-1,1,1};
struct node{
int map[6][6];
int x, y;
int dep;
int flag;
};
map<ll, ll> vis[2];
queue<node> Q;
ll gethash(int map[6][6]) // 字符串hash
{
ll ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
ans = (ans*x+map[i][j]) % mod;
return ans;
}
int bfs(node &s, node &e)
{
while(!Q.empty())
Q.pop();
vis[0].clear();
vis[1].clear();
vis[0][gethash(s.map)] = 0;
vis[1][gethash(e.map)] = 0;
Q.push(s);
Q.push(e);
while(!Q.empty())
{
node x = Q.front();
Q.pop();
ll sta = gethash(x.map);
if(vis[!x.flag].count(sta)) // 表示另一种里面是否有这种情况
{
int num = vis[!x.flag][sta] + x.dep;
if(num <= 20) return num;
else continue;
}
if(x.dep >= 10)
continue;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
node y = x;
y.dep ++;
y.x += mv[i][0];
y.y += mv[i][1];
if(y.x<0 || y.x>=6 || y.y<0 || y.y>y.x) continue;
swap(y.map[x.x][x.y], y.map[y.x][y.y]);
if(!vis[y.flag].count(gethash(y.map)))
vis[y.flag][gethash(y.map)] = y.dep;
Q.push(y);
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while(t--)
{
node s,e;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
scanf("%d", &s.map[i][j]);
if(s.map[i][j] == 0)
{
s.x = i;
s.y = j;
}
e.map[i][j] = i; // 完成的对象
}
}
s.flag = 0; s.dep = 0;
e.x = 0; e.y = 0;
e.flag = 1; e.dep = 0;
int ans = bfs(s, e);
if(ans>=0 && ans<=20)
printf("%d\n", ans);
else
puts("too difficult");
}
return 0;
}