简介:
当我们在做项目的时候,往往需要定义大量的JavaBean,而且每一个实体的每一个成员变量都需要定义getter/setter方法,显得比较繁琐。而Lombok通过注解的方式帮助我们进行去繁琐化,提供一个简洁编程方式。Lombok的注解并没有使用到Java的反射机制,而是通过一些奇淫技巧,在代码编译时期动态的将注解转换为具体的代码。
依赖添加:
>>Gradle:
provided group: 'org.projectlombok', name: 'lombok', version: '1.16.18'
>>Maven::
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.16.18</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency>
Lombok Idea插件安装:
>>Step.1、Setting -> plugins -> Browse repositories -> lombok search -> install
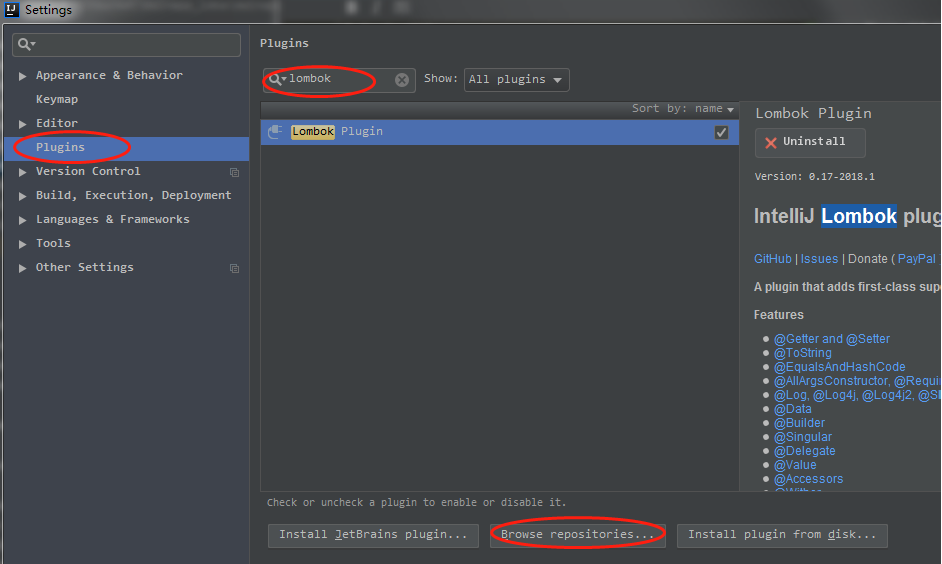
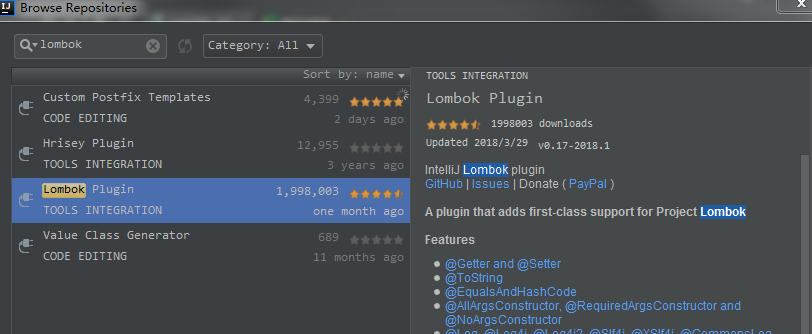
>>Step.2、点击右边的install,然后重启Intellij Idea即可。ps:该截图是因为已经安装完毕,所以没有install按钮
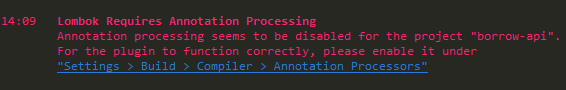
>>Step.3、Lombok安装完成之后,当第一次启动项目的时候,会报:Lombok Requires Annotation Processing的错误,如下所示:
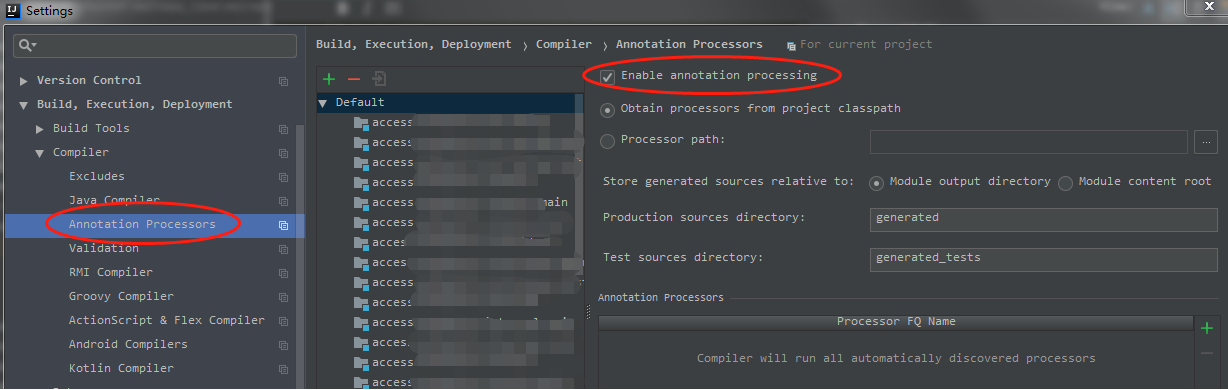
>>Step.4、这个时候是需要为项目开启 Enable annotation processing功能,可以点击蓝色的字直接打开编辑页面,也可以通过setting -> Build,Execution,Deployment -> Annotation Processors打开编辑页面,然后选择 Enable annotation processing前面的勾勾,点击Apply重启Idea即可
Lombok注解:
- @NonNull:在参数中使用时,如果调用时传了null值,会抛出空异常
- @Cleanup:关闭流、连接点
- @Setter:注解在类上,为所有的属性添加set方法、注解在属性上为该属性提供set方法
- @Getter:注解在类上,为所有的属性添加get方法、注解在属性上为该属性提供get方法
- @ToString:创建一个toString方法
- @EqualsAndHashCode:重写equals和hashCode方法
- @NoArgsConstructor:创建一个无参构造函数
- @AllArgsConstructor:创建一个全参构造函数
- @RequiredArgsConstructor:创建一个包含所有非null值字段的构造函数
- @Data:注解在类上,将类提供的所有属性都添加get、set方法,并添加equals、canEquals、hashCode和toString方法
- @Value: 所有字段默认为私有和最终的,并且不会生成setter,是@Data的不可变变体
- @Builder:使用builder模式创建对象。ps:builder模式请参见effective java第一章或google
- @SneakyThrows:代替异常捕获,只需要将异常例外(任意数量的)传递给该注释
- @Synchronized:用于方法,可以锁定指定的对象,如果不指定,则默认创建一个对象锁定
- @Getter(lazy=true):您可以让lombok生成一个getter,它会在第一次调用getter时计算一次值,并从此开始缓存。 如果计算该值需要大量的CPU,或者该值需要大量内存,则这可能很有用。 要使用此功能,请创建一个私有最终变量,使用运行费用较高的表达式对其进行初始化,并使用@Getter(lazy = true)对您的字段进行注释。 该字段将隐藏其余的代码,并且当第一次调用getter时,表达式将被评估不超过一次。 没有神奇的标记值(即使您的昂贵计算结果为空,结果被缓存),并且昂贵的计算不需要线程安全,因为lombok负责锁定。
- @Log:作用于类,创建一个Log属性
官方deamo:
这里只罗列@NonNull、@Data、@Builder、@SneakyThrows四个注解的demo,从demo可与看出将我们的代码复杂度简洁了不少。需要了解其它注解的demo请参考官方网站:https://projectlombok.org/features/
- @nonNull
- With Lombok
import lombok.NonNull; public class NonNullExample extends Something { private String name; public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) { super("Hello"); this.name = person.getName(); } }
- Vanilla Java
import lombok.NonNull; public class NonNullExample extends Something { private String name; public NonNullExample(@NonNull Person person) { super("Hello"); if (person == null) { throw new NullPointerException("person"); } this.name = person.getName(); } }
- With Lombok
- @Data
- With Lombok
import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.Data; import lombok.ToString; @Data public class DataExample { private final String name; @Setter(AccessLevel.PACKAGE) private int age; private double score; private String[] tags; @ToString(includeFieldNames=true) @Data(staticConstructor="of") public static class Exercise<T> { private final String name; private final T value; } }
- Vanilla Java
import java.util.Arrays; public class DataExample { private final String name; private int age; private double score; private String[] tags; public DataExample(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return this.name; } void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return this.age; } public void setScore(double score) { this.score = score; } public double getScore() { return this.score; } public String[] getTags() { return this.tags; } public void setTags(String[] tags) { this.tags = tags; } @Override public String toString() { return "DataExample(" + this.getName() + ", " + this.getAge() + ", " + this.getScore() + ", " + Arrays.deepToString(this.getTags()) + ")"; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof DataExample; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (!(o instanceof DataExample)) return false; DataExample other = (DataExample) o; if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false; if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false; if (this.getAge() != other.getAge()) return false; if (Double.compare(this.getScore(), other.getScore()) != 0) return false; if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.getTags(), other.getTags())) return false; return true; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int PRIME = 59; int result = 1; final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.getScore()); result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getName() == null ? 43 : this.getName().hashCode()); result = (result*PRIME) + this.getAge(); result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32)); result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.getTags()); return result; } public static class Exercise<T> { private final String name; private final T value; private Exercise(String name, T value) { this.name = name; this.value = value; } public static <T> Exercise<T> of(String name, T value) { return new Exercise<T>(name, value); } public String getName() { return this.name; } public T getValue() { return this.value; } @Override public String toString() { return "Exercise(name=" + this.getName() + ", value=" + this.getValue() + ")"; } protected boolean canEqual(Object other) { return other instanceof Exercise; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; if (!(o instanceof Exercise)) return false; Exercise<?> other = (Exercise<?>) o; if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false; if (this.getName() == null ? other.getValue() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false; if (this.getValue() == null ? other.getValue() != null : !this.getValue().equals(other.getValue())) return false; return true; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int PRIME = 59; int result = 1; result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getName() == null ? 43 : this.getName().hashCode()); result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getValue() == null ? 43 : this.getValue().hashCode()); return result; } } }
- With Lombok
- @Builder
- With Lombok
import lombok.Builder; import lombok.Singular; import java.util.Set; @Builder public class BuilderExample { @Builder.Default private long created = System.currentTimeMillis(); private String name; private int age; @Singular private Set<String> occupations; }
- Vanilla Java
import java.util.Set; public class BuilderExample { private long created; private String name; private int age; private Set<String> occupations; BuilderExample(String name, int age, Set<String> occupations) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.occupations = occupations; } private static long $default$created() { return System.currentTimeMillis(); } public static BuilderExampleBuilder builder() { return new BuilderExampleBuilder(); } public static class BuilderExampleBuilder { private long created; private boolean created$set; private String name; private int age; private java.util.ArrayList<String> occupations; BuilderExampleBuilder() { } public BuilderExampleBuilder created(long created) { this.created = created; this.created$set = true; return this; } public BuilderExampleBuilder name(String name) { this.name = name; return this; } public BuilderExampleBuilder age(int age) { this.age = age; return this; } public BuilderExampleBuilder occupation(String occupation) { if (this.occupations == null) { this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>(); } this.occupations.add(occupation); return this; } public BuilderExampleBuilder occupations(Collection<? extends String> occupations) { if (this.occupations == null) { this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>(); } this.occupations.addAll(occupations); return this; } public BuilderExampleBuilder clearOccupations() { if (this.occupations != null) { this.occupations.clear(); } return this; } public BuilderExample build() { // complicated switch statement to produce a compact properly sized immutable set omitted. Set<String> occupations = ...; return new BuilderExample(created$set ? created : BuilderExample.$default$created(), name, age, occupations); } @java.lang.Override public String toString() { return "BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder(created = " + this.created + ", name = " + this.name + ", age = " + this.age + ", occupations = " + this.occupations + ")"; } } }
- With Lombok
- @SneakyThrows
- With Lombok
import lombok.SneakyThrows; public class SneakyThrowsExample implements Runnable { @SneakyThrows(UnsupportedEncodingException.class) public String utf8ToString(byte[] bytes) { return new String(bytes, "UTF-8"); } @SneakyThrows public void run() { throw new Throwable(); } }
- Vanilla Java
import lombok.Lombok; public class SneakyThrowsExample implements Runnable { public String utf8ToString(byte[] bytes) { try { return new String(bytes, "UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { throw Lombok.sneakyThrow(e); } } public void run() { try { throw new Throwable(); } catch (Throwable t) { throw Lombok.sneakyThrow(t); } } }
- With Lombok
Lombok之奇淫技:
其奇就奇在是通过对注解的解析来进行编译时增强的。说到解析我们得对比区分下:
运行时解析:
运行时解析,我们必须使用元注解的RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,这样我们得程序在运行时,我们才可以通过反射的方式拿到该注解。java.lang.reflect反射包中提过了一个接口AnnotatedElment,该接口定义了获取注解信息的几个方法,Class、Constructor、Field、Method、Package等都实现了该接口。
boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass); <T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass); Annotation[] getAnnotations(); Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();
编译时解析:
编译时解析涉及到两种规则(其实自己也没搞懂,这里引用一下别人的区分)
a. Annotation Processing Tool
apt自JDK5产生,JDK7已标记为过期,不推荐使用,JDK8中已彻底删除,自JDK6开始,可以使用Pluggable Annotation Processing API来替换它,apt被替换主要有2点原因:
- api都在com.sun.mirror非标准包下
- 没有集成到javac中,需要额外运行
apt的更多介绍可以参见这里。
b. Pluggable Annotation Processing API
JSR 269,自JDK6加入,作为apt的替代方案,它解决了apt的两个问题,javac在执行的时候会调用实现了该API的程序,这样我们就可以对编译器做一些增强,这时javac执行的过程如下: 
Lombok就是使用这种方式实现的,有兴趣的话可以去看看其Lombok源码,对应注解的实现都在HandleXXX中,比如@Getter注解的实现是HandleGetter.handle()。还有一些其它类库使用这种方式实现,比如Google Auto、Dagger等等。
Lombok问题:
- 无法支持多种参数构造器的重载
- 奇淫巧技,使用会有争议
参考文章:
- https://blog.csdn.net/ghsau/article/details/52334762
- https://blog.mythsman.com/2017/12/19/1/
- https://projectlombok.org/features/experimental/all
- https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/59972#11