左倾堆的介绍
左倾堆(leftist tree 或 leftist heap),又被成为左偏树、左偏堆,最左堆等。
它和二叉堆一样,都是优先队列实现方式。当优先队列中涉及到"对两个优先队列进行合并"的问题时,二叉堆的效率就无法令人满意了,而本文介绍的左倾堆,则可以很好地解决这类问题。
左倾堆的定义
左倾堆是一棵二叉树,它的节点除了和二叉树的节点一样具有左右子树指针外,还有两个属性:键值和零距离。
(01) 键值的作用是来比较节点的大小,从而对节点进行排序。
(02) 零距离(英文名NPL,即Null Path Length)则是从一个节点到一个"最近的不满节点"的路径长度。不满节点是指该该节点的左右孩子至少有有一个为NULL。叶节点的NPL为0,NULL节点的NPL为-1。
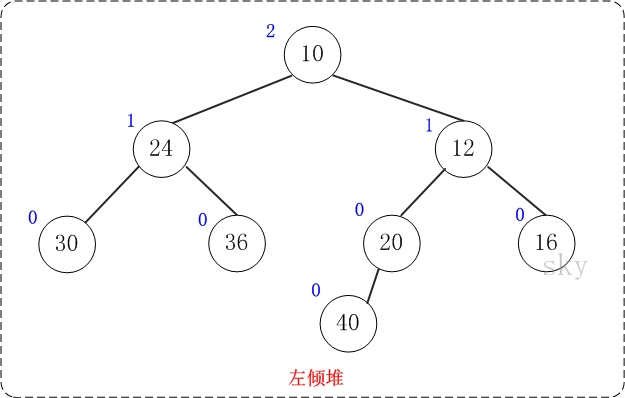
上图是一颗左倾堆,它满足左倾堆的基本性质:
[性质1] 节点的键值小于或等于它的左右子节点的键值。
[性质2] 节点的左孩子的NPL >= 右孩子的NPL。
[性质3] 节点的NPL = 它的右孩子的NPL + 1。
左倾堆,顾名思义,是有点向左倾斜的意思了。它在统计问题、最值问题、模拟问题和贪心问题等问题中有着广泛的应用。此外,斜堆是比左倾堆更为一般的数据结构。当然,今天讨论的是左倾堆,关于斜堆,以后再撰文来表。
前面说过,它能和好的解决"两个优先队列合并"的问题。实际上,左倾堆的合并操作的平摊时间复杂度为O(lg n),而完全二叉堆为O(n)。合并就是左倾树的重点,插入和删除操作都是以合并操作为基础的。插入操作,可以看作两颗左倾树合并;删除操作(移除优先队列中队首元素),则是移除根节点之后再合并剩余的两个左倾树。闲话说到这里,下面开始介绍左倾树的基本方法。
左倾堆的图文解析
合并操作是左倾堆的重点。合并两个左倾堆的基本思想如下:
(01) 如果一个空左倾堆与一个非空左倾堆合并,返回非空左倾堆。
(02) 如果两个左倾堆都非空,那么比较两个根节点,取较小堆的根节点为新的根节点。将"较小堆的根节点的右孩子"和"较大堆"进行合并。
(03) 如果新堆的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL,则交换左右孩子。
(04) 设置新堆的根节点的NPL = 右子堆NPL + 1
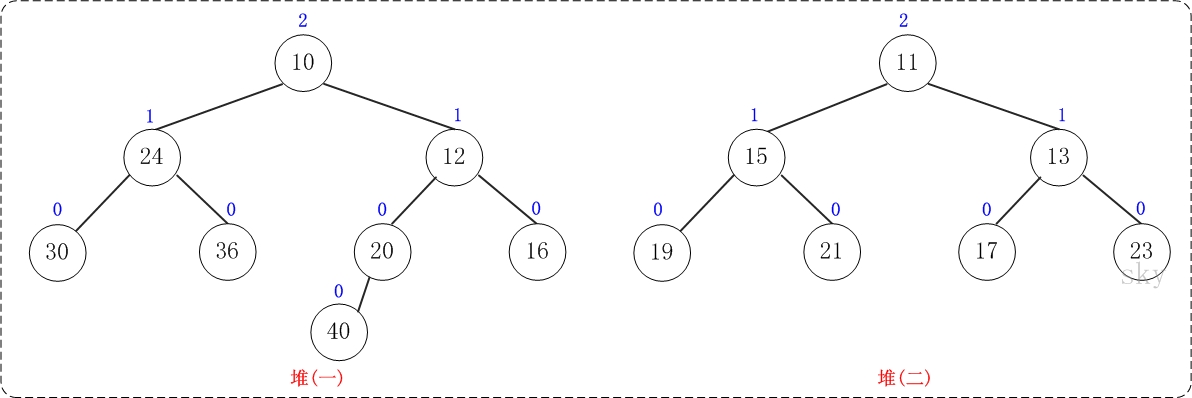
下面通过图文演示合并以下两个堆的过程。
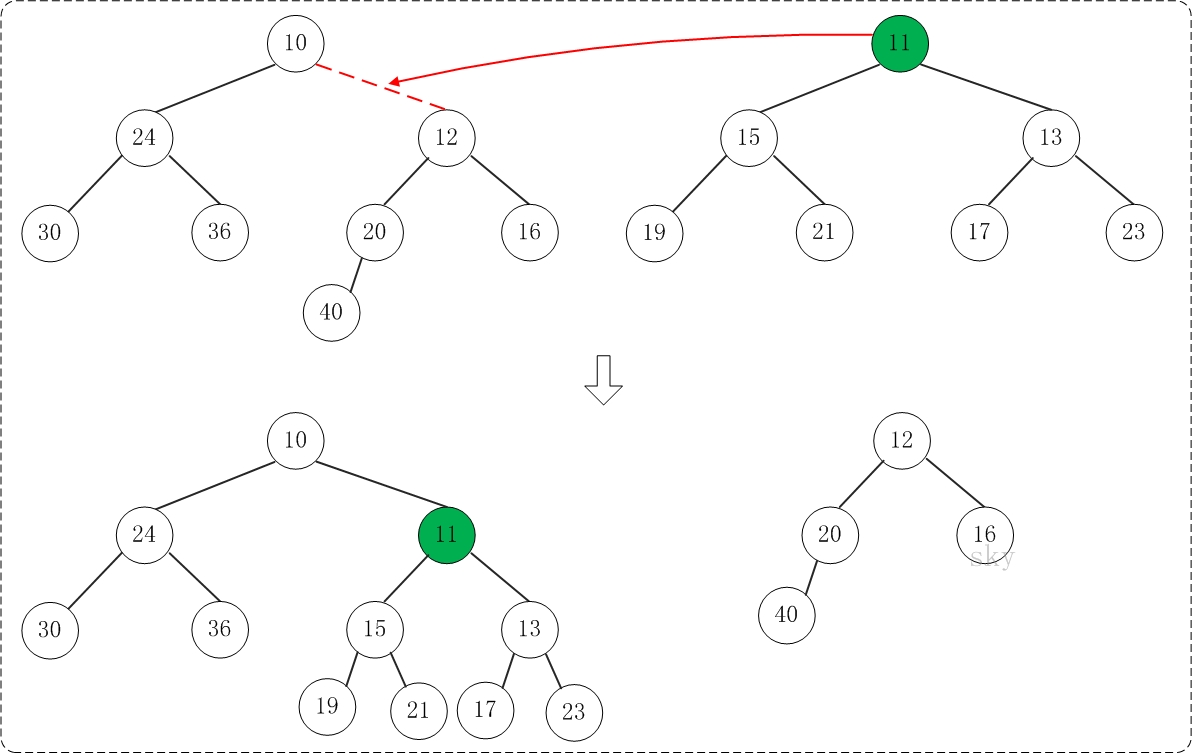
第1步:将"较小堆(根为10)的右孩子"和"较大堆(根为11)"进行合并。
合并的结果,相当于将"较大堆"设置"较小堆"的右孩子,如下图所示:
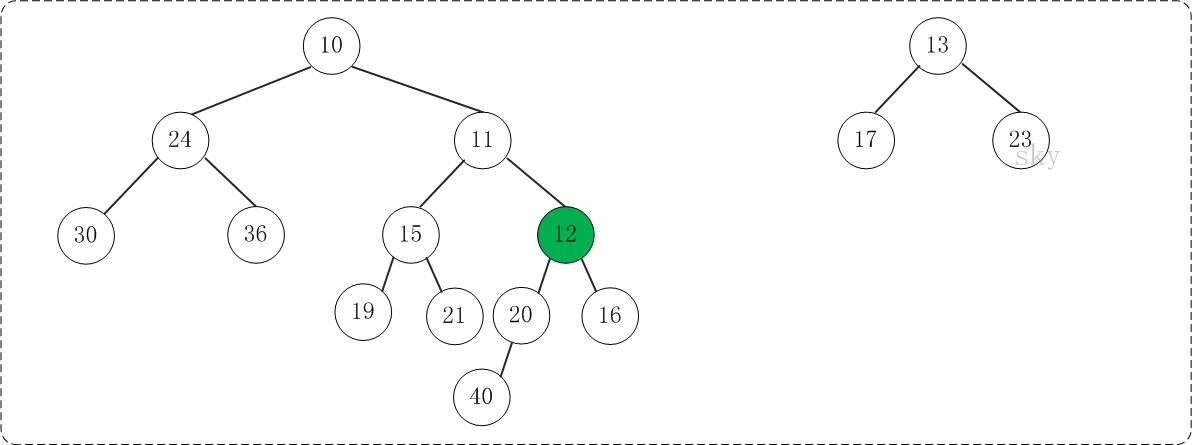
第2步:将上一步得到的"根11的右子树"和"根为12的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
第3步:将上一步得到的"根12的右子树"和"根为13的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
第4步:将上一步得到的"根13的右子树"和"根为16的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
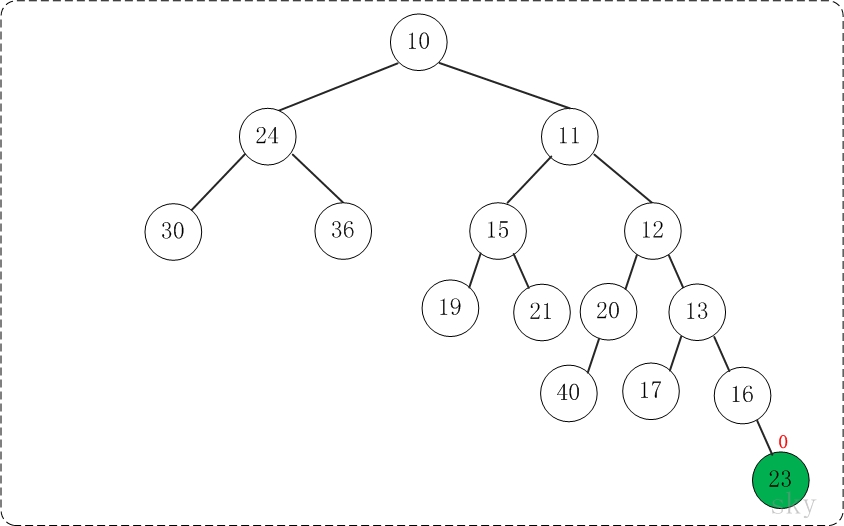
第5步:将上一步得到的"根16的右子树"和"根为23的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
至此,已经成功的将两棵树合并成为一棵树了。接下来,对新生成的树进行调节。
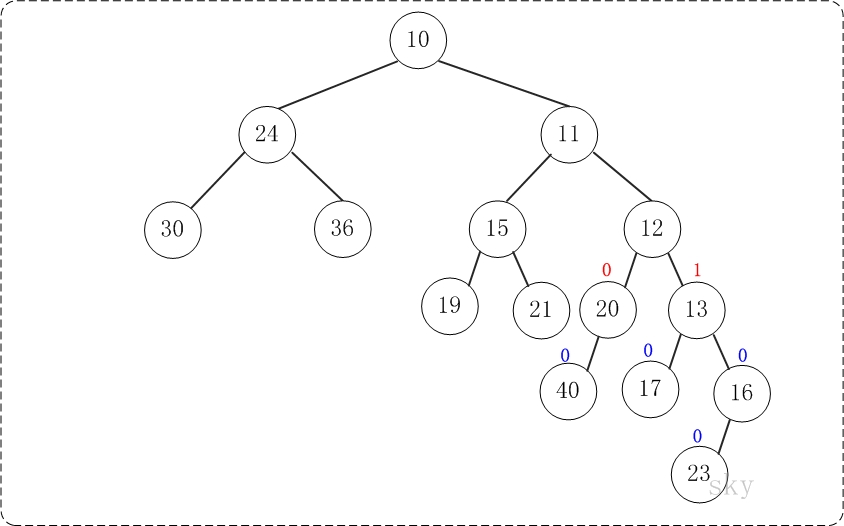
第6步:上一步得到的"树16的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:
第7步:上一步得到的"树12的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:
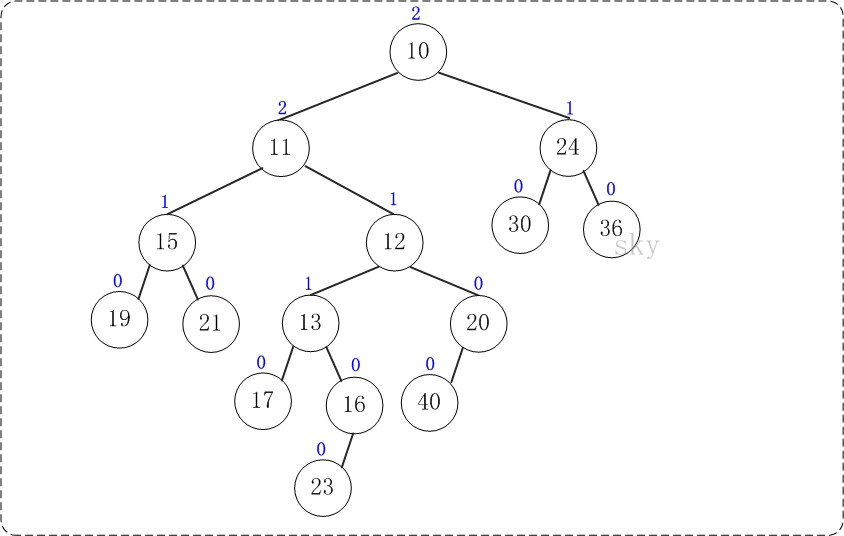
第8步:上一步得到的"树10的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:
至此,合并完毕。上面就是合并得到的左倾堆!
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int Type;
typedef struct _LeftistNode {
Type key; // 关键字(键值)
int npl; // 零路经长度(Null Path Length)
struct _LeftistNode *left; // 左孩子
struct _LeftistNode *right; // 右孩子
}LeftistNode, *LeftistHeap;
/*
* 前序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
void preorder_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap != NULL)
{
printf("%d ", heap->key);
preorder_leftist(heap->left);
preorder_leftist(heap->right);
}
}
/*
* 中序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
void inorder_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap != NULL)
{
inorder_leftist(heap->left);
printf("%d ", heap->key);
inorder_leftist(heap->right);
}
}
/*
* 后序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
void postorder_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap != NULL)
{
postorder_leftist(heap->left);
postorder_leftist(heap->right);
printf("%d ", heap->key);
}
}
/*
* 交换两个节点的内容
*/
static void swap_leftist_node(LeftistNode *x, LeftistNode *y)
{
LeftistNode tmp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = tmp;
}
/*
* 获取最小值
*
* 返回值:
* 成功返回0,失败返回-1
*/
int leftist_minimum(LeftistHeap heap, int *pval)
{
if (heap == NULL)
return -1;
*pval = heap->key;
return 0;
}
/*
* 合并"左倾堆x"和"左倾堆y"
*
* 返回值:
* 合并得到的树的根节点
*/
LeftistNode* merge_leftist(LeftistHeap x, LeftistHeap y)
{
if (x == NULL)
return y;
if (y == NULL)
return x;
// 合并x和y时,将x作为合并后的树的根;
// 这里的操作是保证: x的key < y的key
if (x->key > y->key)
swap_leftist_node(x, y);
// 将x的右孩子和y合并,"合并后的树的根"是x的右孩子。
x->right = merge_leftist(x->right, y);
// 如果"x的左孩子为空" 或者 "x的左孩子的npl<右孩子的npl"
// 则,交换x和y
if (x->left == NULL || x->left->npl < x->right->npl)
{
LeftistNode *tmp = x->left;
x->left = x->right;
x->right = tmp;
}
// 设置合并后的新树(x)的npl
if (x->right == NULL || x->left == NULL)
x->npl = 0;
else
x->npl = (x->left->npl > x->right->npl) ? (x->right->npl + 1) : (x->left->npl + 1);
return x;
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到左倾堆中
*
* 参数说明:
* heap 左倾堆的根结点
* key 插入结点的键值
* 返回值:
* 根节点
*/
LeftistNode* insert_leftist(LeftistHeap heap, Type key)
{
LeftistNode *node; // 新建结点
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if ((node = (LeftistNode *)malloc(sizeof(LeftistNode))) == NULL)
return heap;
node->key = key;
node->npl = 0;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return merge_leftist(heap, node);
}
/*
* 取出根节点
*
* 返回值:
* 取出根节点后的新树的根节点
*/
LeftistNode* delete_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap == NULL)
return NULL;
LeftistNode *l = heap->left;
LeftistNode *r = heap->right;
// 删除根节点
free(heap);
return merge_leftist(l, r); // 返回左右子树合并后的新树
}
/*
* 销毁左倾堆
*/
void destroy_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap == NULL)
return;
if (heap->left != NULL)
destroy_leftist(heap->left);
if (heap->right != NULL)
destroy_leftist(heap->right);
free(heap);
}
/*
* 打印"左倾堆"
*
* heap -- 左倾堆的节点
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
static void leftist_print(LeftistHeap heap, Type key, int direction)
{
if (heap != NULL)
{
if (direction == 0) // heap是根节点
printf("%2d(%d) is root\n", heap->key, heap->npl);
else // heap是分支节点
printf("%2d(%d) is %2d's %6s child\n", heap->key, heap->npl, key, direction == 1 ? "right" : "left");
leftist_print(heap->left, heap->key, -1);
leftist_print(heap->right, heap->key, 1);
}
}
void print_leftist(LeftistHeap heap)
{
if (heap != NULL)
leftist_print(heap, heap->key, 0);
}