用Python开发一个基于线程的FTP服务器,主要功能如下:
-
1.
用户加密认证
-
2.
允许同时多用户登录
-
3.
每个用户有自己的家目录 ,且只能访问自己的家目录
-
4.
对用户进行磁盘配额,每个用户的可用空间不同
-
5.
允许用户在ftp server上随意切换目录
-
6.
允许用户查看当前目录下文件
-
7.
允许上传和下载文件,保证文件一致性(md5)
-
8.
文件传输过程中显示进度条
-
9.
附加功能:支持文件的断点续传
-
10.
在之前开发的FTP基础上,开发支持多并发的功能
-
11.
不能使用SocketServer模块,必须自己实现多线程
-
12.
必须用到队列Queue模块,实现线程池
-
13.
允许配置最大并发数,比如允许只有
10
个并发用户
1,用户加密认证
|
1
2
3
4
|
这个肯定需要用到configparser 和hashlib模块,用md5进行加密,服务端与用户端
进行交互前,肯定需要进行认证,在服务端进行认证,客户端需要发送用户名及密码,但
是为了安全起见,服务端数据库中的密码应该是加密后的密文,客户端登陆认证时也应该
发送密文到服务端,服务端接受到密文与数据库中对应的密文进行比较。
|
2,查看自己的当前目录下的文件
|
1
2
|
这个只需要写一个
dir
就ok
简单的说,使用configparse模块就可以完成
|
3,文件传输中显示进度条
|
1
2
3
|
下载的进度条比较好实现,我们可以从服务端受到将要下载的文件的大小,
上传的进度条,我们可以利用文件操作的tell()方法,获取当前指针位置(字节)
|
4,在之前的基础上实现多并发的功能
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
并发,是伪并行,,即看起来是同时运行的,单个CPU
+
多道技术就可以实现并发
多道技术概念回顾:内存中同时存入多道(多个)程序,cpu从一个进程快速切换
到另外一个,使每个进程各自运行几十或几百毫秒,这样,虽然在某一个瞬间,一个cpu
只能执行一个任务,但在
1
秒内,cpu却可以运行多个进程,这就给人产生了并行的错觉,
即伪并发,以此来区分多处理器操作系统的真正硬件并行(多个cpu共享同一个物理内存)
|
5,不能使用SocketServer模块,必须自己实现多线程
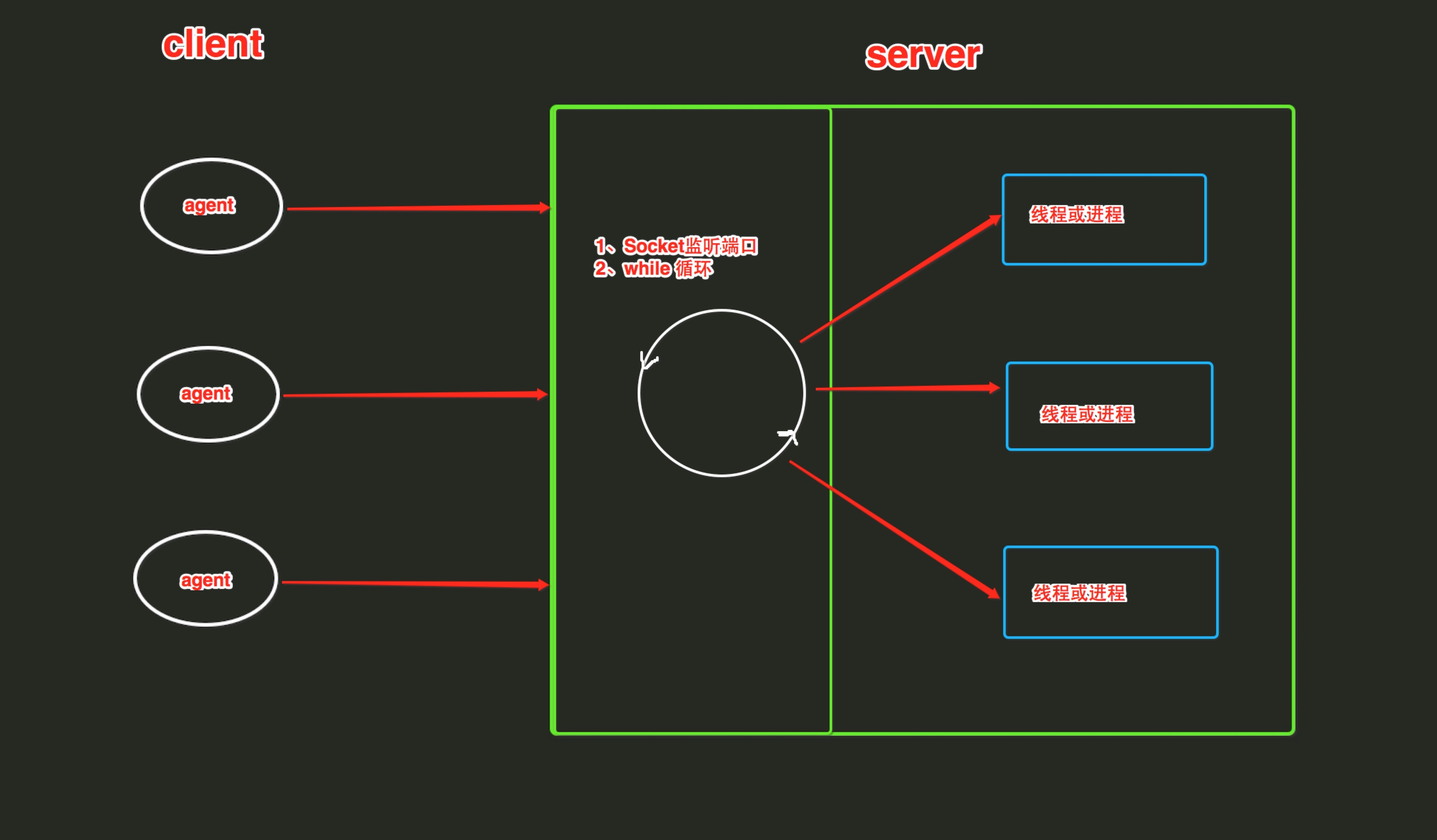
1、服务器启动socket监听端口
2、服务器内部利用while循环监视句柄的变化
3、客户端请求
4、服务器为这个请求分配线程或进程(底层调用select)。
SocketServer模块有两个方法ThreadingTCPServer和ForkingTCPServer,分别创建线程或者进程。
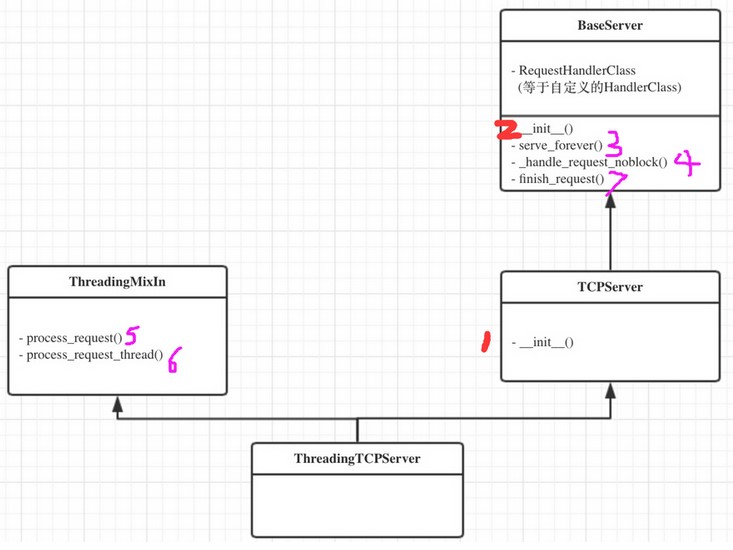
ThreadingTCPServer源码分析(ForkingTCPServer方法类似)
类继承关系图
服务器启动程序后:
1、执行 TCPServer.__init__ 方法,创建服务端Socket对象并绑定 IP 和 端口
解释:class ThreadingTCPServer(ThreadingMixIn, TCPServer): pass,ThreadingTCPServer先要执行__init__构造函数,ThreadingMixIn里没有,就去TCPServer类里去找
2、
执行 BaseServer.__init__ 方法,将
自定义的继承自SocketServer.BaseRequestHandler 的类 MyRequestHandle赋值给self.RequestHandlerClass
解释:TCPServer构造方法中包含BaseServer.__init__(self, server_address, RequestHandlerClass),所以要把自己定义的类传给BaseServer的构造方法
3、执行 BaseServer.server_forever 方法,While 循环一直监听是否有客户端请求到达 ...
解释:serve_forever是BaseServer类中的方法,里面有个while循环,一直调用select.select(),r, w, e =_eintr_retry(select.select, [self], [], [],poll_interval)
客户端接入:
4、执行
BaseServer._handle_request_noblock方法
解释:serve_forever的while循环里有一个判断if self in r:self._handle_request_noblock(),客户端连接句柄发生变化就会把句柄放到r列表里,所以,触发了_handle_request_noblock()。
5、执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request 方法,创建一个 “线程” 用来处理请求
解释:调用process_request方法时,从继承类广度优先原则,所以它先调用ThreadingMixIn类中的process_request
6、执行 ThreadingMixIn.process_request_thread 方法
解释:t = threading.Thread(target = self.process_request_thread,args = (request, client_address))多线程模块方法,调用self.process_request_thread,此时才真正启动了线程。
7、执行 BaseServer.finish_request 方法,执行
self.RequestHandlerClass() 即:执行 自定义 MyRequestHandler 的构造方法(自动调用基类BaseRequestHandler的构造方法,在该构造方法中又会调用自定义的MyRequestHandler的
handle方法)
解释:连接创建完成,此时开始执行handle方法中的内容,开始和客户端交互,执行完,后面再执行shutdown_request方法关闭连接。
源码精简
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
import
socket
import
threading
import
select
def
process(request, client_address):
print
request,client_address
conn
=
request
conn.sendall(
'欢迎致电 10086,请输入1xxx,0转人工服务.'
)
flag
=
True
while
flag:
data
=
conn.recv(
1024
)
if
data
=
=
'exit'
:
flag
=
False
elif
data
=
=
'0'
:
conn.sendall(
'通过可能会被录音.balabala一大推'
)
else
:
conn.sendall(
'请重新输入.'
)
sk
=
socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sk.bind((
'127.0.0.1'
,
8002
))
sk.listen(
5
)
while
True
:
r, w, e
=
select.select([sk,],[],[],
1
)
print
'looping'
if
sk
in
r:
print
'get request'
request, client_address
=
sk.accept()
t
=
threading.Thread(target
=
process, args
=
(request, client_address))
t.daemon
=
False
t.start()
sk.close()
|
6,必须用到队列Queue模块,实现线程池
Python标准模块-concurrent.futures:https://docs.python.org/dev/library/concurrent.futures.html
1 -1介绍
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
concurrent.futures模块提供了高度封装的异步调用接口
ThreadPoolExecutor:线程池,提供异步调用
ProcessPoolExecutor: 进程池,提供异步调用
Both implement the same interface, which
is
defined by the abstract Executor
class
.
1-2 基本方法
|
2,进程池
介绍:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
The ProcessPoolExecutor
class
is
an Executor subclass that uses a pool of
processes to execute calls asynchronously. ProcessPoolExecutor uses the
multiprocessing module, which allows it to side
-
step the Global Interpreter
Lock but also means that only picklable objects can be executed
and
returned.
class
concurrent.futures.ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers
=
None
, mp_context
=
None
)
An Executor subclass that executes calls asynchronously using a pool of at most max_workers processes. If max_workers
is
None
or
not
given, it will default to the number of processors on the machine. If max_workers
is
lower
or
equal to
0
, then a ValueError will be raised.
|
用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
from
concurrent.futures
import
ThreadPoolExecutor,ProcessPoolExecutor
import
os,time,random
def
task(n):
print
(
'%s is runing'
%
os.getpid())
time.sleep(random.randint(
1
,
3
))
return
n
*
*
2
if
__name__
=
=
'__main__'
:
executor
=
ProcessPoolExecutor(max_workers
=
3
)
futures
=
[]
for
i
in
range
(
11
):
future
=
executor.submit(task,i)
futures.append(future)
executor.shutdown(
True
)
print
(
'+++>'
)
for
future
in
futures:
print
(future.result())
|
3,线程池
介绍:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
ThreadPoolExecutor
is
an Executor subclass that uses a pool of threads
to execute calls asynchronously.
class
concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers
=
None
, thread_
name_prefix
=
'')
An Executor subclass that uses a pool of at most max_workers threads to
execute calls asynchronously.
Changed
in
version
3.5
: If max_workers
is
None
or
not
given, it will default
to the number of processors on the machine, multiplied by
5
, assuming that
ThreadPoolExecutor
is
often used to overlap I
/
O instead of CPU work
and
the
number of workers should be higher than the number of workers
for
ProcessPoolExecutor.
New
in
version
3.6
: The thread_name_prefix argument was added to allow
users to control the threading.Thread names
for
worker threads created by
the pool
for
easier debugging.
|
用法:
|
1
|
把ProcessPoolExecutor换成ThreadPoolExecutor,其余用法全部相同
|