转载请注明链接: https://blog.csdn.net/feather_wch/article/details/82086146
本文进行OkHttp源码详细解析。包括异步请求、同步请求、复用连接池、失败重连、底层路由、路由选择器等内容。
如果有帮助的话,请点个赞!万分感谢!
OkHttp源码详解
版本:2018/8/26-1(23:20)
Call(13题)
1、Call的创建源码
//1、创建Call
Call call = okHttpClient.newCall(request);
//2、OkHttpClient.java
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return new RealCall(this, request);
}
//3、RealCall.java
protected RealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest) {
this.client = client;
this.originalRequest = originalRequest;
}2、Call是如何创建的?
- 本质是通过
RealCall进行创建。- 在
RealCall中将OkHttpClient和request进行了保存。
异步请求
enqueue
3、异步请求源码分析
1-异步请求主体流程
//RealCall.java
void enqueue(Callback responseCallback, boolean forWebSocket) {
//1. 转交给Dispatcher执行enqueue
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new RealCall.AsyncCall(responseCallback, forWebSocket));
}
//Dispatcher.java
synchronized void enqueue(RealCall.AsyncCall call) {
//1. 正在运行的异步请求数 < 64 并且 同一个Host的请求数 < 5时
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
//2. 将call放到正在运行的异步队列中
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
//3. 线程池执行该任务
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
//4. 已满,就添加到待运行的异步任务队列中
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}
//Dispatcher.java---将call的host(域名)和运行异步任务队列中的host进行比对,返回相同的任务数
private int runningCallsForHost(RealCall.AsyncCall call) {
int result = 0;
for (RealCall.AsyncCall c : runningAsyncCalls) {
if (c.host().equals(call.host())) result++;
}
return result;
}
/**
* //RealCall.java-内部类AsyncCall
* 1. AsyncCall的父类NamedRunnable继承自Runnable
* 2. 在Runnable的run()方法中会执行execute()
* 3. execute()中完成了异步任务的执行
*/
final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable {
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
// 1. 请求网络
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(forWebSocket);
// 2. 成功: 回调Callback的onResponse
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
...
// 3. 失败:回调Callback的onFailure
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
} finally {
// 4. Dispatcher将执行完的任务进行移除,并将待执行任务添加到运行中队列内部,并且开启任务的执行
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
//RealCall.java
private Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain(boolean forWebSocket) throws IOException {
//1. 创建拦截器链
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealCall.ApplicationInterceptorChain(0, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
//2. 执行拦截器链的proceed
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
//RealCall.java内部类: ApplicationInterceptorChain
@Override
public Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException {
//1. 从拦截器列表中取出拦截器,迭代执行器拦截前动作。
if (index < client.interceptors().size()) {
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealCall.ApplicationInterceptorChain(index + 1, request, forWebSocket);
// 取出拦截器
Interceptor interceptor = client.interceptors().get(index);
/**========================================================
* 存在多个拦截器时,会递归调用所有拦截器的intercept方法
* 1. 调用到自定义拦截器的intercept()---MyInterceptor implements Interceptor
* 2. 内部执行chain.proceed(request)方法
* 3. 执行ApplicationInterceptorChain的proceed(),回到该方法,也就是递归调用
*========================================================*/
Response interceptedResponse = interceptor.intercept(chain);
//返回的其实是最后拦截器执行getResponse的返回值
return interceptedResponse;
}
//2. 网络请求---在最后一个拦截器的intercept()->proceed()中执行该处
return getResponse(request, forWebSocket);
}
//RealCall.java---执行request请求,并且返回响应结果
Response getResponse(Request request, boolean forWebSocket) throws IOException {
...
// 1. 创建HttpEngine
engine = new HttpEngine(client, request, ...);
while (true) {
try {
// 2. 发送Request请求
engine.sendRequest();
// 3. 获取Response响应
engine.readResponse();
} catch (RouteException e / IOException e) {
// 4. 失败重连,重新获取HttpEngine并且continue重新进行请求
HttpEngine retryEngine = engine.recover(e, null);
...
continue;
} finally {
// 5. 遭遇异常情况下,需要释放掉资源
if (releaseConnection) {
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = engine.close();
streamAllocation.release();
}
}
// 返回Response
Response response = engine.getResponse();
Request followUp = engine.followUpRequest();
if (followUp == null) {
if (!forWebSocket) {
engine.releaseStreamAllocation();
}
return response;
}
...
// 6. 其他异常情况,也是进行失败重连
engine = new HttpEngine(client, request, ...);
}
}4、OkHttp发起异步请求时,调用的call.enqueue方法做了哪些事情?
- 在Call创建的时候,在内部创建了RealCall,并且将OkHttpClient和request保存到了内部。
- 执行Call.enqueue(),内部是执行的RealCall.enqueue()
- RealCall.enqueue()内部直接转交给Dispatcher执行enqueue()方法
- Dsipatcher内部做了会去判断是否达到了最大并发任务数64,以及同一个主机的请求数是否达到了5。
- 都没有达到:加入到正在执行的异步请求队列。然后调用线程池去执行这个任务。
- 达到:加入到待执行的异步请求队列
5、OkHttp是如何发起实际的网络请求的?OkHttp是如何处理拦截器/拦截器链的?
- RealCall的getResponseWithInterceptorCahin()发起了实际的网络请求。
- 会创建ApplicationInterceptorChain对象,并执行其proceed()方法
- proceed方法会从request对应的拦截器列表中取出第一个拦截器,执行其intercept方法
- intercept()内部会去执行ApplicationInterceptorChain.proceed()方法,然后取出第二个拦截器。依次层层递归调用。
- 最终在最后一个拦截器之后,执行了ApplicationInterceptorChain.proceed()中的最后一行代码:
getResponse(request, forWebSocket)- getResponse真正发起了请求,并且获取到了Reponse。
6、RealCall的getResponse是如何进行网络请求的?
- 通过HttpEngine进行网络请求
- 内部有一个While循环
- engine.sendRequest():发送Request请求
- engine.readResponse(): 获取Response响应
- 如果出现异常,会通过engine.recover()进行失败重连。
流程图
7、OkHttp异步请求的流程图和要点
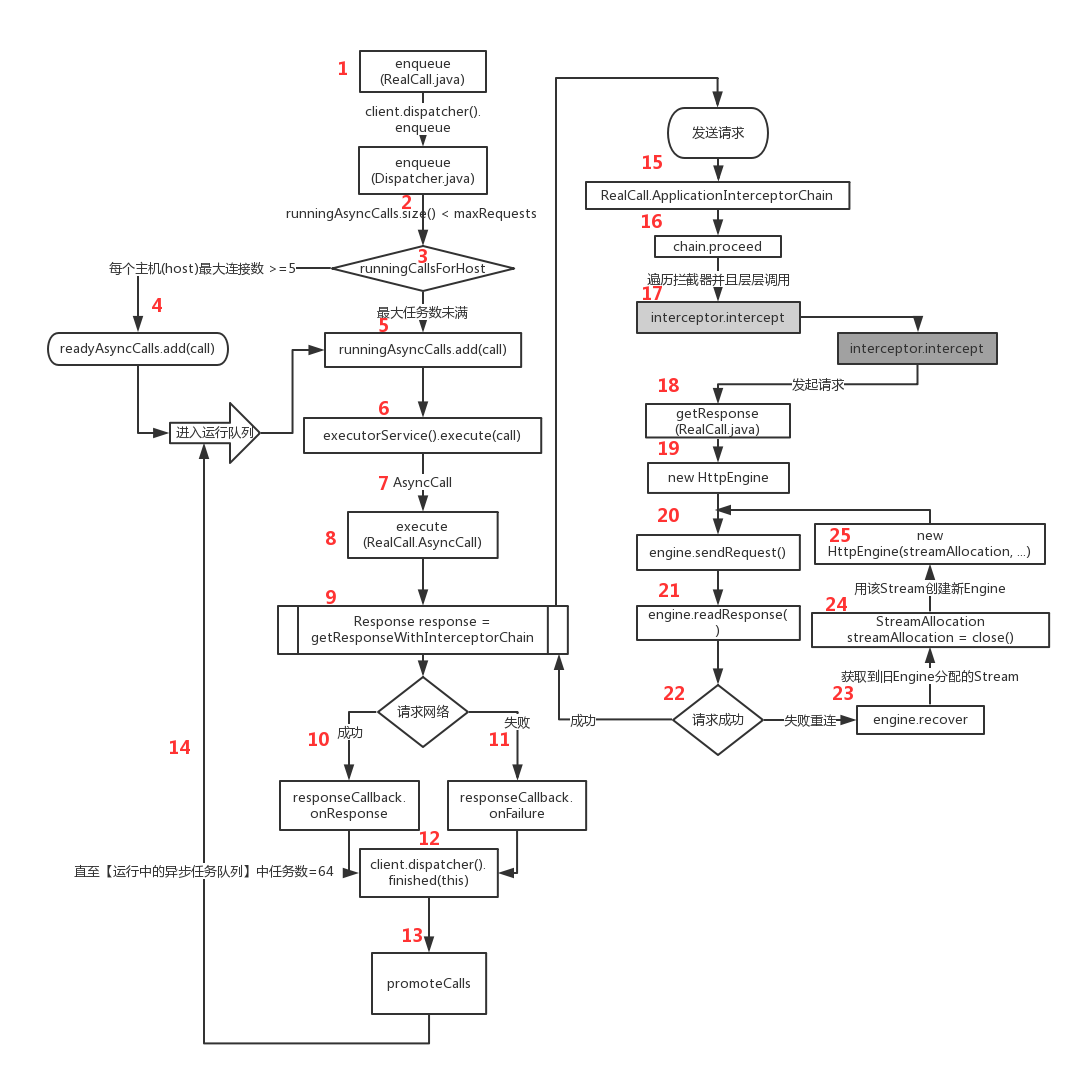
- 调用到
RealCall的enqueue- Dispatcher.enqueue: 会判断当前异步任务数是否<64
- runningCallsForHost:遍历运行中任务,比较和这次请求的Host(域名)一样的有多少,是否 < 5
- (2)(3)任何一个条件不满足,就直接添加到【待运行的异步任务队列】
- runningAsyncCalls.add(call): 将任务添加到【运行中的异步任务队列】
- executorService().execute(call): 线程池中执行该任务
- AsyncCall: 本质是Runnable,run()中执行execute()
- AsyncCall.execute(): 进行网络请求、请求成功/失败都会回调对应方法、 进行任务提升
- getResponseWithInterceptorChain(): 进行网络请求
- responseCallback.onResponse(): 请求成功的回调
- responseCallback.onFailure(): 请求失败的回调
- client.dispatcher().finished(this): 将任务从【正在运行的异步任务队列】中移除
- promoteCalls(): 继续进行(2)(3)的条件判断,满足条件就将待运行任务提升至运行中的任务。
- 1、从【待运行队列】中移除任务 2、将任务添加到【运行中任务队列】 3、线程池执行任务
- RealCall.ApplicationInterceptorChain(): 创建Interceptor.Chain
- chain.proceed(): 调用拦截器链的proceed进行后续请求工作。
- 层层调用interceptor的intercept方法。
- getResponse(): 在最内存拦截器处调用该方法,进行网络请求。
- new HttpEngine(): 创建HttpEngine
- engine.sendRequest(): 发送请求
- engine.readResponse(): 接受响应信息
- 请求成功直接返回;不成功需要进行失败重连。
- engine.recover(): 进行Stream的复用
- 获取到请求失败的旧Engine分配的Stream
- 使用该Stream创建新的HttpEngine
- 重复(20)(21)(22)的任务
8、如何进行失败重连?
- HttpEngine里面通过sendRequest和readResponse进行网络请求
- 如果出现了RouteException或者IOException,会通过HttpEngine.recover进行恢复且返回新的HttpEngine。
- 因为是While循环,continue后会继续进行网络请求。
同步请求
9、同步请求源码分析
call.execute(xxx);
//RealCall.java
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
...
try {
// 1. 添加到【运行中的同步队列】
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
// 2. 请求网路
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(false);
return result;
} finally {
// 3. 从【运行中的同步队列】中移除该任务
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
//Dispatcher.java---添加到【运行中的同步队列】
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}
//Dispatcher.java---从【运行中的同步队列】中移除该任务
synchronized void finished(Call call) {
if (!runningSyncCalls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");
}
- 添加到【运行中的同步队列】
- getResponseWithInterceptorChain()进行网络请求
- 从【运行中的同步队列】中移除该任务
Dispatcher
10、Dispatcher是什么?
- 用于控制并发的请求。
- 定义了最大并发数:64
- 定义了每个主机的最大请求数:5
- 内部具有消费者线程池,可以构造时指定。默认的线程池类似于CachedThreadPool,适合大量且耗时较少的任务。
- 内部具有3个队列(正在运行的异步请求队列、即将运行的异步请求队列、正在运行的同步请求队列)
public final class Dispatcher {
private int maxRequests = 64;
private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;
// 线程池
private ExecutorService executorService;
// 将要运行的异步请求队列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 正在运行的异步请求队列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 正在运行的同步请求队列
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
public Dispatcher(ExecutorService executorService) {
this.executorService = executorService;
}
public Dispatcher() {
}
// 用默认线程池进行构造。
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
}
return executorService;
}
}11、Dispatcher在请求任务完成后,如何进行的清理工作?
- getResponseWithInterceptorChain()进行网络请求后,会调用Dispatcher.finished()进行清理工作。
- 会将任务从正在运行的异步任务队列中移除
- 在满足最大并发数和主机最大请求数的情况下,将待执行的异步任务进行提升到正在运行的异步任务队列,并且通过线程池执行该任务。
//Dispatcher.java
synchronized void finished(RealCall.AsyncCall call) {
//1. 将任务从[正在运行的异步任务队列]中移除
if (!runningAsyncCalls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("AsyncCall wasn't running!");
/**============================================
* 2. 取出一个[待运行的异步任务]并且添加到[正在运行的异步任务队列中]
* 3. 通过线程池执行新任务
*==================================*/
promoteCalls();
}
//Dispatcher.java
private void promoteCalls() {
//1. 判断是否超过最大的并发任务数
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return;
//2. 判断是否存在待执行的异步任务
if (readyAsyncCalls.isEmpty()) return;
//3. 取出待执行的异步任务,执行任务,直到已经达到最大并发任务数
for (Iterator<RealCall.AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealCall.AsyncCall call = i.next();
if (runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
// 取出待执行的异步任务
i.remove();
// 添加到正在执行的队列中
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
// 线程池运行任务
executorService().execute(call);
}
// 判断是否超过最大的并发任务数
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) return; // Reached max capacity.
}
}AsyncCall
12、AsyncCall是什么?
- RealCall的内部类
- 继承自
NamedRunnable,间接继承Runnable- 在run()中会执行execute():完成了异步任务的执行
- 用于Dispatcher内部的待运行/运行中的异步任务队列
13、AysncCall的execute方法中做了哪些工作?(4个)
1-请求网络
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(forWebSocket);2-请求成功: 回调Callback的onResponse
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);3-请求失败: 回调Callback的onFailure
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);4-Dispatcher将执行完的任务进行移除,并将待执行任务添加到运行中队列内部,并且开启任务的执行。(finally中一定执行)
client.dispatcher().finished(this);HttpEngine(12题)
1、HttpEngine是什么?
- 处理单个Http的请求和响应
构造
2、HttpEngine的构造
- 主要是将OkHttpClient、request、streamAllocation等保存到了内部。
- StreamAllocation的构造:将address、connectionPool、RouteSelector保存在内部。
- RouteSelector:用于选择合适的Route去访问服务器。
//HttpEngine.java-构造HttpEngine
public HttpEngine(OkHttpClient client, okhttp3.Request request, boolean bufferRequestBody,
boolean callerWritesRequestBody, boolean forWebSocket, StreamAllocation streamAllocation,
RetryableSink requestBodyOut, Response priorResponse) {
// 1、OkHttpClient
this.client = client;
// 2、request
this.userRequest = request;
//...所有参数都作为成员变量保存...
// 3、创建streamAllocation
this.streamAllocation = streamAllocation != null? streamAllocation
: new StreamAllocation(client.connectionPool(), //返回OkHttpClient中的ConnectionPool
createAddress(client, request));
}sendRequest
3、HttpEngine.sendRequest()发送请求的源码分析
- sendRequest(): 并不会真正的发送请求,而是找到合适的Socket封装到了HttpStream中。
- Internal.instance.internalCache(client):获取到客户端中的Cache,Cache在初始化时会读取缓存目录中曾经请求过的所有信息。
- responseCache.get(request):获取到上次与服务器交互时缓存的Response。
- new CacheStrategy.Factory: 获取到缓存策略
- if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null): 如果既没有使用网络,也没有缓存(或过期)。直接新建并且返回报504错误的Response
- 如果仅仅是没有网络,会获取到缓存的Response,进行Gzip解压后返回。
- 如果有网络,就会调用connect进行连接,并且获取到httpstream。
//HttpEngine.java
public void sendRequest() throws RequestException, RouteException, IOException {
/**===========================================================================
* 0. request加上header
* 1- Host:www.wanandroid.com
* 2- Connection:Keep-Alive
* 3- Accept-Encoding: gzip
* 4- Cookie: cookieJar().loadForRequest()获取到cookie列表, 转换为String,添加到header
* 5- User-Agent:okhttp/3.2.0
*===========================================================================*/
Request request = networkRequest(userRequest);
/**===========================================================================
* 1. 获取Client中的Cache,Cache在初始化时会读取缓存目录中曾经请求过的所有信息。
* 1- Internal.instance.internalCache实现就是OkHttpClient的internalCache()方法
* 2- responseCache:就是Cache内部的internalCache
*===========================================================================*/
InternalCache responseCache = Internal.instance.internalCache(client);
// 2. responseCache.get(request): 获取到上次与服务器交互时缓存的Response。从中可以读取到Header
Response cacheCandidate = responseCache != null
? responseCache.get(request) //
: null;
// 3. 获取到缓存策略
cacheStrategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, request, cacheCandidate).get();
// 4. 网络Request请求;如果为null则表示这次调用没有使用网络
networkRequest = cacheStrategy.networkRequest;
// 5. 缓存的Response或者过期失效;如果为null则表示不使用缓存
cacheResponse = cacheStrategy.cacheResponse;
// 6. 如果没有网络request,并且缓存不存在或者过期。直接新建并返回报504错误的Response(网关超时)。
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
userResponse = new Response.Builder().request(userRequest)
.code(504)
.body(EMPTY_BODY)
.build();
return;
}
// 7. 网络Request不存在,就直接返回缓存的Response
if (networkRequest == null) {
userResponse = cacheResponse.newBuilder().request(userRequest).build();
// 8. Gzip解压缩
userResponse = unzip(userResponse);
return;
}
// 9. 网络存在的情况下,会进行连接(找到合适的Socket封装到了HttpStream中)
httpStream = connect();
httpStream.setHttpEngine(this);
// 10. 返回并且保存request Body可以写入的output stream
requestBodyOut = httpStream.createRequestBody(networkRequest, contentLength);
...
}readResponse
4、HttpEngine.readResponse()获取响应信息的源码分析
/**====================================================
* // HttpEngine.java
* 1. 刷新剩下的request header和request body
* 2. 解析Http response header
* 3. 开始读取Http response body
*==============================================*/
public void readResponse() throws IOException {
// 1、第一次请求是null,不会执行。
if (userResponse != null) {
return; // Already ready.
}
// 2、没有网络,但是有缓存的Response。会要求需要先调用sendRequest
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("call sendRequest() first!");
}
// 3、没有网络
if (networkRequest == null) {
return; // No network response to read.
}
Response networkResponse;
// 4、从Call.enqueue->RealCall.enqueue中,设置forWebSocket = false
if (forWebSocket) {
httpStream.writeRequestHeaders(networkRequest);
networkResponse = readNetworkResponse();
}
// 5、默认callerWritesRequestBody = false,一定会进入该代码块
else if (!callerWritesRequestBody) {
// 6、调用NetworkInterceptorChain的proceed()进行网络请求,并且返回Response
networkResponse = new HttpEngine.NetworkInterceptorChain(0, networkRequest).proceed(networkRequest);
} else {
//xxx
}
// 7、回调cookieJar.saveFromResponse()方法
receiveHeaders(networkResponse.headers());
// 8、存在缓存的Response
if (cacheResponse != null) {
// 9、判断是使用缓存Response还是网络Response
if (validate(cacheResponse, networkResponse)) {
// 10、继续使用缓存的Response
userResponse = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest)
.priorResponse(stripBody(priorResponse))
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
// 11、关闭网络Response的连接
networkResponse.body().close();
releaseStreamAllocation();
// 12、更新缓存
InternalCache responseCache = Internal.instance.internalCache(client);
responseCache.update(cacheResponse, stripBody(userResponse));
// 13、Gzip解压后,返回该Response
userResponse = unzip(userResponse);
return;
}
}
// 14、没有缓存或者缓存已经过期
userResponse = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.request(userRequest)
.priorResponse(stripBody(priorResponse))
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
// 15、Response有Body,缓存,并且读取到userResponse
if (hasBody(userResponse)) {
maybeCache();
userResponse = unzip(cacheWritingResponse(storeRequest, userResponse));
}
}
// 网络拦截器链
class NetworkInterceptorChain implements Interceptor.Chain {
private final Request request;
NetworkInterceptorChain(int index, Request request) {
this.index = index;
this.request = request;
}
@Override public Response proceed(Request request) throws IOException {
// 1、层层递归调用拦截器的intercept
if (index < client.networkInterceptors().size()) {
HttpEngine.NetworkInterceptorChain chain = new HttpEngine.NetworkInterceptorChain(index + 1, request);
Interceptor interceptor = client.networkInterceptors().get(index);
Response interceptedResponse = interceptor.intercept(chain);
return interceptedResponse;
}
/**===============================
* 2、最后一个拦截器才会执行到这部分
* 1. 会向请求中写入Header
* 2. 并将Stream中写入Request Body
*===================================*/
// 1. 向请求中写入Header
httpStream.writeRequestHeaders(request);
// 2. 获取到可以写入request Body的outputstream,并通过Okio进行转换
Sink requestBodyOut = httpStream.createRequestBody(request, request.body().contentLength());
BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut);
// 3. 将request body写入到Stream中
request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody);
// 4. 关闭Stream
bufferedRequestBody.close();
/**===============================
* 3、获取到Response,并且返回
* 1. 获取到Response
* 2. 处理返回码为204/205的情况
*===================================*/
// 1. 获取到Response
Response response = readNetworkResponse();
// 2. 处理返回码为204/205的情况
int code = response.code();
if ((code == 204 || code == 205) && response.body().contentLength() > 0) {
throw new ProtocolException("HTTP " + code + " had non-zero Content-Length: " + response.body().contentLength());
}
// 3. 返回response
return response;
}
}
// HttpEngine.java
private Response readNetworkResponse() throws IOException {
// 1、真正完成请求:将请求刷新到底层的Scoket中
httpStream.finishRequest();
// 2、通过HttpStream(Http1xStream)获取到Reponse的Headers
Response networkResponse = httpStream.readResponseHeaders()
.request(networkRequest)
.handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake())
.header(OkHeaders.SENT_MILLIS, Long.toString(sentRequestMillis))
.header(OkHeaders.RECEIVED_MILLIS, Long.toString(System.currentTimeMillis()))
.build();
// 3、openResponseBody:返回能读取Response Body的stream
if (!forWebSocket) {
networkResponse = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.body(httpStream.openResponseBody(networkResponse)) // openResponseBody:
.build();
}
if ("close".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.request().header("Connection"))
|| "close".equalsIgnoreCase(networkResponse.header("Connection"))) {
streamAllocation.noNewStreams();
}
// 4、返回
return networkResponse;
}
// HttpEngine.java-回调CookieJar的saveFromResponse方法
public void receiveHeaders(Headers headers) throws IOException {
List<Cookie> cookies = Cookie.parseAll(userRequest.url(), headers);
if (cookies.isEmpty()) return;
client.cookieJar().saveFromResponse(userRequest.url(), cookies);
}
// HttpEngine.java-如果缓存可用,return true;缓存不可用,需要采用网络,return false;
private static boolean validate(Response cached, Response network) {
// 1、304:表示没有更改过,缓存的数据可以继续使用
if (network.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
return true;
}
/**=======================================
* 2、比较缓存和网络的Last-Modified的时间
* 1. 网络获取的最后修改时间 < 缓存的最后修改时间,return true : 继续用缓存
* 2. 否则,return false: 会使用网络Response
* Last-Modified:用于标记资源在服务端最后被修改的时间
*=====================================*/
Date lastModified = cached.headers().getDate("Last-Modified");
if (lastModified != null) {
Date networkLastModified = network.headers().getDate("Last-Modified");
if (networkLastModified != null
&& networkLastModified.getTime() < lastModified.getTime()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}recover
5、HttpEngine如何进行失败重连?
- 通过HttpEngine.recover()方法
/**=================================================
* // HttpEngine.java
* 1. 获取到旧Engine分配的Stream
* 2. 用该Stream创建新Engine
*=========================================*/
public HttpEngine recover(IOException e, Sink requestBodyOut) {
...
// 1. 获取到旧Engine分配的Stream
StreamAllocation streamAllocation = close();
// 2. 用该Stream创建新Engine
return new HttpEngine(client, ..., streamAllocation, ...);
}6、返回码504
- 获得具有该返回码的Response表示:网关超时
- HttpEngine的sendRequest()中,如果既没有网络,有没有缓存,就会返回具有504的Response。
7、返回码204/205
- 204: 响应报文中包含若干首部和一个状态行,但是没有实体的主体内容。使用场景:对于一些提交到服务器处理的数据,只需要返回是否成功,此时不需要返回数据。可以使用204。
- 205: 告知浏览器清除当前页面中的所有html表单元素,也就是表单重置。
- NetworkInterceptorChain.proceed()中获取到最终的Response时,会处理返回码为204/205的情况。
- 当code=204/205时,Body的Content长度 > 0, 会抛出ProtocolException。
8、返回码304
- 表示资源没有更改过。
- HttpEngine的invalidate()方法用于判断是采用缓存还是网络的Response
- 如果netWork.code = 304,则直接使用缓存数据。
- 如果netWork.code != 304, 会继续去判断缓存和网络的
Last-Modified。- 缓存的最后修改时间更大,就采用缓存。
- 网络的最后修改时间更大,就采用网络数据。
CacheStrategy
9、CacheStrategy是什么?
- 缓存策略
- 返回和request对应的Cached Response。
- 决定了是否使用网络、缓存,还是两者都使用。
1.
10、OkHttp如何缓存的Reponse?
- OkHttpClient中保存了缓存:Cache cache
- 缓存实现于
Cache.java- 采用DiskLruCache进行缓存。
//OkHttpClient.java
InternalCache internalCache() {
return cache != null ? cache.internalCache : internalCache;
}
//OkHttpClient.java
final Cache cache;
/**=================================
* //Cache.java
* 缓存策略:从DiskLruCache中获取上次请求对应的所有信息
*=================================*/
private final DiskLruCache cache;
Response get(Request request) {
// 1. key就是请求中url的md5: return Util.md5Hex(request.url().toString())
String key = urlToKey(request);
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot;
// 2. 根据key获取到快照
snapshot = cache.get(key);
// 3. 从快照中获取到Entry(Cache.java的内部类)
Cache.Entry entry = new Cache.Entry(snapshot.getSource(ENTRY_METADATA));
// 4. 将快照中的数据作为Response的body,以及其他信息,组合成一个Response
Response response = entry.response(snapshot);
// 5. 将Response返回
return response;
}
//Cache.java的内部类:Entry---保存了url、响应的头、请求的方法等。
public Entry(Response response) {
this.url = response.request().url().toString();
this.requestMethod = response.request().method();
this.protocol = response.protocol();
this.message = response.message();
this.responseHeaders = response.headers();
...
}11、CacheStrategy的构造源码
cacheStrategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, request, cacheCandidate).get();
// CacheStrategy.java-存储cacheReponse中的通用报头、实体报头
public Factory(long nowMillis, okhttp3.Request request, Response cacheResponse) {
// 1. 遍历headers进行本地存储
if (cacheResponse != null) {
Headers headers = cacheResponse.headers();
for (int i = 0, size = headers.size(); i < size; i++) {
String fieldName = headers.name(i);
String value = headers.value(i);
// 2. 通用报头:表示消息产生的日期和时间
if ("Date".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
servedDate = HttpDate.parse(value);
servedDateString = value;
// 3. 实体报头:响应过期的日期和时间
} else if ("Expires".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
expires = HttpDate.parse(value);
// 4. 实体报头:资源最后修改的日期和时间
} else if ("Last-Modified".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
lastModified = HttpDate.parse(value);
lastModifiedString = value;
/**==============================================================
* 5. ETag:帮助服务端进行缓存验证。请求时发送给服务端。
* 服务端验证该哈希值和服务端哈希值一致,表明没有变化,返回304表示未修改。
* 如果不一致,表明数据发生改变,返回200.
*==============================================================*/
} else if ("ETag".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
etag = value;
// 6. Age:该Reponse从产生那一刻起到现在所经过的时间。
} else if ("Age".equalsIgnoreCase(fieldName)) {
ageSeconds = HeaderParser.parseSeconds(value, -1);
}
//xxx
}
}
}HttpStream
12、sendRequest()中获取到HttpStream的流程
httpStream = connect();
// HttpEngine.java: 获取到HttpStream
private HttpStream connect() throws RouteException, RequestException, IOException {
boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks = !networkRequest.method().equals("GET");
return streamAllocation.newStream(client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis(),
client.retryOnConnectionFailure(), doExtensiveHealthChecks);
}
// StreamAllocation.java
public HttpStream newStream(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
boolean connectionRetryEnabled, boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks)
throws RouteException, IOException {
try {
// 1、找到健康的Connection
RealConnection resultConnection = findHealthyConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout, connectionRetryEnabled, doExtensiveHealthChecks);
HttpStream resultStream;
// 2、framedConnection == null
if (resultConnection.framedConnection != null) {
resultStream = new Http2xStream(this, resultConnection.framedConnection);
} else {
resultConnection.socket().setSoTimeout(readTimeout);
resultConnection.source.timeout().timeout(readTimeout, MILLISECONDS);
resultConnection.sink.timeout().timeout(writeTimeout, MILLISECONDS);
// 3、创建Http1xStream(Http 1x 版本的Stream)
resultStream = new Http1xStream(this, resultConnection.source, resultConnection.sink);
}
// 4、返回Http1xStream
synchronized (connectionPool) {
stream = resultStream;
return resultStream;
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// IO异常就抛出Route异常
throw new RouteException(e);
}
}
/**==================================================
* // StreamAllocation.java
* 1. 找到healthy connection
* 2. 如果connection不健康,会一直寻找,直到找到healthy connection。
*==============================================*/
private RealConnection findHealthyConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, boolean connectionRetryEnabled, boolean doExtensiveHealthChecks)
throws IOException, RouteException {
while (true) {
// 1、获取到RealConnection(内部的socket已经和服务器建立链接)
RealConnection candidate = findConnection(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout,
connectionRetryEnabled);
// 2、如果是崭新的connection,跳过昂贵的健康检查,直接返回
synchronized (connectionPool) {
if (candidate.successCount == 0) {
// 直接返回
return candidate;
}
}
// 3、不是崭新的connection,经过健康检查后,return
if (candidate.isHealthy(doExtensiveHealthChecks)) {
return candidate;
}
// 4、连接失败-StreamAllocation.java: routeSelector.connectFailed(route, e);将Route添加到黑名单。
connectionFailed(new IOException());
}
}
/**======================================================================
* //StreamAllocation.java
* 返回一个connection(host a new stream)
* 1. 这更倾向于已经存在的connection
* 2. 然后才是connection pool
* 3. 最后才会新建一个connection
*========================================================================*/
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException, RouteException {
Route selectedRoute;
synchronized (connectionPool) {
// 1、第一次进来StreamAllocation内部的connection = null
RealConnection allocatedConnection = this.connection;
if (allocatedConnection != null && !allocatedConnection.noNewStreams) {
// 不会进入
return allocatedConnection;
}
// 2、尝试从connection pool中获取到connection
RealConnection pooledConnection = Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this);
if (pooledConnection != null) {
// 不会进入
this.connection = pooledConnection;
return pooledConnection;
}
// 3、选择的route = null
selectedRoute = route;
}
// 4、选择的route = null
if (selectedRoute == null) {
// 5、从RouteSelector中获取到有效的Route--next()内部会去寻找到有效的route,没找到会继续递归调用next
selectedRoute = routeSelector.next();
synchronized (connectionPool) {
// 6、StreamAllocation内部存储这个route的引用
route = selectedRoute;
}
}
// 7、构造RealConnection:内部仅仅是保存该Route
RealConnection newConnection = new RealConnection(selectedRoute);
// 8、StreamAllocation内部的allocation列表中,持有这个connection的引用
acquire(newConnection);
// 9、将connection添加到连接池中
Internal.instance.put(connectionPool, newConnection);
// 10、StreamAllocation内部保存这个connection
this.connection = newConnection;
// 11、从Route中获取address和port,创建Socket,并且调用socket的connect去连接address。(socket保存在RealConnection内部)
newConnection.connect(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, address.connectionSpecs(),
connectionRetryEnabled);
// 12、将Route从黑名单中移除
routeDatabase().connected(newConnection.route());
return newConnection;
}
// RealConnection.java
public void connect(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
List<ConnectionSpec> connectionSpecs, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws RouteException {
// 0、原来就已经连接上了,抛出状态异常。
if (protocol != null) throw new IllegalStateException("already connected");
RouteException routeException = null;
ConnectionSpecSelector connectionSpecSelector = new ConnectionSpecSelector(connectionSpecs);
// 1、Route中获取proxy、address
Proxy proxy = route.proxy();
Address address = route.address();
// 2、路由异常,之后再分析。
if (route.address().sslSocketFactory() == null
&& !connectionSpecs.contains(ConnectionSpec.CLEARTEXT)) {
throw new RouteException(new UnknownServiceException("CLEARTEXT communication not supported: " + connectionSpecs));
}
// 3、while循环,直到连接成功(protocol != null)
while (protocol == null) {
try {
// 4、Direct或者http会调用socketFactory的createSocket
rawSocket = proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.DIRECT || proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.HTTP
? address.socketFactory().createSocket()
//5、其他会调用new Socket(proxy)
: new Socket(proxy);
// 6、socket.connect去连接address
connectSocket(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, connectionSpecSelector);
} catch (IOException e) {
closeQuietly(socket);
closeQuietly(rawSocket);
// 抛出Route Exception
throw new RouteException(e);
}
}
}
// RealConnection.java-做所有必要工作用于在原始套接字(raw socket)上构建HTTP/HTTPS的连接
private void connectSocket(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout,
ConnectionSpecSelector connectionSpecSelector) throws IOException {
// 1、设置read超时时间
rawSocket.setSoTimeout(readTimeout);
try {
// 2、调用socket的connect去连接address
Platform.get().connectSocket(rawSocket, route.socketAddress(), connectTimeout);
} catch (ConnectException e) {
throw new ConnectException("Failed to connect to " + route.socketAddress());
}
// 3、获取到读写Stream
source = Okio.buffer(Okio.source(rawSocket));
sink = Okio.buffer(Okio.sink(rawSocket));
// 4、成员变量socket设置为rawSocket
protocol = Protocol.HTTP_1_1;
socket = rawSocket;
}
// Platform.java-进行socket的连接
@Override public void connectSocket(Socket socket, InetSocketAddress address, int connectTimeout) throws IOException {
// 调用socket的connect方法,去连接address
socket.connect(address, connectTimeout);
// xxx
}socket的构建:
// SocketFactory.java:内部类DefaultSocketFactory
public Socket createSocket() {
return new Socket();
}
// Socket.java
public Socket() {
setImpl();
}
// Socket.java-Proxy构造Socket(socks socket或者一般的socket)
public Socket(Proxy proxy) {
Proxy.Type type = p.type();
// 1、Proxy类型为Socks
if (type == Proxy.Type.SOCKS) {
// xxx
// 2、构造socks socket
impl = new SocksSocketImpl(p);
impl.setSocket(this);
} else {
// 3、构造Plain Socket
if (p == Proxy.NO_PROXY) {
impl = new PlainSocketImpl();
impl.setSocket(this);
}
}
}ConnectionPool(14题)
1、OkHttp的复用连接池
- TCP的三次握手和四次挥手,会导致效率低下。
- HTTP有一种keepalive connection机制
- OkHttp支持5个并发socket连接
- OkHttp默认keppAlive时间为5分钟
2、OkHttp的ConnectionPool
具有五种主要变量:
1. 空闲的最大连接数:默认5
1. keepAlive时间:默认5分钟
1. 线程池:后台用于清理需要清理的线程
1. 双向队列:维护者RealConnections(socket物理连接的包装)
1. routeDatabase-连接失败的路线名单:连接失败时,会将失败的路线添加进去
1. cleanupRunning:表明是否正在进行清理工作
1. cleanupRunnable:清理任务,每隔一定时间间隔就进行下次清理工作。
/**=============================================
* //ConnectionPool.java-管理HTTP和SPDY连接的复用,用于减少网络延迟。
* 1. 共享相同Address的Http请求可能会共享同一个Connection。
* 2. 实现了复用策略:决定哪个连接能为复用而保持open
*===============================================*/
public final class ConnectionPool {
// 1、每个address的空闲最大连接数(socket)
private final int maxIdleConnections;
// 2、keepAlive时间
private final long keepAliveDurationNs;
// 构造方法-最大连接数:5;keepAlive:5分钟
public ConnectionPool() {
this(5, 5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
public ConnectionPool(int maxIdleConnections, long keepAliveDuration, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
this.maxIdleConnections = maxIdleConnections;
this.keepAliveDurationNs = timeUnit.toNanos(keepAliveDuration);
}
/**=================================================
* 3、线程池: 后台线程用于清理需要清理的连接
* 类似于CachedThreadPool,并且阻塞队列采用没有容量的SynchronousQueue
*=================================================*/
private static final Executor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0 /* corePoolSize */,
Integer.MAX_VALUE /* maximumPoolSize */, 60L /* keepAliveTime */, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp ConnectionPool", true));
// 4、双向队列,同时具有队列和栈的性质,经常在缓存中使用。内部存储着RealConnection,也就是对socket物理连接的包装。
private final Deque<RealConnection> connections = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 5、记录连接失败的路线名单。连接失败时就会把失败的路线加进去。
final RouteDatabase routeDatabase = new RouteDatabase();
// 6、表明是否正在进行清理工作
boolean cleanupRunning;
// 7、清理任务:循环调用cleanup进行清理工作,并且wait一定时间间隔,然后继续进行清理工作
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
//清理工作
}
};
}3、RealConnection的作用?
是对socket物理连接的包装
4、ConnectionPool是什么时候创建的?
在OkHttpClient构造时,创建的ConnectionPool
5、Deque是什么?
- Deque是Queue的子接口
- 既具有stack栈的性质,也具有queue队列的性质。
缓存操作
6、ConnectionPool关于缓存的操作有哪些?
- 也就是对
Deque<RealConnection>双向队列的操作。- 提供了四种操作:放入连接-put;获取连接-get;移除连接-connectionBecameIdle;移除所有连接-evictAll
put: 存放缓存
// ConnectionPool.java
void put(RealConnection connection) {
// 1、第一次进入时,cleanupRunning = false,会通过executor执行cleanupRunnable进行清理工作。
if (!cleanupRunning) {
cleanupRunning = true;
// 2、 执行完ConnectionPool的cleanup(),并且会继续将cleanupRunning设置为false
executor.execute(cleanupRunnable);
}
// 3、将RealConnection添加到双向队列中
connections.add(connection);
}get:获取缓存
// ConnectionPool.java-返回复用的连接到address的connection,如果不存在连接返回null
RealConnection get(Address address, StreamAllocation streamAllocation) {
// 1、遍历双向队列中的RealConnection
for (RealConnection connection : connections) {
// 2、连接的allocations的次数小于限制的大小,并且request的address和该连接的地址完全匹配
if (connection.allocations.size() < connection.allocationLimit
&& address.equals(connection.route().address)
&& !connection.noNewStreams) {
streamAllocation.acquire(connection);
// 3、直接返回connection,用于复用
return connection;
}
}
return null;
}connectionBecameIdle: 移除连接
// ConnectionPool.java-移除连接
boolean connectionBecameIdle(RealConnection connection) {
// 1、connection进入空闲状态或者最大的空闲连接数=0
if (connection.noNewStreams || maxIdleConnections == 0) {
// 2、立即从连接队列中,将该连接移除
connections.remove(connection);
return true;
} else {
// 3、否则,去通知cleanup线程进行可能的清理工作
notifyAll(); // 去唤醒cleanupRunnable中对ConnectionPool对象的wait,继续去进行清理任务
return false;
}
}evictAll: 移除所有连接
// ConnectionPool.java-移除所有连接
public void evictAll() {
List<RealConnection> evictedConnections = new ArrayList<>();
synchronized (this) {
// 1、将connection从连接队列中移除,并且加入到待移除的连接队列中
for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealConnection connection = i.next();
if (connection.allocations.isEmpty()) {
connection.noNewStreams = true;
// 添加到待移除连接队列中
evictedConnections.add(connection);
// 从连接队列中移除
i.remove();
}
}
}
// 2、遍历待移除的连接队列,将connection中的socket进行关闭
for (RealConnection connection : evictedConnections) {
closeQuietly(connection.socket());
}
}自动回收连接
7、ConnectionPool的自动回收连接
- OkHttp是根据StreamAllocation的引用计数是否为0来实现自动回收连接.
- ConnectionPool具有一个cleanup线程
- ConnectionPool.put()方法缓存connection时,会开启cleanup线程进行清理工作。
// ConnectionPool.java-清理任务
private final Runnable cleanupRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
while (true) {
// 1、cleanup进行清理工作
long waitNanos = cleanup(System.nanoTime());
// 2、因为没有使用中、idle中的connection,直接退出cleanup线程
if (waitNanos == -1) return;
if (waitNanos > 0) {
long waitMillis = waitNanos / 1000000L;
waitNanos -= (waitMillis * 1000000L);
// 3、多线程同步,等待一定时间
synchronized (okhttp3.ConnectionPool.this) {
try {
okhttp3.ConnectionPool.this.wait(waitMillis, (int) waitNanos);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
};
/**===============================================================
* // ConnectionPool.java---清理工作
* 1. 在连接池中进行维护工作,将idle时间最长并且已经超过了keep alive限制,或者idle连接上限的connection进行清除
* 2. 返回时间:直至下一次执行cleanup需要sleep的时间
* 3. 返回-1:已经没有进一步的清理工作。
*==================================================================*/
long cleanup(long now) {
// 使用中的connection数据
int inUseConnectionCount = 0;
// 空闲的connection数据
int idleConnectionCount = 0;
// 空闲时间最长的connection
RealConnection longestIdleConnection = null;
// 空闲时间最长的connection的空闲时间
long longestIdleDurationNs = Long.MIN_VALUE;
synchronized (this) {
/**========================================================
* 1、遍历连接队列connections,获取到idle时间最长的connection
*==========================================================*/
for (Iterator<RealConnection> i = connections.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
RealConnection connection = i.next();
// 1. 如果该connection正在使用中,继续搜索
if (pruneAndGetAllocationCount(connection, now) > 0) {
// 2. 使用中的连接数 + 1
inUseConnectionCount++;
continue;
}
// 3. 该connection处于idle状态,idle的连接数 + 1
idleConnectionCount++;
/**======================================
* 2、通过算法获取到idle时间最长的connection
*=====================================*/
// 1. 计算得到该connection空闲了多少时间
long idleDurationNs = now - connection.idleAtNanos;
if (idleDurationNs > longestIdleDurationNs) {
// 2. 保存空闲最长的时间
longestIdleDurationNs = idleDurationNs;
// 3. 保存空闲最长的connection
longestIdleConnection = connection;
}
}
/**=============================================
* 3、idle时间超过了keepAlive时间,或者,idle的connection数量想超过最大idle连接数。立即清理。
*=============================================*/
if (longestIdleDurationNs >= this.keepAliveDurationNs
|| idleConnectionCount > this.maxIdleConnections) {
// 1. 从连接队列中移除该connection
connections.remove(longestIdleConnection);
// 2. 立即关闭该connection的socket连接
closeQuietly(longestIdleConnection.socket());
// 3. 返回0,表示立即再次进行cleanup
return 0;
} else if (idleConnectionCount > 0) {
/**=============================================
* 4、具有idle的connection,计算距离keepAlive还有多少时间,return后进行sleep
*=============================================*/
return keepAliveDurationNs - longestIdleDurationNs;
} else if (inUseConnectionCount > 0) {
/**=============================================
* 5、所有的connection都处于使用中。return keepAlive。默认是睡眠5分钟。
*=============================================*/
return keepAliveDurationNs;
} else {
/**=============================================
* 6、没有空闲的connection,也没有使用中的connection。-1会退出cleanup线程。等待之后通过线程池开启。
*=============================================*/
cleanupRunning = false;
return -1;
}
}
}8、清理线程的工作流程?以及四种情况的处理办法?
9、ConnectionPool.pruneAndGetAllocationCount()的源码分析
- 用于判断connection是空闲连接还是使用中的连接。
- return 0: idle connection
- return >0: connection处于使用中
/**=======================================================
* //ConnectionPool.java
* 1. 去除任何泄露的allocations(分配),并且返回在connection上存活的allocations数量
* 2. Allocations会被泄露:如果connection正在追踪它们,但是app代码已经遗弃了它们。
* 3. 泄露检测是不准确的并且依赖于GC
*=========================================================*/
private int pruneAndGetAllocationCount(RealConnection connection, long now) {
// 1、获取到RealConnection中的StreamAllocation列表
List<Reference<StreamAllocation>> references = connection.allocations;
for (int i = 0; i < references.size(); ) {
// 2、获取到StreamAllocation
Reference<StreamAllocation> reference = references.get(i);
// 3、如果已经被应用或者GC清理,会返回null
if (reference.get() != null) {
i++;
continue;
}
/**=============================================
* 4、找到泄露的allocation,并从StreamAllocation列表中移除该allocation
* 1. 移除该allocation
* 2. 设置noNewStreams标志
*=========================================*/
Internal.logger.warning("A connection to " + connection.route().address().url() + " was leaked. Did you forget to close a response body?");
// 1. 从StreamAllocation列表中移除该allocation
references.remove(i);
// 2. connection没有新的stream。该标志可以用于connectionBecameIdle、evictAll中移除连接。
connection.noNewStreams = true;
// 5、当前是最后一个allocation,该connection符合立即释放的条件。
if (references.isEmpty()) {
// 设置idle的时间
connection.idleAtNanos = now - keepAliveDurationNs;
// 表明该connection是空闲连接
return 0;
}
}
// 6、返回Allocation的数量
return references.size();
}StreamAllocation
10、StreamAllocation是什么?
- OkHttp中使用了类似于引用计数的方式追踪socket流的调用。
- 该计数对象就是StreamAllocation
- 具有两个重要方法:acquire()、release()—本质是改变RealConnection中StreamAllocation的List的大小。
构造
11、StreamAllocation的构造
将connectionPool、address、routeselector保存到内部
/**===============================================================================
* // StreamAllocation.java
* 1、address:createAddress(client, request) 通过OkHttpClient和请求的Request进行构造
* 1. host: 如www.wanandroid.com
* 2. scheme:http
* 3. port:80
* 4. url:http://www.wanandroid.com/
* 2、connectionPool: new OkHttpClient()时会在内部创建connectionPool。一个Client一个pool
*==========================================================================*/
public StreamAllocation(ConnectionPool connectionPool, Address address) {
this.connectionPool = connectionPool;
this.address = address;
this.routeSelector = new RouteSelector(address, //目标Address
routeDatabase()); //将OkHttpClient的connectionPool中的RouteDatabase保存到RouteSelector内部
}acquire()、release()
12、StreamAllocation的acquire()和release()源码
/**======================================================
* // StreamAllocation.java
* 1. 使用该allocation去持有connection。
* 2. 每次调用acquire()方法,都必须要配套的调用release()方法在同一个connection上。
*===============================================================*/
public void acquire(RealConnection connection) {
// 将该StreamAllocation添加到RealConnection内部的allocation列表中
connection.allocations.add(new WeakReference<>(this));
}
// StreamAllocation.java---从RealConnection的allocation列表中删除当前allocation
private void release(RealConnection connection) {
// 1、遍历allocations
for (int i = 0, size = connection.allocations.size(); i < size; i++) {
Reference<StreamAllocation> reference = connection.allocations.get(i);
// 2、查找到当前StreamAllocation
if (reference.get() == this) {
// 3、从allocations列表中删除这个allocation
connection.allocations.remove(i);
return;
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException();
}RealConnection
13、RealConnection是什么?有什么用?
- 是socket物理连接的包装
- 维护了
List<Reference<StreamAllocation>> allocations- StreamAllocation的数量也就是socket被引用的次数
- 如果计数 = 0,表明该连接处于idle状态,需要经过算法进行回收。
- 如果计数 != 0, 表明该连接处于使用中,无需关闭。
14、RealConnection的源码和构造方法
public final class RealConnection extends FramedConnection.Listener implements Connection {
// Route
private final Route route;
// 底层的 TCP socket.
private Socket rawSocket;
// 应用层socket
public Socket socket;
public volatile FramedConnection framedConnection;
// Allocation队列
public final List<Reference<StreamAllocation>> allocations = new ArrayList<>();
// 构造方法
public RealConnection(Route route) {
this.route = route;
}
}Request(12)
1、Request的作用
- 用于Http的请求
- 使用OkHttp之前都需要对Request进行构造。
2、OkHttp请求的构造
GET:通过Builder去构造Request
//1. 通过Builder构建Request
Request.Builder requestBuilder = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://www.baidu.com/")
.method("GET", null);POST:通过FormBody去构造requestBody,然后再通过Builder和requestBody构造Request。
//1. 通过FormBody创建RequestBody
RequestBody requestBody = new FormBody.Builder()
.add("ip", getIPAddress(this)) //本机IP
.build();
//2. 创建Request(通过Builder和RequestBody)
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://ip.taobao.com/service/getIpInfo.php")
.post(requestBody)
.build();3、Request源码
- 具有五个重要的字段。
public final class Request {
// 请求的url
private final HttpUrl url;
// GET、POST
private final String method;
// 头部全部存放在里面
private final Headers headers;
// request的body,包括MediaType、Charset、ContentType等内容
private final RequestBody body;
// tag标签,用于取消请求。
private final Object tag;
private Request(okhttp3.Request.Builder builder) {
this.url = builder.url;
this.method = builder.method;
this.headers = builder.headers.build();
this.body = builder.body;
this.tag = builder.tag != null ? builder.tag : this;
}
public okhttp3.Request.Builder newBuilder() {
return new okhttp3.Request.Builder(this);
}
public static class Builder {
//buidler相关
}
}4、Request有哪些重要的字段?
- url
- method
- headers
- body
- tag
Builder
5、Request.Builder的构造方法
默认构造:默认Get请求
Request构造:将一些字段保存在内部。
// Request.Builder-默认构造方法
public Builder() {
this.method = "GET";
this.headers = new Headers.Builder();
}
// Request进行构造
private Builder(okhttp3.Request request) {
this.url = request.url;
this.method = request.method;
this.body = request.body;
this.tag = request.tag;
this.headers = request.headers.newBuilder();
}
public okhttp3.Request build() {
return new okhttp3.Request(this);
}6、url()
/**=================================================
* //Request.Builder: 将String的url转换为HttpUrl
* 1. HttpUrl具有字段:scheme、host、port等所有Http相关字段
*==================================================*/
public okhttp3.Request.Builder url(String url) {
HttpUrl parsed = HttpUrl.parse(url);
return url(parsed);
}
public okhttp3.Request.Builder url(HttpUrl url) {
this.url = url;
return this;
}7、method()
// Request.Builder: 将method,如“GET”直接保存在内部。RequestBody也是保存在内部。
public okhttp3.Request.Builder method(String method, RequestBody body) {
this.method = method;
this.body = body;
return this;
}8、header相关:header()、addHeader()、removeHeader()、headers()
// Request.Builder:将名为name参数的header的数值替换为value
public okhttp3.Request.Builder header(String name, String value) {
// headers的set
headers.set(name, value);
return this;
}
// Request.Builder:添加一个header,名为name,值为value
public okhttp3.Request.Builder addHeader(String name, String value) {
headers.add(name, value);
return this;
}
// Request.Builder:移除名为name的所有header
public okhttp3.Request.Builder removeHeader(String name) {
headers.removeAll(name);
return this;
}
// Request.Builder:移除原来所有headers,将参数的headers全部添加进来
public okhttp3.Request.Builder headers(Headers headers) {
this.headers = headers.newBuilder();
return this;
}9、cacheControl(): 设置Http协议中请求和响应的缓存机制
// Request.Builder:用于设置Http协议中的Cache-Control(请求和响应的缓存机制)
public okhttp3.Request.Builder cacheControl(CacheControl cacheControl) {
String value = cacheControl.toString();
if (value.isEmpty()) return removeHeader("Cache-Control");
return header("Cache-Control", value);
}10、tag():通过tag可以取消请求
// Request.Builder:给Request设置tag标签,可以用于之后取消请求。方便统一管理OkHttp请求。
public okhttp3.Request.Builder tag(Object tag) {
this.tag = tag;
return this;
}11、build(): 构造Request
// Request.Builder:构造Request
public okhttp3.Request build() {
return new okhttp3.Request(this);
}12、内部通过method()方法实现的API:get()、head()、post()、delete()、put()、patch()
/**==================================================================
* // Request.Builder: 系列方法都是内部通过method()方法将GET、POST和body保存到内部
*=============================================================*/
// GET
public okhttp3.Request.Builder get() {
return method("GET", null);
}
// HEAD
public okhttp3.Request.Builder head() {
return method("HEAD", null);
}
// POST
public okhttp3.Request.Builder post(RequestBody body) {
return method("POST", body);
}
// DELETE
public okhttp3.Request.Builder delete(RequestBody body) {
return method("DELETE", body);
}
// PUT
public okhttp3.Request.Builder put(RequestBody body) {
return method("PUT", body);
}
// PATCH
public okhttp3.Request.Builder patch(RequestBody body) {
return method("PATCH", body);
}Address(5)
1、Address的作用
- 连接说明书:用于和源服务器进行连接
- 如果是简单的connections,这就是server的hostname和port。
- 如果是具有明确的proxy请求,这也会包括一些proxy信息。
- 如果是安全性的connections, 也会包含SSL socket factory,hostname verifier, certificate(证书)。
2、Address源码
/**==================================================================
* 和源服务器的连接说明书(A specification for a connection)
* 1. 如果是简单的connections,这就是server的hostname和port
* 2. 如果是具有明确的proxy请求,这也会包括一些proxy信息。
* 3. 如果是安全性的connections, 也会包含SSL socket factory,hostname verifier, certificate(证书)。
* * Http请求如果共享同一个Address,也会共享同一个connection
*==============================================================*/
public final class Address {
// 1、 Http所有相关字段:如scheme、host、port
final HttpUrl url;
// 2、dns
final Dns dns;
final SocketFactory socketFactory;
final List<Protocol> protocols;
final Proxy proxy;
final SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory;
final HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier;
final CertificatePinner certificatePinner;
xxx
}3、构造Address
用host、port、dns、protocols等内容去构造Address
private static Address createAddress(OkHttpClient client, okhttp3.Request request) {
SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory = null;
HostnameVerifier hostnameVerifier = null;
CertificatePinner certificatePinner = null;
// 1、判断scheme是否是https
if (request.isHttps()) {
sslSocketFactory = client.sslSocketFactory();
hostnameVerifier = client.hostnameVerifier();
certificatePinner = client.certificatePinner();
}
// 1、host、port、dns、protocols等去构造Address
return new Address(request.url().host(), request.url().port(), client.dns(),
client.socketFactory(), sslSocketFactory, hostnameVerifier, certificatePinner,
client.proxyAuthenticator(), client.proxy(), client.protocols(),
client.connectionSpecs(), client.proxySelector());
}Proxy
4、Proxy是什么?
- proxy的相关设置
- type: 决定类型(direct、http、socks)
- SocketAddress:socket地址
/**=======================================================
* // Proxy.java
* proxy的相关设置,包括type(http代理还是socks代理)、socket地址
*========================================================*/
public class Proxy {
// proxy的类型
private java.net.Proxy.Type type;
// proxy的socket地址。如果属于直连则返回null(没有代理)
private SocketAddress sa;
public enum Type {
// 直接的连接或者没有proxy
DIRECT,
// 应用层协议的代理(HTPP、FTP等)
HTTP,
// Socks代理(v4或者v5)
SOCKS
};
}SocketFactory
5、SocketFactory
/**=================================================
* // SocketFactory.java
* 用于创建socket。可以被继承,用于创建特殊的socket子类,
* 并且提供了一种框架用于增加socket层面的功能。
*===============================================*/
public abstract class SocketFactory
{
public static void setDefault(javax.net.SocketFactory factory){...}
//xxx
}Route(6)
1、Route的作用
连接到服务器的connection需要使用该Route路由。
/**=============================================================
* 1、该具体Route被连接到抽象源服务器的connection所使用。
*
* 2、当创建connection时,客户端可以由很多选项:
* HTTP proxy(Http代理): 一个代理服务器可能为该客户端进行了明确的配置。
* 否则会使用ProxySelector,可能会返回多个proxy用于尝试。
* IP address(IP地址):无论是直连源服务器还是代理服务器,打开一个socket都需要一个IP地址。
* DNS服务器会返回多个IP地址用于尝试。
*
* 3、每个路由对用这些选项都有明确的选择。
*========================================================*/
public final class Route {
final Address address;
final Proxy proxy;
final InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress;
}InetSocketAddress
2、InetSocketAddress是什么?
/**===========================================
* // InetSocketAddress.java
* 用于实现 IP Socket地址(IP地址 + port号)
* 也可以是hostname + port号
*==============================================*/
public class InetSocketAddress extends SocketAddress {
private static class InetSocketAddressHolder {
// 1、Socket Address's 主机名
private String hostname;
// 2、Socket Address's IP 地址
private InetAddress addr;
// 3、Socket Address's 端口号
private int port;
}
}RouteDatabase
3、RouteDatabase的作用?
- 路由黑名单
- 用于避免使用那些连接失败的Route
/**=================================================================
* 失败的Route(路由)的黑名单
* 1. 用于避免创建和目标address有关的connection
* 2. 如果尝试连接一个指定的IP地址或者proxy server出现了失败,
* 会进行记录并且优先修改这个路由。
*============================================================*/
public final class RouteDatabase {
// LinkedHashSet存储Route
private final Set<Route> failedRoutes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 将连接失败的route添加到黑名单中
public synchronized void failed(Route failedRoute) {
failedRoutes.add(failedRoute);
}
// 将成功连接的route从黑名单中移除
public synchronized void connected(Route route) {
failedRoutes.remove(route);
}
// 如果route最近失败过,return true,需要推迟这个route。
public synchronized boolean shouldPostpone(Route route) {
return failedRoutes.contains(route);
}
// 失败的route数量
public synchronized int failedRoutesCount() {
return failedRoutes.size();
}
}RouteSelector
4、RouteSelector
/**
* // RouteSelector.java
* 1. 选择routes去连接到源服务器。
* 2. 每个connection需要在proxy servver、IP address、TLS mode中进行选择。
* 3. Connections也可能会被回收
*/
public final class RouteSelector {
// 请求的目标地址信息,如http://www.wanandroid.com/
private final Address address;
// Route黑名单
private final RouteDatabase routeDatabase;
// 最近使用的Porxy、socketAddress
private Proxy lastProxy;
private InetSocketAddress lastInetSocketAddress;
// Proxy列表
private List<Proxy> proxies = Collections.emptyList();
// socket Address列表。
private List<InetSocketAddress> inetSocketAddresses = Collections.emptyList();
// index
private int nextProxyIndex;
private int nextInetSocketAddressIndex;
// 失败的Route列表
private final List<Route> postponedRoutes = new ArrayList<>();
}构造
5、构造方法
// RouteSelector.java-构造方法
// 调用层次关系:
// HttpEngine.sendRequest() -> new HttpEngine() -> new StreamAllocation() -> new RouteSelector()
public RouteSelector(okhttp3.Address address, okhttp3.internal.RouteDatabase routeDatabase) {
// 1、保存address
this.address = address;
// 2、保存route黑名单
this.routeDatabase = routeDatabase;
// 3、将proxy存储到内部列表中
resetNextProxy(address.url(), address.proxy());
}
// RouteSelector.java-准备proxy server相关的proxy
private void resetNextProxy(HttpUrl url, java.net.Proxy proxy) {
if (proxy != null) {
// 1、Porxy不为null,建立proxy列表
proxies = Collections.singletonList(proxy);
}
nextProxyIndex = 0;
}next()
6、next(): 获取有效的Route
// RouteSelector.java-获取Route,如果该Route失败过,去找下个Route
public Route next() throws IOException {
if (!hasNextInetSocketAddress()) {
// 1、有下一个Proxy: nextProxyIndex = 0 < proxies.size() = 1
if (!hasNextProxy()) {
return nextPostponed();
}
// 2、获取到Proxy列表中nextProxyIndex下标的proxy
lastProxy = nextProxy();
}
// 3、获取到socket address列表中nextInetSocketAddressIndex下标的socket地址
lastInetSocketAddress = nextInetSocketAddress();
// 4、RouteSlector初始化传入的address;最新的proxy,type=Direct;最新的socket address-47.104.74.165
Route route = new Route(address, lastProxy, lastInetSocketAddress);
// 5、判断该route最近是否失败过。true-失败过;
if (routeDatabase.shouldPostpone(route)) {
postponedRoutes.add(route);
// 6、如果该Route失败过,会去递归调用next,直到找到不失败的Route
return next();
}
// 7、返回Route
return route;
}
// RouteSelector.java-返回下一个proxy
private Proxy nextProxy() throws IOException {
// 1、返回proxy列表中index指向的元素。Result = “DIRECT”
Proxy result = proxies.get(nextProxyIndex++);
// 2、重置下一个Internet Socket Address(将dns下所有的address添加到了RouteSelector内部的adress列表中)
resetNextInetSocketAddress(result);
return result;
}
// RouteSelector.java-为当前的proxy或者主机准备socket address。
// 通过dns去查找host下所有address和port,并且存入inet socket address列表中
private void resetNextInetSocketAddress(java.net.Proxy proxy) throws IOException {
// 1、清除socket address。
inetSocketAddresses = new ArrayList<>();
String socketHost;
int socketPort;
// 2、proxy的type为Direct(直连),或者为Socks。都是直接将address的主机和端口号,作为socket的主机和端口号。
if (proxy.type() == Type.DIRECT || proxy.type() == Type.SOCKS) {
// 直接将address的主机,作为socket的主机
socketHost = address.url().host();
// 直接将address的port,作为socket的port
socketPort = address.url().port();
}
// 3、非Direct,非socks,表示采用http、ftp等高层协议的代理
else {
// 4、采用proxy的address
SocketAddress proxyAddress = proxy.address();
InetSocketAddress proxySocketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) proxyAddress;
// 5、获取到代理的socket address中的host和port
socketHost = getHostString(proxySocketAddress);
socketPort = proxySocketAddress.getPort();
}
// 6、1 <= 端口号 <= 65535 才是合法端口
if (socketPort < 1 || socketPort > 65535) {
throw new SocketException("No route to " + socketHost + ":" + socketPort + "; port is out of range");
}
// 7、proxy type = spcks时,向internet socket address列表中添加unresolved的host和port
if (proxy.type() == java.net.Proxy.Type.SOCKS) {
inetSocketAddresses.add(InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(socketHost, socketPort));
} else {
// 8、address的dns去查找addresses。会返回socketHost的所有ip地址,OkHttp会依次尝试,如果一个地址的连接失败,会去尝试连接下一个地址。
List<InetAddress> addresses = address.dns().lookup(socketHost);
for (int i = 0, size = addresses.size(); i < size; i++) {
/**==================================================================
* 将InetAddress都添加到RouteSelector内部的inetSocketAddress列表中
* 1. InetAddress位于java.net包中。
* 2. inetAddress = www.wanandroid.com/47.104.74.169; socketport = 80.
*===================================================================*/
InetAddress inetAddress = addresses.get(i);
inetSocketAddresses.add(new InetSocketAddress(inetAddress, socketPort));
}
}
nextInetSocketAddressIndex = 0;
}
// ReouteSelector.java- 返回SocketAddresses列表中下标为nextInetSocketAddressIndex的socket地址。
private InetSocketAddress nextInetSocketAddress() throws IOException {
return inetSocketAddresses.get(nextInetSocketAddressIndex++);
}总结题
1、如何使用OkHttp进行异步网络请求,并根据请求结果刷新UI
- 通过构造器创建RequestBody
- 创建Request
- 创建OkHttpClient
- 创建Call
- 发起Call的enqueue异步网络请求
- 在response的回调中根据数据改变UI(OKHTTP3.0中不需要切换线程)
2、可否介绍一下OkHttp的整个异步请求流程
3、OkHttp发起异步请求时,调用的call.enqueue方法做了哪些事情?
- 在Call创建的时候,在内部创建了RealCall,并且将OkHttpClient和request保存到了内部。
- 执行Call.enqueue(),内部是执行的RealCall.enqueue()
- RealCall.enqueue()内部直接转交给Dispatcher执行enqueue()方法
- Dsipatcher内部做了会去判断是否达到了最大并发任务数64,以及同一个主机的请求数是否达到了5。
- 都没有达到:加入到正在执行的异步请求队列。然后调用线程池去执行这个任务。
- 达到:加入到待执行的异步请求队列
4、异步请求队列中的元素AsyncCall是什么?
5、OkHttp对于网络请求都有哪些优化,如何实现的
6、OkHttp框架中都用到了哪些设计模式
7、OkHttp的缓存策略是什么?
8、OkHttp底层是如何实现缓存的?
- HttpClient的sendRequest完成了实际的请求工作。
- 采用DiskLruCache进行缓存
- key = 请求url中的md5 value = Snapshot(存储了所有响应的信息—包括url、响应头、请求的方法、protocol等)
- 在
HttpClient.readResponse()会对数据进行缓存。
9、OkHttp中涉及到的Http返回码
- 504: 网关超时
- 204/205: 在获取到返回Response后,如果code=204/205, 但是Body的Content长度>0,会抛出异常:ProtocolException
- 304:数据没有更改过。比如请求图片,如果图片在上次访问后没有更新过,就不用重新下载,直接返回304,告诉客户端可以直接使用缓存。
10、Http表单是什么
- 本质上是一种HTTP的
Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 数据本质上是通过HTTP body传输。- OkHttp的post通过FormBody.builder去构造RequestBody能进行表单的传输。
11、Http的patch操作是什么?
PATCH方法是新引入的,是对PUT方法的补充,用来对已知资源进行局部更新
12、Http中的Cache-Control是什么?
- 指定了请求和响应遵循的缓存机制。
- 可以减少对网络带宽的占用,可以提高访问速度,提高用户的体验,还可以减轻服务器的负担。
13、代理服务器中的HTTP代理与SOCKS代理有什么区别?
- Http代理:在浏览网页,下载数据等场景下就是http代理。它通常绑定在代理服务器的80、3128、8080等端口上。
- 采用socks协议的代理服务器就是SOCKS服务器,是一种通用的代理服务器。
- Socks不要求应用程序遵循特定的操作系统平台,Socks 代理与应用层代理、 HTTP 层代理不同,Socks 代理只是简单地传递数据包,而不必关心是何种应用协议(比如FTP、HTTP和NNTP请求)。所以,Socks代理比其他应用层代理要快得多。它通常绑定在代理服务器的1080端口上。
14、Http的ETag是什么?
- ETag(Entity Tag), 实体标签
- ETag是Http 1.1中加入的属性,用于帮助服务器控制缓存验证。
- 当客户端请求服务端的资源A时,会通过A计算出Hash值,如
3f80f-1b6-3e1cb03b,就是ETag- 客户端会将
ETag和资源A都保存在本地。- 下次请求资源A时,会通过类似
If-None-Match: "3f80f-1b6-3e1cb03b的请求头,将ETag发给服务器。- 服务端会进行比较,如果一致,返回304表示数据未修改。客户端直接用本地缓存的资源A。
- 如果不一致,表明数据修改过,会将资源A返回给客户端(返回码为200)
15、返回码200的作用?
表示客户端请求成功。
16、Http Age的作用
- 当Reponse是从缓存里获取时,HTTP/1.1协议规定要添加
Ageheader字段。- Age的值是响应报文在源服务器中产生或者过期验证的那一刻起,到现在为止所经过时间的一个估计值。
- 经常和max-age一起来验证缓存是否过期,即如果
Age的值比max-age的值还大,表明缓存已经过期。