G Trace
- 33.08%
- 1000ms
- 262144K
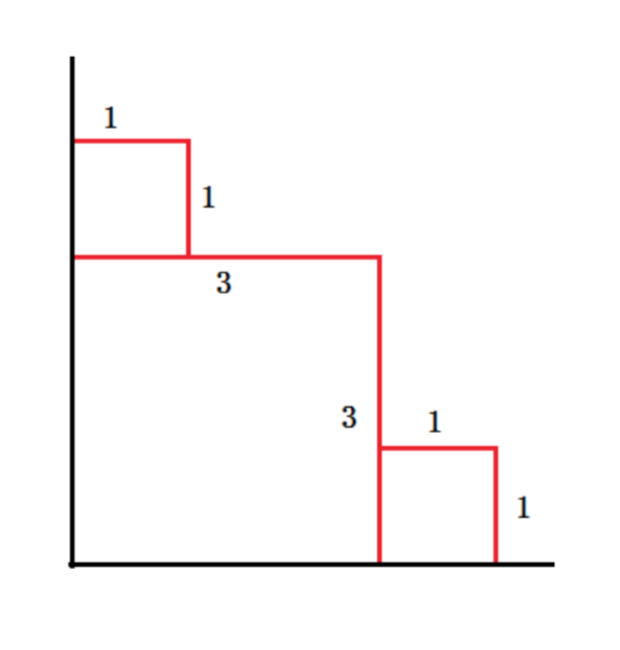
There's a beach in the first quadrant. And from time to time, there are sea waves. A wave ( xxx , yyy ) means the wave is a rectangle whose vertexes are ( 000 , 000 ), ( xxx , 000 ), ( 000 , yyy ), ( xxx , yyy ). Every time the wave will wash out the trace of former wave in its range and remain its own trace of ( xxx , 000 ) -> ( xxx , yyy ) and ( 000 , yyy ) -> ( xxx , yyy ). Now the toad on the coast wants to know the total length of trace on the coast after n waves. It's guaranteed that a wave will not cover the other completely.
Input
The first line is the number of waves n(n≤50000)n(n \le 50000)n(n≤50000).
The next nnn lines,each contains two numbers xxx yyy ,( 0<x0 < x0<x , y≤10000000y \le 10000000y≤10000000 ),the iii-th line means the iii-th second there comes a wave of ( xxx , yyy ), it's guaranteed that when 1≤i1 \le i1≤i , j≤nj \le nj≤n ,xi≤xjx_i \le x_jxi≤xj and yi≤yjy_i \le y_jyi≤yj don't set up at the same time.
Output
An Integer stands for the answer.
Hint:
As for the sample input, the answer is 3+3+1+1+1+1=103+3+1+1+1+1=103+3+1+1+1+1=10
样例输入
3 1 4 4 1 3 3
样例输出
10
题目来源
题意很好理解就是有矩形的海浪,冲过来有先后顺序,后过来的海浪会将之前的海浪给覆盖掉,求最后的剩余的海浪的长度,
这一道题目我当时的思路是太麻烦了导致最后也没有a掉,但是后来问了一下别人的思路真是神的一匹,我当时排了一个顺序
然后出现了两个数值都与我们要求的数值有关就是二分里面再写一个log(n)的时间复杂度,显然这样是没有什么比较好的解决方案,我看了一下别人的解决思路就感觉但是自己的那个排序就是败笔,,,
我们先看y
正解是这样的我们可以按照海浪来的顺序从后往前看,到了i个海浪时,后面的海浪如果冲刷掉这个海浪,这个海浪的y掉后面海浪中y最大的那个就可以了,就是当前剩下的,我们可以用set来维护一下顺序,用二分来查找比当前海浪(y)小的最大的哪一个y就是可以了
x的话类似
对于这一道题目,我感觉如果是出现了需要二分后在优化时间的可能是自己的排序出现了问题,前面的思维也可以就是有点麻烦,队友使用二分加上RMQ过掉的;
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll ;
#define rep(i,s,n) for(int i=s;i<=n;i++)
#define per(i,n,s) for(int i=n;i>=s;i--)
const int Max = 2e5+10;
ll x[Max],y[Max];
int n;
ll d(ll a[]){
set <ll> q;
set <ll> :: iterator it;
ll sum=0;
per(i,n,1){
it=q.lower_bound(a[i]);
if(it==q.begin()) sum+=a[i];
else {
it--;
sum+=a[i]-*it;
}
q.insert(a[i]);
}
return sum;
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
rep(i,1,n) scanf("%lld %lld",&x[i],&y[i]);
ll ans=d(x)+d(y);
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}