1146 Topological Order(25 分)
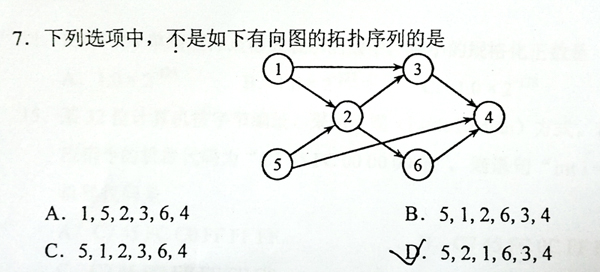
This is a problem given in the Graduate Entrance Exam in 2018: Which of the following is NOT a topological order obtained from the given directed graph? Now you are supposed to write a program to test each of the options.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 1,000), the number of vertices in the graph, and M (≤ 10,000), the number of directed edges. Then M lines follow, each gives the start and the end vertices of an edge. The vertices are numbered from 1 to N. After the graph, there is another positive integer K (≤ 100). Then K lines of query follow, each gives a permutation of all the vertices. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
Print in a line all the indices of queries which correspond to "NOT a topological order". The indices start from zero. All the numbers are separated by a space, and there must no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line. It is graranteed that there is at least one answer.
Sample Input:
6 8
1 2
1 3
5 2
5 4
2 3
2 6
3 4
6 4
5
1 5 2 3 6 4
5 1 2 6 3 4
5 1 2 3 6 4
5 2 1 6 3 4
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output:
3 4
题意:给定一个图,然后给出n个序列,让你判断给定的这些序列是否为该图的一个拓扑排序,如果不是则输出其序号。
思路1:(最后一个Case超内存)但写法是标准的递归版拓扑排序。定义一个indegree[]存储每个节点的入度,然后根据结点入度使用拓扑排序函数求所有的拓扑序列,由于要把所有的拓扑序列,求出来并保存然后在与给定的序列逐个比较,所以需要在求出每个拓扑序列后,恢复indegree[]和vis[]数组,然后接着求下一个数组。求完后与给定的每个序列逐个比较对应输出即可。
参考代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
int n,m,k;
int indegree[maxn],temp_in[maxn];
bool vis[maxn]={false};
vector<int> adj[maxn];
vector<vector<int>> ans;
void TopSort(int u,int d,bool vis[],int indegree[],vector<int> temp){
temp.push_back(u);
vis[u]=true;
if(d==n){
ans.push_back(temp);
}
for(int i=0;i<adj[u].size();i++){
int v=adj[u][i];
indegree[v]--;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(indegree[i]==0&&!vis[i])
TopSort(i,d+1,vis,indegree,temp);
}
for(int i=0;i<adj[u].size();i++){
int v=adj[u][i];
indegree[v]++;
}
temp.pop_back();
vis[u]=false;
}
int main()
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
adj[u].push_back(v);
indegree[v]++;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(indegree[i]==0){
vector<int> temp;
TopSort(i,1,vis,indegree,temp);
}
}
scanf("%d",&k);
bool flag=false;//flag=false表示为第一次输出
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
vector<int> temp;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
scanf("%d",&u);
temp.push_back(u);
}
int l=0;
while(l<ans.size()&&ans[l]!=temp)
l++;
if(l==ans.size()&&!flag){
printf("%d",i);
flag=true;
}else if(l==ans.size())
printf(" %d",i);
}
return 0;
}
思路2:不求拓扑序列,直接按拓序列性质,对所给序列按从前往后顺序依次判断该点的入度是否为零,若为零则将图中对应的后继定点indegree[]减一,继续求下一顶点,直到所有顶点均符合要求或存在某个当前点的入度不为零,输出。
参考代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1010;
int n,m,k,u,v,flag=0,indegree[maxn],in[maxn];
vector<int> adj[maxn];
bool isTopSeq(vector<int> t,int in[]){
for(int i=0;i<t.size();i++){
int u=t[i];
if(in[u])
return false;
for(int j=0;j<adj[u].size();j++) in[adj[u][j]]--;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
adj[u].push_back(v);
indegree[v]++;
}
scanf("%d",&k);
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
vector<int> temp(n);
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
scanf("%d",&temp[j]);
}
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) in[j]=indegree[j];
if(!isTopSeq(temp,in)){
printf("%s%d",flag?" ":"",i);
flag=true;
}
}
return 0;
}