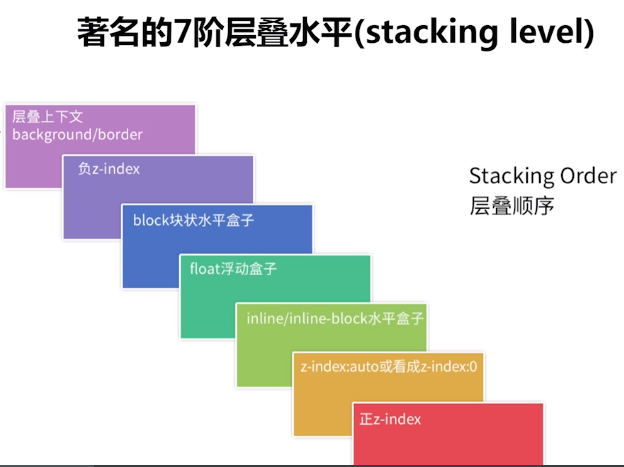
层叠水平顺序(W3C):
- 形成堆叠上下文环境的元素的背景与边框.
- 拥有负 z-index 的子堆叠上下文元素 (z-index的值越小层级越低).
- 正常流式布局,非 inline-block,无 position 定位(除了static)的子元素.
- 无 position 定位(static除外)的 float 浮动元素.
- 正常流式布局, inline-block元素,无 position 定位(除了static)的子元素
- (包括 inline-table 和 inline-block).
- 拥有 z-index:0 的子堆叠上下文元素.
- 拥有正 z-index: 的子堆叠上下文元素(z-index的值越小层级越低).
Within each stacking context, the following layers are painted in
back-to-front order:
1、the background and borders of the element forming the stacking context.
2、the child stacking contexts with negative stack levels (most negative first).
3、the in-flow, non-inline-level, non-positioned descendants.
4、the non-positioned floats.
5、the in-flow, inline-level, non-positioned descendants, including inline tables and inline blocks.
6、the child stacking contexts with stack level 0 and the positioned descendants with stack level 0.
7、the child stacking contexts with positive stack levels (least positive first).
对于拥有相同父元素的子元素,默认情况下inline-block的子元素会堆叠在float浮动子元素上方(无论DOM顺序如何)。
文档中的层叠上下文由满足以下任意一个条件的元素形成:
- 根元素 (HTML),
- z-index 值不为 "auto"的 绝对/相对定位,
- 一个 z-index 值不为 "auto"的 flex 项目 (flex item),即:父元素 display:
flex|inline-flex, - opacity 属性值小于 1 的元素,
- transform 属性值不为 "none"的元素,
- mix-blend-mode 属性值不为 "normal"的元素,
- filter值不为“none”的元素,
- perspective值不为“none”的元素,
- isolation 属性被设置为 "isolate"的元素,
- position: fixed
- 在 will-change 中指定了任意 CSS 属性,即便你没有直接指定这些属性的值
- -webkit-overflow-scrolling 属性被设置 "touch"的元素(in Safari Mobile)
总结:
- 给一个 HTML 元素定位和 z-index 赋值创建一个层叠上下文,(opacity 值不为 1 的也是相同)。
- 层叠上下文可以包含在其他层叠上下文中,并且一起创建一个有层级的层叠上下文。
- 每个层叠上下文完全独立于它的兄弟元素:当处理层叠时只考虑子元素。
- 每个层叠上下文是自包含的:当元素的内容发生层叠后,整个该元素将会 在父层叠上下文中 按顺序进行层叠。