A successful Git branching model
In this post I present the development model that I’ve introduced for some of my projects (both at work and private) about a year ago, and which has turned out to be very successful. I’ve been meaning to write about it for a while now, but I’ve never really found the time to do so thoroughly, until now. I won’t talk about any of the projects’ details, merely about the branching strategy and release management.

Why git?
For a thorough discussion on the pros and cons of Git compared to centralized source code control systems, see the web. There are plenty of flame wars going on there.
As a developer, I prefer Git above all other tools around today. Git really changed the way developers think of merging and branching. From the classic CVS/Subversion world I came from, merging/branching has always been considered a bit scary (“beware of merge conflicts, they bite you!”) and something you only do every once in a while.
But with Git, these actions are extremely cheap and simple, and they are considered one of the core parts of your daily workflow, really. For example, in CVS/Subversion books, branching and merging is first discussed in the later chapters (for advanced users), while in every Git book, it’s already covered in chapter 3 (basics).
As a consequence of its simplicity and repetitive nature, branching and merging are no longer something to be afraid of.
Version control tools are supposed to assist in branching/merging more than anything else.
Enough about the tools, let’s head onto the development model. The model that I’m going to present here is essentially no more than a set of procedures that every team member has to follow in order to come to a managed software development process.
Decentralized but centralized
The repository setup that we use and that works well with this branching model, is that with a central “truth” repo. Note that this repo is only considered to be the central one (since Git is a DVCS, there is no such thing as a central repo at a technical level). We will refer to this repo as origin, since this name is familiar to all Git users.
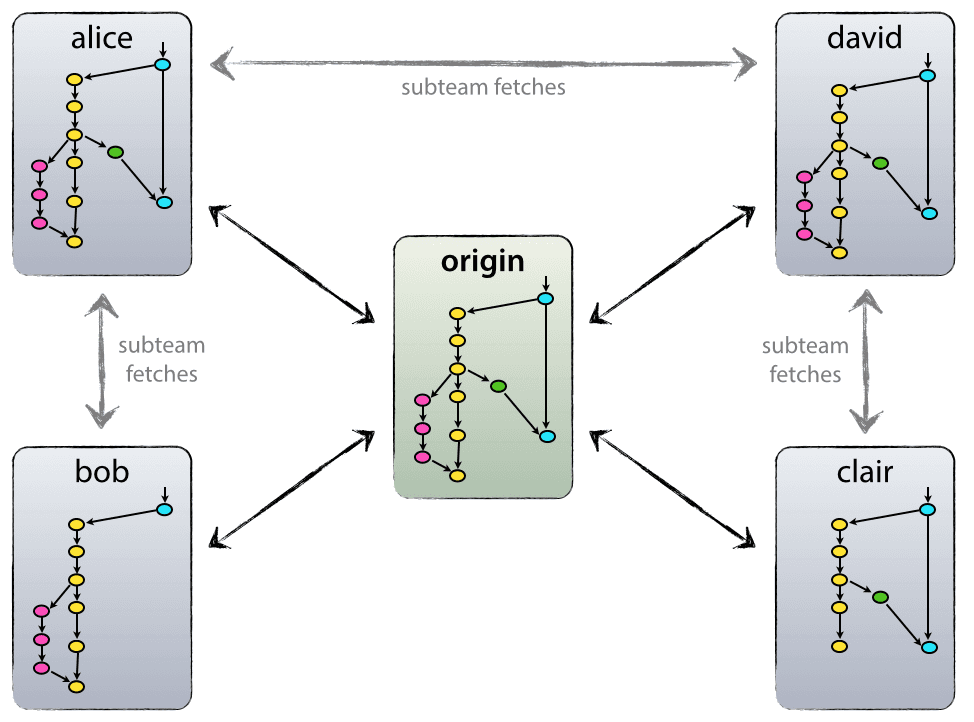
Each developer pulls and pushes to origin.
But besides the centralized push-pull relationships, each developer may also pull changes from other peers to form sub teams.
For example, this might be useful to work together with two or more developers on a big new feature, before pushing the work in progress to origin prematurely. In the figure above, there are subteams of Alice and Bob, Alice and David, and Clair and David.
Technically, this means nothing more than that Alice has defined a Git remote, named bob, pointing to Bob’s repository, and vice versa.
The main branches
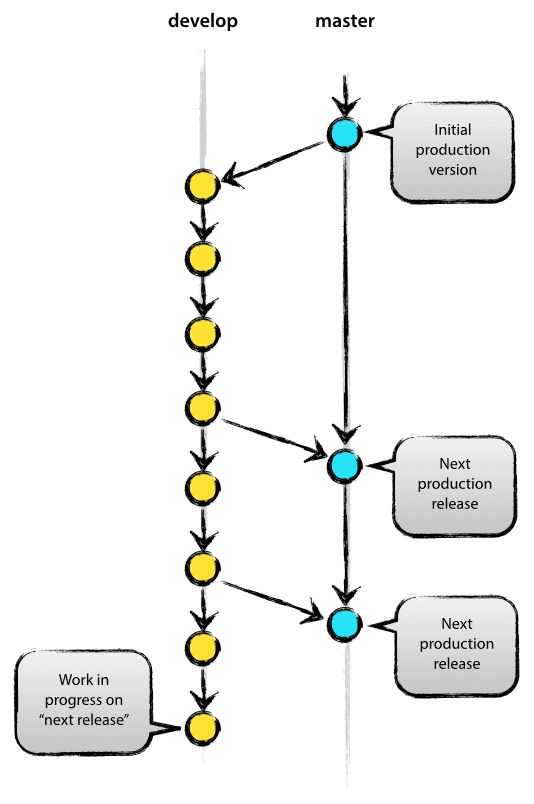
At the core, the development model is greatly inspired by existing models out there. The central repo holds two main branches with an infinite lifetime:
masterdevelop
The master branch at origin should be familiar to every Git user. Parallel to the master branch, another branch exists called develop.
We consider origin/master to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects a production-ready state.
We consider origin/develop to be the main branch where the source code of HEAD always reflects a state with the latest delivered development changes for the next release. Some would call this the “integration branch”. This is where any automatic nightly builds are built from.
When the source code in the develop branch reaches a stable point and is ready to be released, all of the changes should be merged back into master somehow and then tagged with a release number. How this is done in detail will be discussed further on.
Therefore, each time when changes are merged back into master, this is a new production release by definition. We tend to be very strict at this, so that theoretically, we could use a Git hook script to automatically build and roll-out our software to our production servers everytime there was a commit on master.
Supporting branches
Next to the main branches master and develop, our development model uses a variety of supporting branches to aid parallel development between team members, ease tracking of features, prepare for production releases and to assist in quickly fixing live production problems.
Unlike the main branches, these branches always have a limited life time, since they will be removed eventually.
The different types of branches we may use are:
- Feature branches
- Release branches
- Hotfix branches
Each of these branches have a specific purpose and are bound to strict rules as to which branches may be their originating branch and which branches must be their merge targets. We will walk through them in a minute.
By no means are these branches “special” from a technical perspective. The branch types are categorized by how we use them. They are of course plain old Git branches.
Feature branches
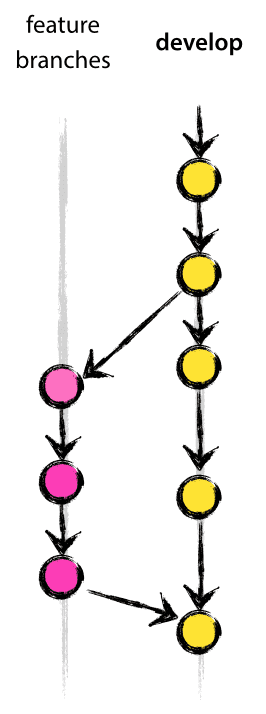
- May branch off from:
-
develop - Must merge back into:
-
develop - Branch naming convention:
-
anything
except
master,develop,release-*, orhotfix-*
Feature branches (or sometimes called topic branches) are used to develop new features for the upcoming or a distant future release. When starting development of a feature, the target release in which this feature will be incorporated may well be unknown at that point. The essence of a feature branch is that it exists as long as the feature is in development, but will eventually be merged back into develop (to definitely add the new feature to the upcoming release) or discarded (in case of a disappointing experiment).
Feature branches typically exist in developer repos only, not in origin.