半平面交 - (S & I algorithm)
参考论文 算法合集之《半平面交的新算法及其实用价值》
问题简介:
给出多个如 \(ax + by + c \ge 0\) 的限制( 接下来都以 \(ax+by+c \ge 0\) 为例) , 求解 \((x,y)\) 的集合
可以转化为多个直线在平面上围成的凸包
step1
将所有直线按角度排序,角度相同的保留下需要的一个(如图)
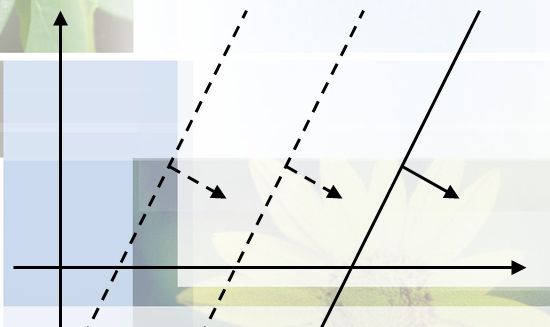
step2
用一个双端队列存储当前半平面交,每次通过判断队首与队尾第一个交点是否满足当前直线来更新
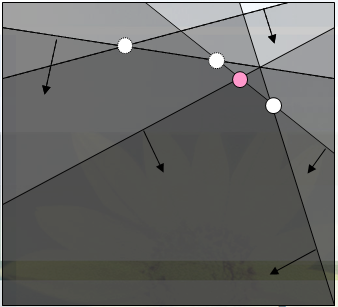
step3
先用队尾判定队首交点是否合法,再用队首判断队尾交点是否合法
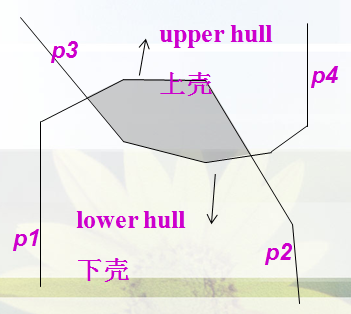
step4
现在队列中的相邻半平面的交点即为凸包的节点, 如果剩余半平面数量小于3则无解
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
4162653 查看本文章


Code(POJ1279)
\\ 满足Plane a的点为a.s->a.t的逆时针方向
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define sz q.size()
using namespace std;
inline char nc()
{
// return getchar();
static char buf[100000], * l = buf, * r = buf;
if(l == r) r = (l = buf) + fread(buf, 1, 100000, stdin);
if(l == r) return EOF;
return *l++;
}
template<class T> void readin(T & x)
{
x = 0; int f = 1, ch = nc();
while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=nc();}
while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10-'0'+ch;ch=nc();}
x *= f;
}
const double eps = 1e-9;
int sign(double a)
{
if(fabs(a) < eps) return 0;
return a < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
struct Point
{
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double x, double y) : x(x), y(y) {}
};
inline Point operator + (const Point & a, const Point & b)
{
return Point(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
inline Point operator - (const Point & a, const Point & b)
{
return Point(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);
}
inline Point operator * (const Point & a, const double & b)
{
return Point(a.x * b, a.y * b);
}
inline Point operator / (const Point & a, const double & b)
{
return Point(a.x / b, a.y / b);
}
inline double cross(Point a, Point b)
{
return a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x;
}
inline double angle(Point a)
{
return atan2(a.y, a.x);
}
inline Point intersection(Point p0, Point p1, Point q0, Point q1)
{
return p0 + (p1 - p0) * cross(q1 - q0, p0 - q0) / cross(p1 - p0, q1 - q0);
}
inline double area(Point * p, int n)
{
double res = 0;
p[n + 1] = p[1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
res += cross(p[i], p[i + 1]);
}
return fabs(res / 2.0);
}
struct Plane
{
Point s, t;
double ang;
Plane() {}
Plane(Point s, Point t) : s(s), t(t)
{
ang = angle(t - s);
}
};
int m;
Point s[1505];
int comp(const Plane & a, const Plane & b)
{
double r = a.ang - b.ang;
if(sign(r) != 0) return sign(r) == -1;
return sign(cross(a.t - a.s, b.t - a.s)) == -1;
}
int judge(Plane p, Plane a, Plane b)
{
Point q = intersection(a.s, a.t, b.s, b.t);
return sign(cross(p.t - p.s, q - p.s)) == -1;
}
bool SI(Plane * l, int n)
{
sort(l + 1, l + n + 1, comp);
int t = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if(i == 1 || sign(l[i].ang - l[i - 1].ang) != 0)
{
l[++t] = l[i];
}
}
n = t;
if(n < 3) return false;
deque<Plane> q;
q.push_front(l[1]);
q.push_front(l[2]);
for(int i = 3; i <= n; i++)
{
while(sz > 1 && judge(l[i], q[0], q[1])) q.pop_front();
while(sz > 1 && judge(l[i], q[sz - 1], q[sz - 2])) q.pop_back();
q.push_front(l[i]);
}
while(sz > 1 && judge(q[sz - 1], q[0], q[1])) q.pop_front();
while(sz > 1 && judge(q[0], q[sz - 1], q[sz - 2])) q.pop_back();
if(q.size() < 3) return false;
m = q.size();
q.push_back(q[0]);
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
s[i] = intersection(q[i - 1].s, q[i - 1].t, q[i].s, q[i].t);
}
return true;
}
int T, n;
Plane l[1505];
Point p[1505];
double solve()
{
p[n + 1] = p[1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
l[i] = Plane(p[i + 1], p[i]);
}
if(!SI(l, n)) return 0;
return area(s, m);
}
int main()
{
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
cout << fixed;
readin(T);
for(int kase = 1; kase <= T; kase++)
{
readin(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
readin(p[i].x);
readin(p[i].y);
}
cout << setprecision(2) << solve() << endl;
}
return 0;
}