描述
In an extended version of the game Lights Out?, is a puzzle with 5 rows of 6 buttons each (the actual puzzle has 5 rows of 5 buttons each). Each button has a light. When a button is pressed, that button and each of its (up to four) neighbors above, below, right and left, has the state of its light reversed. (If on, the light is turned off; if off, the light is turned on.) Buttons in the corners change the state of 3 buttons; buttons on an edge change the state of 4 buttons and other buttons change the state of 5. For example, if the buttons marked X on the left below were to be pressed, the display would change to the image on the right.

The aim of the game is, starting from any initial set of lights on in the display, to press buttons to get the display to a state where all lights are off. When adjacent buttons are pressed, the action of one button can undo the effect of another. For instance, in the display below, pressing buttons marked X in the left display results in the right display. Note that the buttons in row 2 column 3 and row 2 column 5 both change the state of the button in row 2 column 4, so that, in the end, its state is unchanged.

Note:
- It does not matter what order the buttons are pressed.
- If a button is pressed a second time, it exactly cancels the effect of the first press, so no button ever need be pressed more than once.
- As illustrated in the second diagram, all the lights in the first row may be turned off, by pressing the corresponding buttons in the second row. By repeating this process in each row, all the lights in the first four rows may be turned out. Similarly, by pressing buttons in columns 2, 3 ..., all lights in the first 5 columns may be turned off.
Write a program to solve the puzzle.
输入
The first line of the input is a positive integer n which is the number of puzzles that follow. Each puzzle will be five lines, each of which has six 0's or 1's separated by one or more spaces. A 0 indicates that the light is off, while a 1 indicates that the light is on initially.
输出
For each puzzle, the output consists of a line with the string: "PUZZLE #m", where m is the index of the puzzle in the input. Following that line, is a puzzle-like display (in the same format as the input) . In this case, 1's indicate buttons that must be pressed to solve the puzzle, while 0's indicate buttons, which are not pressed. There should be exactly one space between each 0 or 1 in the output puzzle-like display.
样例输入
2
0 1 1 0 1 0
1 0 0 1 1 1
0 0 1 0 0 1
1 0 0 1 0 1
0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 1 0
1 0 1 0 1 1
0 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 1 0 0
样例输出
PUZZLE #1
1 0 1 0 0 1
1 1 0 1 0 1
0 0 1 0 1 1
1 0 0 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0
PUZZLE #2
1 0 0 1 1 1
1 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 0 1
1 0 1 1 0 1
摘抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/titicia/p/5396997.html
题意:给出一个5*6的图,每个灯泡有一个初始状态,1表示亮,0表示灭。每对一个灯泡操作时,会影响周围的灯泡改变亮灭,问如何操作可以使得所有灯泡都关掉。
思路:因为每盏灯,如果操作两次就相当于没有操作,所以相当于(操作次数)%2,即异或操作。
考虑一个2*3的图,最后需要的状态是 : ,如果初始状态为:
,如果初始状态为: 。对这两个矩阵的每个数字做异或操作可以得到线性方程组每个方程的答案。
。对这两个矩阵的每个数字做异或操作可以得到线性方程组每个方程的答案。
总共6盏灯,0-5。那么可以列出6个方程。
对于第0盏灯,会影响到它的是第0, 1, 3盏灯,因此可以列出方程1*x0 + 1*x1 + 0*x2 + 1*x3 + 0*x4 + 0*x5= 0。
对于第1盏灯,会影响到它的是第0, 1, 2,4盏灯,因此可以列出方程1*x0 + 1*x1 + 1*x2 + 0*x3 + 1*x4 + 0*x5 = 1。
对于第2盏灯,会影响到它的是第1, 2, 5盏灯,因此可以列出方程0*x0 + 1*x1 + 1*x2 + 0*x3 + 0*x4 + 1*x5 = 0。
.....
所以最后可以列出增广矩阵: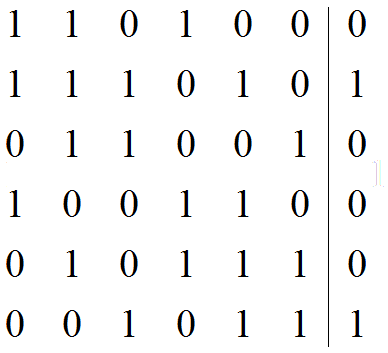
然后用高斯消元求这个矩阵的解就可以了。
PS:TOJ要行末有空格才行,没有的话反而会PE。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int MAXN=500;
int a[MAXN][MAXN];//增广矩阵
int x[MAXN];//解集
void init()
{//每盏灯影响了身边的灯
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
{
int pos=i*6+j;
a[pos][pos]=1;
if(i>0) a[pos][(i-1)*6+j]=1;
if(i<4) a[pos][(i+1)*6+j]=1;
if(j>0) a[pos][i*6+j-1]=1;
if(j<5) a[pos][i*6+j+1]=1;
}
}
}
void Gauss(int equ,int var)
{
int i,j,k,max_r;// 当前这列绝对值最大的行.
int col;//当前处理的列
col=0;
for(k=0;k<equ&&col<var;k++,col++)
{
max_r=k;
for(i=k+1;i<equ;i++)
{
if(abs(a[i][col])>abs(a[max_r][col]))
max_r=i;
}
if(max_r!=k)
{
for(j=k;j<var+1;j++)
swap(a[k][j],a[max_r][j]);
}
if(a[k][col]==0)
{
k--;
continue;
}
for(i=k+1;i<equ;i++)
{
if(a[i][col]!=0)
{
for(j=col;j<var+1;j++)
{
a[i][j]^=a[k][j];
}
}
}
}
for(i=var-1;i>=0;i--)
{
x[i]=a[i][var];
for(j=i+1;j<var;j++)
{
x[i]^=(a[i][j]&&x[j]);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,equ,var,mod,n,t,op=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
equ=30;var=30;
while(t--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
init();
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i*6+j][30]);
}
}
Gauss(equ,var);
printf("PUZZLE #%d\n",op++);
for(i=0;i<5;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<6;j++)
{
printf("%d ",x[i*6+j]);
/*if(j==0)
printf("%d",x[i*6+j]);
else
printf(" %d",x[i*6+j]);*/
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}