之前使用的第三方搭建的ftp客户伪源因机房搬迁问题,因此需要构建ftp源站,因为之前采用ftp主从模式,遇到故障需手动迁移,现在将增加一层keepalived进行通过vip访问,自动故障转移。(因为公网IP和客户域名不方便透露,这里采用内网的IP以及测试域名)
服务器信息:
#ip地址:
centos6.7 192.168.43.200 (主)=》BJ_CTL_43_200:主
centos6.7 192.168.43.201 (主)=》BJ_CTL_43_201:从
#磁盘信息:
12*8T容量
#内存信息:
126G
一:软raid5配置
raid分为硬raid和软raid,其功能相同,但是因为软raid没有独立的硬件控制,因此性能上不如硬raid,但是软raid配置实现简单
常用raid级别:raid0,raid1,raid5,raid10(raid10就是raid0和raid1)各级别对比如下

注:n表示磁盘总数,raid5可以坏一块磁盘
这里采用的raid5,以下是raid5的配置
1:安装工具
yum -y install mdadm parted
2:进行磁盘分区
parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel gpt mkpart primary 1 100%
parted -s /dev/sdc mklabel gpt mkpart primary 1 100%
parted -s /dev/sdd mklabel gpt mkpart primary 1 100%
3:创建raid5
mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l5 -n3 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1 /dev/sdd1
说明:
-C表示创建
-l指定raid级别
-n表示磁盘个数
/dev/md0表示设备名称
-x表示有几块热备盘
4:创建挂载点
mkdir /cache
5:格式化磁盘
mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
6:挂载磁盘
mount /dev/md0 /cache/
7:加入到fstab中
echo "/dev/md0 /cache ext4 defaults 0 0" >> /etc/fstab
8:准备配置文件
echo DEVICE /dev/sd{b..d}1 > /etc/mdadm.conf
mdadm --detail -s >> /etc/mdadm.conf
具体的raid操作详细见(https://www.cnblogs.com/spadeslinux/p/9063200.html)
二:FTP文件系统
ftp有两种工作模式:
- 主动模式:客户端随机开启一个端口去连接服务器的21号端口,服务器收到请求后,接受连接建立一条命令通道,当需要传输数据时,客户端会再次开启一个大于1024的随机端口通过之前建立的命令通道发送给服务器,然后服务器的20号端口去连接客户端的该端口,通过三次握手后建立连接传输数据。
- 被动模式:客户端随机开启一个端口去连接服务器的21号端口,服务器收到请求后,接受连接建立一条命令通道,当需要传输数据时,客户端从命令通过发送数据请求上传或下载,服务器收到请求后随机开启一个端口并通过命令通道发送给客户端,客户端收到该端口后也会开启一个端口并连接服务器的端口,通过三次握手后建立连接传输数据。
注意:ftp是基于tcp协议工作的,ftp的两个数据端口(主动模式20号,被动模式不确定),命令端口为21。
以下是ftp的安装配置,这里采用的是主动模式和本地用户
1:安装vsftpd yum -y install vsftpd 2:配置vsftpd(只列出修改部分) cat /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf #禁止匿名用户 anonymous_enable=NO #将用户禁锢在自己的家目录 chroot_local_user=YES #ftp日志 xferlog_file=/var/log/ftp.log 3:启动ftp并配置自启 /etc/init.d/vsftpd restart chkconfig vsftpd on 4:添加测试用户进行上传下载 useradd -s /sbin/nologin -d /cache/test test echo "123456"|passwd --stdin test 注意:后期这里是通过ansible来管理的,因此通过ansible的user模块来创建用户
#测试上传
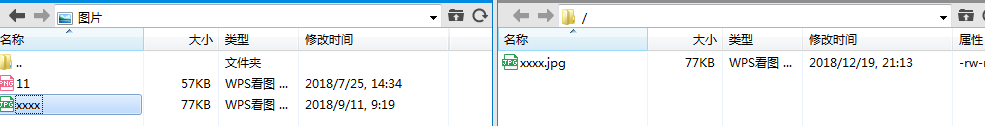
#测试下载
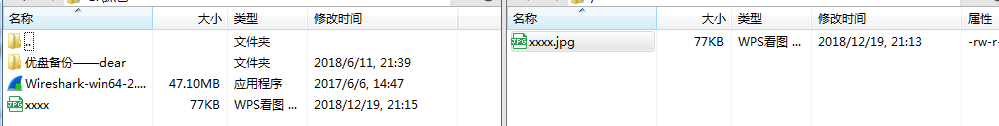
#查看日志

注意:i表示为上传(input),o表示为下载(output)
三:rsync同步
刚刚测试了上传下载没有问题,接下来需要通过rsync自动同步数据,安装单独的rsync不采用xinetd
刚才将数据传送给了43.200主节点,接下来配置rsync从下载数据 ====================主节点操作 1:安装rsync yum -y install rsync 2:配置rsync cat /etc/rsyncd.conf uid = root gid = root use chroot = no max connections = 180 strict modes = yes port = 873 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log transfer logging = yes log format = %t (%p) %o %h (a) %m (%u) %f %l [%n] %M [test] path=/cache/test comment=this is test data auth users=test uid=test gid=test incoming chmod = u+rwx,g+rwx,o+rx secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.secrets read only = no list=no 3:设置权限 chmod 777 -R /cache/ 4:准备密码文件 cat /etc/rsyncd.secrets test:123456 #权限必须是600 chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd.secrets 5:启动rsync rsync --daemon ============================从节点同步 yum -y install rsync ls -l /cache/test/ total 0 #客户端下载 rsync -avzP [email protected]::test /cache/test/ #客户端上传 rsync -avzP file [email protected]::test 解析将从配置为主,将主配置为从。
此时两个主从节点都已可以互相同步,接下来需要监控cache目录,只要目录下发生变化就自动同步。采用rsync+inotify
这里实时监控cache目录并进行同步
#rsync配置
cat /etc/rsyncd.conf
uid = root
gid = root
use chroot = no
max connections = 180
strict modes = yes
port = 873
pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid
lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock
log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log
transfer logging = yes
log format = %t (%p) %o %h (a) %m (%u) %f %l [%n] %M
[cache]
path=/cache
comment=this is cache data
auth users=cache
uid=cache
gid=cache
incoming chmod = u+rwx,g+rwx,o+rx
secrets file = /etc/rsyncd.secrets
read only = no
list=no
cat /etc/rsyncd.secrets
cache:cache!@#
useradd -s /sbin/nologin -d /cache cache
============================主节点配置
1:下载源码inotify包
wget http://github.com/downloads/rvoicilas/inotify-tools/inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
2:编译安装
tar -zxf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz
cd inotify-tools-3.14
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/inotify
make && make install
3:设置系统环境变量
grep "inotify" /etc/profile
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/inotify/bin
source /etc/profile
4:添加库文件
grep "inotify" /etc/ld.so.conf
/usr/local/inotify/lib
ldconfig
5:修改inotify默认参数
#查看默认值参数
sysctl -a | grep max_queued_events
fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 16384
sysctl -a | grep max_user_watches
fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 8192
fs.epoll.max_user_watches = 95682
sysctl -a | grep max_user_instances
fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 128
#修改参数
sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_queued_events="99999999"
sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_user_watches="99999999"
sysctl -w fs.inotify.max_user_instances="65535"
说明:
max_queued_events:inotify队列的长度,如果值太小会导致监控文件不准确
max_user_watches:要同步的文件包含多少目录,必须大于源文件目录
max_user_instances:每个用户创建inotify实例最大值
6:编写脚本实现监控已经同步
cat rsync_inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
#监控cache目录下的文件,发生改变则同步到备份
backup_dir=/cache
user=cache
backup_ip=192.168.43.201
mod_rsync=cache
#监控目录
/usr/local/inotify/bin/inotifywait -mrq --timefmt '%d/%m/%y %H:%M' --format '%T %w%f%e' -e close_write,modify,delete,create,attrib,move $backup_dir \
|while read file
do
#进行上传
rsync -az $backup_dir ${user}@${backup_ip}::${mod_rsync} --password-file=/etc/cache.ps
done
7:准备密码文件
cat /etc/cache.ps
cache!@#
chmod 600 /etc/cache.ps
8:执行脚本
nohup sh rsync_inotify.sh &
9:在cache下载创建一个文件