Android调试命令总结
am工具的含义为Activity Manager。
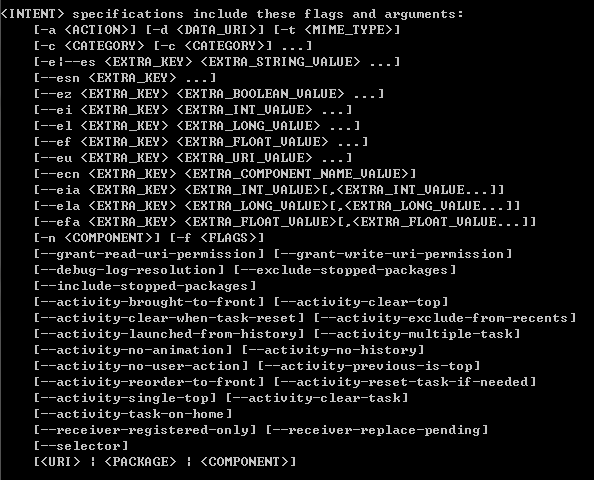
usage: am [subcommand] [options]
start an Activity: am start [-D] [-W]
-D: enable debugging
-W: wait for launch to complete
start a Service: am startservice
send a broadcast Intent: am broadcast
start an Instrumentation: am instrument [flags]
-r: print raw results (otherwise decode REPORT_KEY_STREAMRESULT)
-e : set argument to
-p : write profiling data to
-w: wait for instrumentation to finish before returning
start profiling: am profile start
stop profiling: am profile stop
start monitoring: am monitor [--gdb ]
--gdb: start gdbserv on the given port at crash/ANR
主要参数Intent:
显式启动Activity:
am start -n {包名}/{包名}.{活动名}
隐式启动Activity:
am start -a {指定的action} -d {URI}
隐式启动服务:
am startService -a {指定的action}
隐式发送广播:
am broadcast -a {指定的action}
启动Calculator应用:
am start -n com.Android.calculator2/com.android.calculator2.Calculator
Starting: Intent { cmp=com.android.calculator2/.Calculator }
am start -n com.android.calculator2/.Calculator
Starting: Intent { cmp=com.android.calculator2/.Calculator }
启动应用并带有URL参数:
am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d http://www.baidu.com
Starting: Intent { act=android.intent.action.VIEW dat=http://www.baidu.com }
am start -a android.intent.action.CALL -d tel:12345
Starting: Intent { act=android.intent.action.CALL dat=tel:xxx-xxx-xxxx }
几种VIEW类型(查看)的启动:
am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d file:///sdcard/image.jpg -t image/*
am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d file:///sdcard/audio.mp3 -t audio/*
am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d file:///sdcard/video.3gp -t video/*
几种GET_CONTENT类型(获取)的启动:
am start -a android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT -t image/*
am start -a android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT -t video/*
am start -a android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT -t audio/*
注意:
[–activity-brought-to-front]等的参数和 android.content.Intent类的FLAG_XXX内容相对应。
-f参数可以直接加代表10进制或者16进制的FLAG数字。
PM工具的含义为Package Manager。
usage: pm [list|path|install|uninstall]
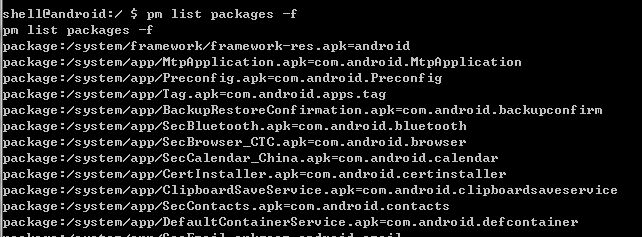
pm list packages [-f]
pm list permission-groups
pm list permissions [-g] [-f] [-d] [-u] [GROUP]
pm list instrumentation [-f] [TARGET-PACKAGE]
pm list features
pm path PACKAGE
pm install [-l] [-r] [-t] [-i INSTALLER_PACKAGE_NAME] [-s] [-f] PATH
pm uninstall [-k] PACKAGE
pm enable PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
pm disable PACKAGE_OR_COMPONENT
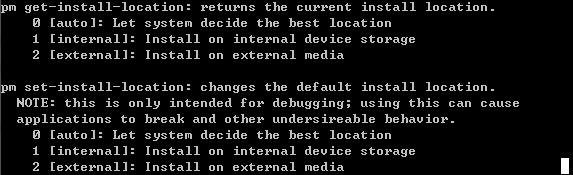
pm setInstallLocation [0/auto] [1/internal] [2/external]
列出安装包的信息。
pm list packages -f
另一个文件: /data/system/packages.xml
禁止包(或者组件),清除包的数据,可以排除个别包的影响。
pm disable {包名.组件名}
pm enable {包名.组件名}
pm clear {包名}
直接安装包
pm install /sdcard/SkeletonApp.apk
pkg: /sdcard/SkeletonApp.apk Success D/installd( 36): DexInv:
— BEGIN ‘/data/app/com.example.android.skeletonapp-1.apk’ — D/dalvikvm( 763): DexOpt: load 37ms, verify+opt 52ms D/installd(
36): DexInv: — END ‘/data/app/com.example.android.skeletonapp-1.apk’
(success) —
指定路径,进行安装
pm set-install-location
pm get-install-location
input工具用于模拟用户的按键输入和文本输入。
input
usage: input [text|keyevent]
input text
input keyevent
input tap
input swipe
模拟按键的输入,按键码参考 android.View.KeyEvent。
input keyevent 82 # 菜单事件(MENU)
input keyevent 4 # 回退事件 (BACK)
input text “i_love_beijing” # 输入文字
模拟按键输入可以用于简单的程序调试,在Activity中实现onKeyUp()方法即可。
Android 4.0+才可以使用tap和swipe子命令。
ime工具用于输入法管理。
ime
usage: ime list [-a] [-s]
ime enable ID
ime disable ID
ime set ID
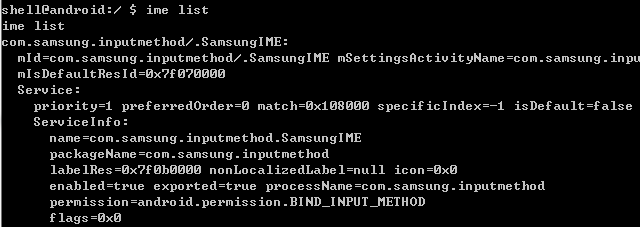
列出输入法:
ime list
选择输入法
ime set
脚本实际上是利用了Android的shell系统运行的,同样可以传入命令行的参数。 通过使用am调用Activity,通过input进行输入事件,可以模拟一个可执行程序的执行过程。 脚本中还可以传递shell中传入的参数。
编写一个自动化脚本:
echo $*
am start -a android.intent.action.VIEW -d about://blank
echo "Enter Browser"
input keyevent 82
echo "Browser Menu"
input keyevent 22
input keyevent 22
input keyevent 66
input keyevent 4
echo "Browser Main"
运行脚本:
chmod 777 test.sh
./test.sh
(我就不告诉你,很多同学通过这种方式去抓别人app的数据)
Android应用程序APK调试的几个要点:
- 核心方法是利用命令行的Intent。
- 单次调用可使用BroadcastReceiver组件
- 后台调用可使用Service组件
- BroadcastReceiver组件也可放入其他组件内部
- 调用的参数使用Intent传入;
启动:am startservice和am broadcast
首要参数使用-a,数据参数为-d
AndroidManifest.xml当中要定义IntentFilter
带数据的Intet和不带数据的Intent命令行不同
:// : //…/ # ?
Host是字符串,Port是整数,Path是多个字符串, Segments是字符串,QueryParameter是无顺序的多个参数。
android.net.Uri类可以完成参数的
public abstract String getScheme ()
public abstract String getHost()
public abstract int getPort()
public abstract String getFragment()
public abstract String getPath()
public abstract List getPathSegments()
public String getQueryParameter(String key)
public List getQueryParameters(String key)
方法:
am startservice -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub1 command://?key=10
am startservice -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub1 -d command://?key=5
am startservice -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub2 -d “command://?key1=hello&key2=120”
am broadcast -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub
am broadcast -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub command://abc:1234#hello
am broadcast -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub command:#/sdcard/test.txt
am broadcast -a android.intent.action.testtools.stub command://abc/hi1/hi2/hi3#hello
参数解析方法
String action = intent.getAction();
Uri data = intent.getData();
Log.i(TAG, "action = " + action + " data = " + data);
if(null != data){
String host = data.getHost();
int port = data.getPort();
String path = data.getPath();
String fragment = data.getFragment();
Log.i(TAG, "[Host]:[" + host + "] " + "[Port]:[" + port + "] " + "[Path]:[" + path + "] " + "[Fragment]:[" + fragment + "] ");
List pathlist = data.getPathSegments();
for(int i=0;i< pathlist.size();i++ ){
Log.i(TAG, "PATH["+i+"]:[" + pathlist.get(i) + "] ");
}
}
注意:不同的Android版本组件是否可以直接使用的问题。
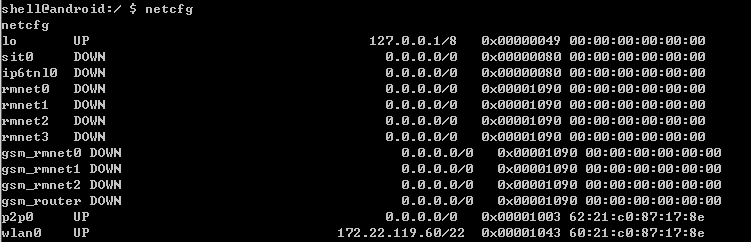
netcfg -h
usage: netcfg [ {dhcp|up|down}]
netcfg
vdc volume list
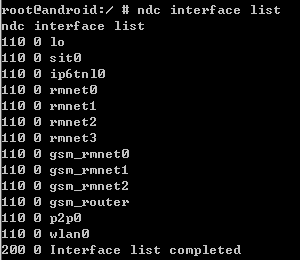
ndc interface list
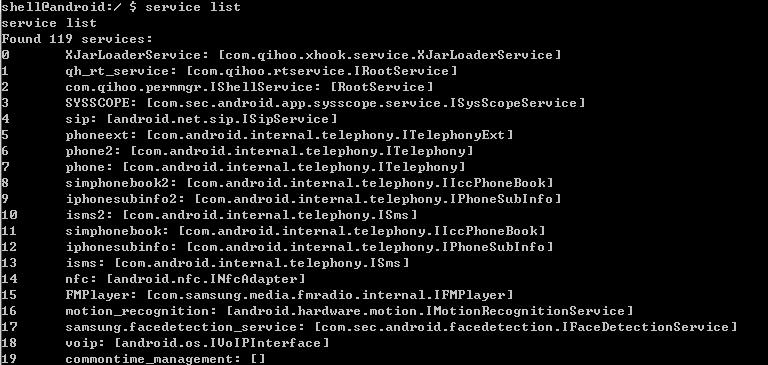
service -h
Usage: service [-h|-?]
service list
service check SERVICE
service call SERVICE CODE [i32 INT | s16 STR] … Options: i32: Write the integer INT into the send parcel. s16: Write the
UTF-16 string STR into the send parcel.
service list
iphonesubinfo等就是ServiceManager管理的服务名称。
直接利用Binder方式调用。
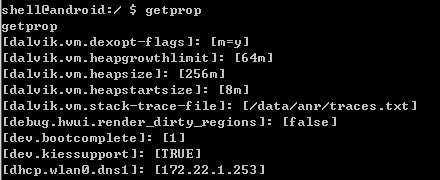
Android具有prop属性系统,使用getprop和setprop可以获得属性和设置属性。
getprop查看属性值
getprop ro.secure
setprop 设置属性值
usage: setprop
watchprops检测属性值变化
watchprops用于监测属性的变化,直接运行这个命令,将形成循环,将把系统每一个属性的变化列出。
watchprops
<时间> 属性 = ‘属性值’ ……
<时间> 属性 = ‘属性值’
start和stop命令,用于开始和停止init进程中的service。
start {service_name}
stop {service_name}
解决Android系统的daemon被kill之后重新启动的问题
Android中还提供了dumpstate、dumpsys、bugreport等几个工具,用于查看系统各个方面的信息。
- dumpstate
工具用于将系统设备的状态导出,通过访问sys文件系统和调用其他工具来完成。 - dumpsys
用于查看应用的状态。
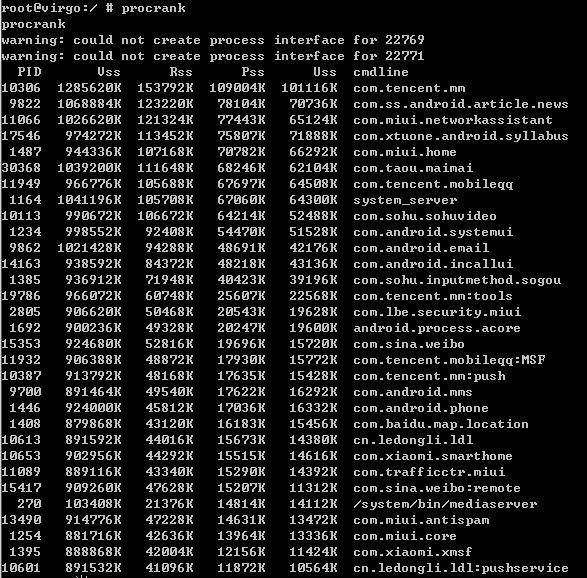
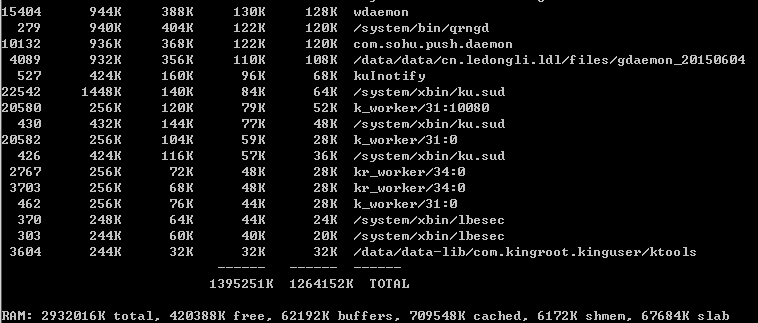
由于dumpstate和dumpsys两个工具导出的内容都较多,最好在主机端配合adb来使用。 - procrank抓取内存信息
procrank工具用于抓取Android进程的内存使用信息。
procrank
VSS = Virtual Set Size
RSS = Resident Set Size
PSS = Proportional Set Size
USS = Unique Set Size