一、什么是Service
Service(服务)--Android四大组件之一。
Service是Android中实现程序后台运行的解决方案,它非常适用于去执行那些不需要和用户交互而且还要求长期运行的任务。Service默认并不会运行在子线程中,它也不运行在一个独立的进程中,它同样执行在UI线程中,因此,不要在Service中执行耗时的操作,除非你在Service中创建了子线程来完成耗时操作。
Service的运行不依赖于任何用户界面,即使程序被切换到后台或者用户打开另一个应用程序,Service仍然能够保持正常运行,这也正是Service的使用场景。当某个应用程序进程被杀掉时,所有依赖于该进程的Service也会停止运行
二、 Service分类
1.分类
图片转自:https://blog.csdn.net/carson_ho/article/details/53160231
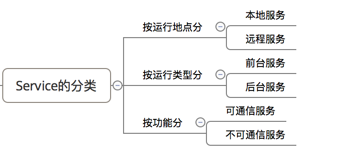
2.特点

3.本地Service
3.1两种启动方式
(1)startService()方法开启Service
- 定义一个类并继承Service。
- 在AndroidManifest.xml文件中配置该Service。
- 使用Context的startService(Intent)方法启动该Service。
- 不再使用该Service时,调用Context的stopService(Intent)方法停止该Service。
(2)bindService方法开启Service
- 定义一个类并继承Service。并在类中创建一个实现Binder接口的实现实例对象并提供公共方法给Activity调用。
- 从onBind()回调方法返回此Binder实例。
- Activity中继承ServiceConnection接口,从onServiceConnected回调方法接收Binder实例,使用此Binder实例来调用Service提供给Activity的公共方法。
- 调用bindService(intent)来绑定Service后,便会执行onServiceConnected回调方法。
- unbindService()来解除绑定Service.
3.2 Service的生命周期
- 启动服务-onCreate()-onStartCommand()-服务运行-onDestory()-服务被销毁
- 绑定服务-onCreate()-onBind()-服务运行-onUnBind()-onDestory()-服务被销毁
关于Service:
- 被启动的服务的生命周期:如果一个Service被某个Activity 调用 Context.startService 方法启动,那么不管是否有Activity使用bindService绑定或unbindService解除绑定到该Service,该Service都在后台运行。如果一个Service被startService 方法多次启动,那么onCreate方法只会调用一次,onStart将会被调用多次(对应调用startService的次数),并且系统只会创建Service的一个实例(因此你应该知道只需要一次stopService调用)。该Service将会一直在后台运行,而不管对应程序的Activity是否在运行,直到被调用stopService,或自身的stopSelf方法。当然如果系统资源不足,android系统也可能结束服务。
- 被绑定的服务的生命周期:如果一个Service被某个Activity 调用 Context.bindService 方法绑定启动,不管调用 bindService 调用几次,onCreate方法都只会调用一次,同时onStart方法始终不会被调用。当连接建立之后,Service将会一直运行,除非调用Context.unbindService 断开连接或者之前调用bindService 的 Context 不存在了(如Activity被finish的时候),系统将会自动停止Service,对应onDestroy将被调用。
- 被启动又被绑定的服务的生命周期:如果一个Service又被启动又被绑定,则该Service将会一直在后台运行。并且不管如何调用,onCreate始终只会调用一次,对应startService调用多少次,Service的onStart便会调用多少次。调用unbindService将不会停止Service,而必须调用 stopService 或 Service的 stopSelf 来停止服务。
- 当服务被停止时清除服务:当一个Service被终止(1、调用stopService;2、调用stopSelf;3、不再有绑定的连接(没有被启动))时,onDestroy方法将会被调用,在这里你应当做一些清除工作,如停止在Service中创建并运行的线程。
特别注意:
- 在调用 bindService 绑定到Service的时候,就应当保证在某处调用 unbindService 解除绑定(尽管 Activity 被 finish 的时候绑定会自动解除,并且Service会自动停止);
- 注意 使用 startService 启动服务之后,一定要使用 stopService停止服务,不管你是否使用bindService;
- 同时使用 startService 与 bindService 要注意到,Service 的终止,需要unbindService与stopService同时调用,才能终止 Service,不管 startService 与 bindService 的调用顺序,如果先调用 unbindService 此时服务不会自动终止,再调用 stopService 之后服务才会停止,如果先调用 stopService 此时服务也不会终止,而再调用 unbindService 或者 之前调用 bindService 的 Context 不存在了(如Activity 被 finish 的时候)之后服务才会自动停止;
- 当在旋转手机屏幕的时候,当手机屏幕在“横”“竖”变换时,此时如果你的 Activity 如果会自动旋转的话,旋转其实是 Activity 的重新创建,因此旋转之前的使用 bindService 建立的连接便会断开(Context 不存在了),对应服务的生命周期与上述相同。
3.3 Service与Activity的通信方式
- Service与Activity的两种通信方式见以下链接,包含了Service应用的源码
- https://blog.csdn.net/Gods_magic/article/details/84558169
4.远程Service
4.1 远程Service与本地Service的区别
- 远程服务与本地服务最大的区别是:远程Service与调用者不在同一个进程里(即远程Service是运行在另外一个进程);而本地服务则是与调用者运行在同一个进程里。
- 二者区别的详细区别如下图:

4.2 具体使用
为了让远程Service与多个应用程序的组件(四大组件)进行跨进程通信(IPC),需要使用AIDL。
- IPC:Inter-Process Communication,即跨进程通信
- AIDL:Android Interface Definition Language,即Android接口定义语言;用于让某个Service与多个应用程序组件之间进行跨进程通信,从而可以实现多个应用程序共享同一个Service的功能。
在多进程通信中,存在两个进程角色:服务器端和客户端
服务器端:
- 新建定义AIDL文件,并声明该服务需要向客户端提供的接口
- 在Service子类中实现AIDL中定义的接口方法,并实现其生命周期的各个方法。
- 在AndroidMainfest.xml中注册服务 & 声明为远程服务(android:process设置为remote)
客户端:
- 原封不动拷贝服务端的AIDL文件到目录下
- 使用Stub.asInterface接口获取服务器的Binder,根据需要调用服务提供的接口方法
- 通过Intent指定服务端的服务名称和所在包,绑定远程Service
Demo举例:
使用两个工程,一个做服务器端,一个做客户端。
服务器端设置AIDL文件,同时建立Service,将Activity传来的数据进行操作。
客户端绑定远程服务,获取Service返回的数据,进行更新UI显示。
注:因客户端获取不到服务器端Service的实例,所以无法实现监听Service的数据变化进行实时的UI显示。本地Service可以实现实时显示,已在Service与Activity的两种通信方式中实现。
服务器端源码:
AIDL文件:
interface MyAIDLInterface {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
//void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
// double aDouble, String aString);
//void AIDLService();
void TransferData(int mData);
int getData();
}Service文件:
/**
* 实现了AIDL接口的Service
* 远程Service
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
private boolean isConnected = false;
private Callback callback;
public int data = 0;
MyAIDLInterface.Stub binder = new MyAIDLInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public void TransferData(int mData) throws RemoteException {
data = mData;
}
@Override
public int getData() throws RemoteException {
return data;
}
};
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return binder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
isConnected = true;
//开启一个线程,对数据进行处理
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (isConnected) {
if (callback != null) {
callback.onDataChange(data + "");
}
data++;
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
isConnected = false;
}
}
客户端源码:
AIDL文件:同服务器端
Activity文件:
/**
* ServiceActivity 和 远程Service进行通信
* 通过AIDL接口 Service在远程或者其他app中
*/
public class ServiceActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener, ServiceConnection {
private TextView textView;
private boolean isBind = false;
private int TransforData;
//定义AIDL接口变量
private MyAIDLInterface myAIDLInterface;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_service2);
TransforData = 0;
textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
Button bindBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind_service2);
Button unBindBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind_service2);
Button clearBt = (Button) findViewById(R.id.clear);
bindBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
unBindBtn.setOnClickListener(this);
clearBt.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//将binder对象转换成了 MyAIDLInterface接口对象
myAIDLInterface = MyAIDLInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
try {
//向Service传递数据 TransforData
myAIDLInterface.TransferData(TransforData);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.bind_service2:
if (!isBind) {
isBind = true;
//服务绑定后,会调用 onServiceConnected
//绑定远程服务
Intent bindIntent = new Intent("com.example.cptestapp.MyAIDLInterface");
bindIntent.setPackage("com.example.cptestapp");
bindService(bindIntent, this, BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
Toast.makeText(this, "Bind Service Success!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
case R.id.unbind_service2:
if (isBind) {
try {
//从Service中获取data数值
TransforData = myAIDLInterface.getData();
//获取数据后,更新UI
Message msg = new Message();
msg.obj = TransforData;
handler.sendMessage(msg);
unbindService(this);
isBind = false;
Toast.makeText(this, "unBind Service Success!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
break;
case R.id.clear:
if (!isBind) {
TransforData = 0;
textView.setText("0");
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
//在此处更新UI
textView.setText(msg.obj.toString());
}
};
}
参考博文: