给定一个二叉树
struct TreeLinkNode {
TreeLinkNode *left;
TreeLinkNode *right;
TreeLinkNode *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
说明:
- 你只能使用额外常数空间。
- 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
给定二叉树,
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 7
调用你的函数后,该二叉树变为:
1 -> NULL
/ \
2 -> 3 -> NULL
/ \ \
4-> 5 -> 7 -> NULL
解题思路
和之前问题类似Leetcode 116:填充同一层的兄弟节点(超详细的解法!!!)
我们可以直接采用之前的第一种解法。
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return
q = [root, None]
while q:
node = q.pop(0)
if node:
node.next = q[0]
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
else:
if q:
q.append(None)
同样可以减少空间复杂度,我们可以建立两个指针dummy和node,并且二者初始时引用同一节点。
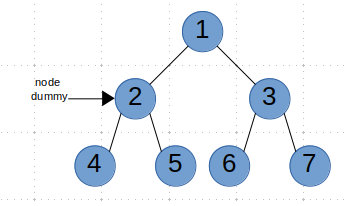
如果root.left不为空的话,我们就将node.next=root.left,并且node=node.next。
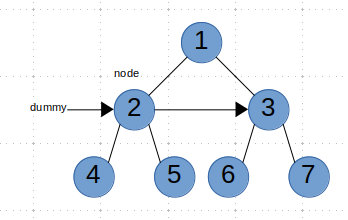
如果root.right不为空的话,我们就将node.next=root.right,并且node=node.next。然后我们看root.next是不是空,如果不是的话,继续root.next的链接,否则进入下一层root=dummy.next。(和之前的第二种解法类似)
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
while root:
node = dummy = TreeLinkNode(0)
while root:
if root.left:
node.next = node = root.left
if root.right:
node.next = node = root.right
root = root.next
root = dummy.next
同样这个问题我们也可以通过递归来解决。关键问题在于找到同一层上非空的节点,我们可以单独建立一个函数findNext实现相关操作。这个函数也非常容易实现,如果root为空,我们直接返回。如果root.left不为空,我们返回root.left。如果root.right不为空,我们返回root.right。
class Solution:
# @param root, a tree link node
# @return nothing
def connect(self, root):
if not root:
return
if root.left:
if root.right:
root.left.next = root.right
else:
root.left.next = self.findNext(root.next)
if root.right:
root.right.next = self.findNext(root.next)
self.connect(root.right)
self.connect(root.left)
def findNext(self, cur):
if not cur:
return None
if cur.left:
return cur.left
if cur.right:
return cur.right
return self.findNext(cur.next)
这里要注意一个细节,我们在主函数中递归遍历的顺序和之前问题相反,先root.right再root.left。我们举个例子
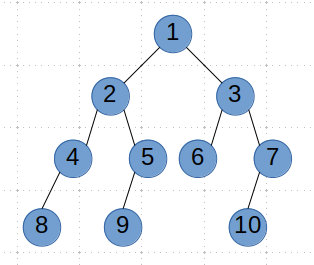
如果我们先left再right的话,我们的9是无法指向10的。因为我们的5.right是空,所以我们会通过findNext(5.next)去寻找非空节点,但是由于6的左右都为空,所以会继续findNext(6.next),但是此时我们6和7还未链接,所以结果就是8 → 9 → null。
但是如果我们先right再left的话,此时我们的6和7可以保证链接,那么此时findNext(6)找不到的话,我们会继续findNext(6.next)也就是findNext(7)。
reference:
我将该问题的其他语言版本添加到了我的GitHub Leetcode
如有问题,希望大家指出!!!