代码及结果
python代码:anneal.py
贪心算法:
- 结果:greedy_result
- 具体结果:greedy_detail_result
模拟退火:
- 结果:anneal_result
- 具体结果:anneal_detail_result
禁忌搜索:
- 结果:tabu_result
- 具体结果:tabu_detail_result
目录
题目描述
题意分析
样例格式
贪心算法
- python代码(部分)
- Detailed solution (部分)
模拟退火
- python代码(部分)
- Detailed solution (部分)
禁忌搜索
- python代码(部分)
- Detailed solution (部分)
题目描述
Suppose there are n facilities and m customers. We wish to choose:
- which of the n facilities to open
- the assignment of customers to facilities
The objective is to minimize the sum of the opening cost and the assignment cost.
The total demand assigned to a facility must not exceed its capacity.
题意分析
可以这样理解:

有n个facility, 每个facility具有一个capacity,如果开启这个facility,那么就会产生一个open cost。
有m个customer, 每个customer具有一个demond,customer可以自由选择去哪个facility, 但是选择这个facility的所有customer的demond之和不能大于它的capacity。每当customer选定一个facility,就会产生一个assign cost。
题目还有个隐含条件:所有customer的demond都要满足。
因此,总的cost可以表示为:所有开启了的facility的open cost之和 + 所有customer选择facility所产生的assign cost之和
我们的目标是令总的cost最小。
样例格式


例如:

1 贪心算法
我们可以让customer按顺序选择facility,当一个customer在选择时,它可以从所有facility中选择最优惠的那个。那么什么样的facility才是最优惠的呢?我目前想到三种方案:
- assign cost 最小的
- assign cost + open cost 最小的
- assign cost (如果该facility未开启,+ open cost) 最小的
实践证明,第一种方案得到的cost最小。第二种方案由于未考虑facility已开启的情况,导致错过了更优惠的facility,而第三种方案,由于过于在意facility是否开启,最终更倾向于已开启的facility,导致错过了很多开启后可能更优惠的facility。
1.1 python代码(部分)
def greedy():
global total_cost
// 对于每个customer
for i in range(len(assign[0])):
min_cost = -1
fac = -1
cus = -1
// 对于每个facility
for j in range(len(assign)):
// facility的剩余capacity要能满足customer的demond
if get_fac_cap(j) < customers[i].demond:
continue
temp_cost = assign_cost[j][i]
// temp_cost = temp_cost + facilities[j].open_cost
// 选择最优惠的facility
if min_cost == -1 or temp_cost < min_cost:
fac = j
cus = i
min_cost = temp_cost
// 如果没有facility能满足该customer的demond, return
if min_cost == -1:
print "false!"
return
// 选择该facility
else:
facilities[fac].open = 1
assign[fac][cus] = 1
customers[cus].assign = fac
1.2 Detailed solution (部分)
p1
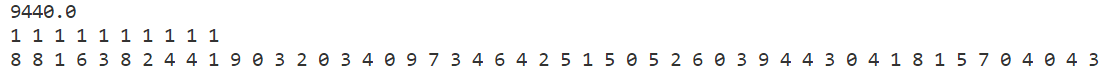
p2
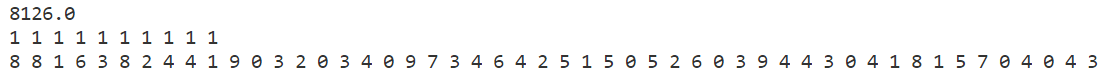
p3
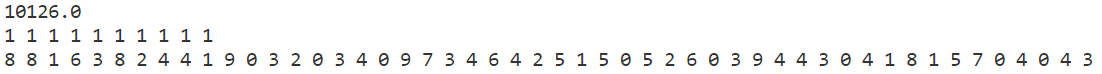
p4
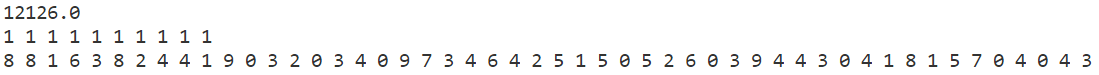
p5
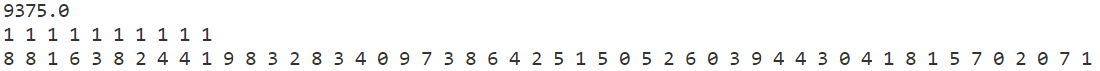
2 模拟退火
贪心算法看起来已经帮我们找到了一个最低的cost,但是这个cost很有可能是局部最优的,而不是全局最优的。至少,我们的贪心算法没有考虑顾客的顺序,如果让顾客按另一种顺序选择facility,也许cost会更低。
为了跳出这个局部最优解,我们在这个解的基础上,随机选择一个customer和一个facility,如果customer当前选择的不是这个facility,而且该facility还有足够的capacity来满足customer的demond,那么就计算让customer改选到这个facility的cost,如果这个新的cost低于旧的cost,那么就真的让这个customer改选到这个facility,否则,我们也按一定的概率接受这次改选。
刚开始时,我们可以大胆地接受cost更高的改选,随着温度降低,我们接受这种改选的概率也会越来越低。
2.1 python代码(部分)
def run_anneal():
global total_cost
print "\n-----\nanneal\n-----"
readFile()
// 在贪心算法得到的解的基础上进行计算
greedy()
total_cost = get_total_cost()
anneal()
print_result()
def anneal():
global t, total_cost
min_cost = total_cost
while t > 1:
for i in range(200):
// 随机选择一个customer和一个facility
customer, facility_from, facility_to = random_choice()
// 计算新的cost
new_cost = cal_new_cost(facility_from, facility_to, customer)
// 当new_cost小于当前最优解时,接受该解,或者以一定概率接受比当前解要差的解
if new_cost < min_cost or np.random.rand() < np.exp(-(new_cost-min_cost)/t):
accept(facility_from, facility_to, customer)
if new_cost < total_cost:
min_cost = new_cost
// 降温
t = t * 0.9
total_cost = min_cost
2.2 Detailed solution (部分)
p1
模拟退火
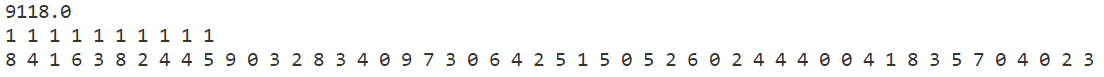
贪心算法
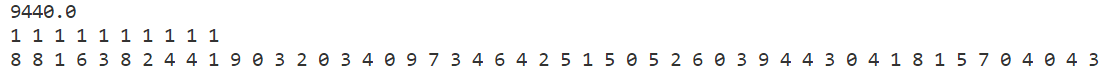
p2
模拟退火

贪心算法
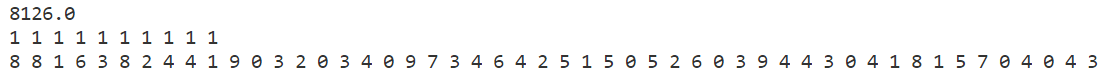
p3
模拟退火
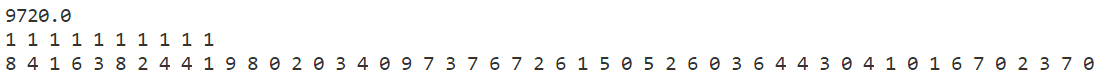
贪心算法
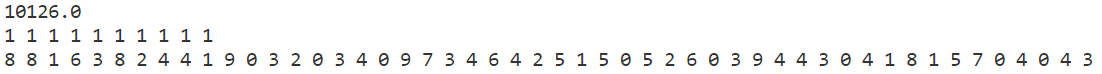
p4
模拟退火
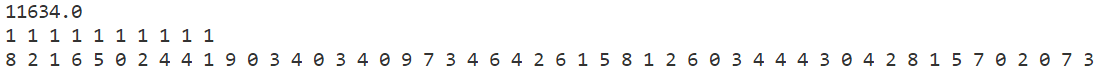
贪心算法
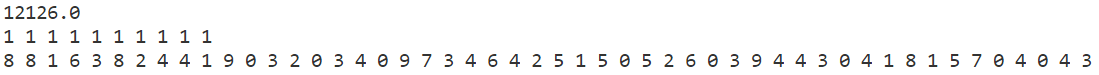
p5
模拟退火
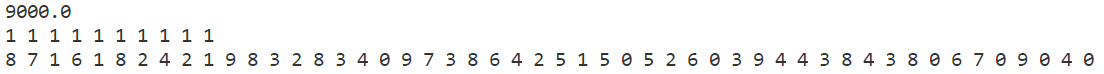
贪心算法
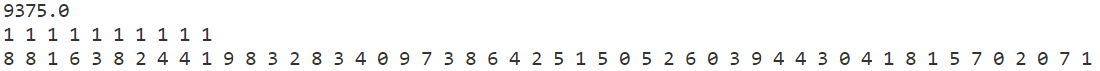
对比可知,模拟退火比简单的贪心算法要进步很多。
3 禁忌搜索
模拟退火也有不足,就比如兔子在爬山,一只兔子的力量是渺小的,而一群兔子可以互相转告,哪里的山已经找过,并且找过的每一座山他们都留下一只兔子做记号。他们制定了下一步去哪里寻找的策略。这就是禁忌搜索。
禁忌搜索也将在贪心算法的基础上进行计算。
首先建立一个候选集,也就是一组改选的方式,从中选出最优的,如果这种该选方式已经出现在了禁忌条目中,那么,如果新的cost小于历史上最优的cost,就破除禁忌,接受这次改选,否则就继续按优劣顺序另选一个。
当然,从候选集中选出的最优并不一定会比历史最优更低,只要找到这个最优的,我们就接受它。最终的结果为历史最优解。
当禁忌表已满,要加入新的禁忌条目时,移除最早加入的条目。
3.1 python代码(部分)
def tabu():
global total_cost, history_min_cost, tabu_customers, tabu_facilities
history_min_cost = total_cost
for n in range(cus_num * fac_num * 4 / 5):
now_min_cost = 99999
fac_from = facilities[0]
fac_to = facilities[0]
cus = customers[0]
// 在当前最优解的基础上,在候选集中寻找cost更低,
// 且不在禁忌表中(或者比历史最低cost更低)的exchange
now_min_cost, fac_from, fac_to, cus = find_best_change(now_min_cost, fac_from, fac_to, cus)
// 更新禁忌表
update_tabu_list(fac_to, cus)
// 接受该更改
accept(fac_from, fac_to, cus)
// 当新的cost小于历史最低cost时,更新历史最低cost,并记录此时的facilities和customers状况
if now_min_cost < history_min_cost:
history_min_cost = now_min_cost
tabu_facilities = facilities
tabu_customers = customers
3.2 Detailed solution (部分)
p1
禁忌搜索
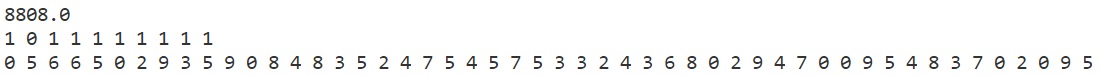
模拟退火
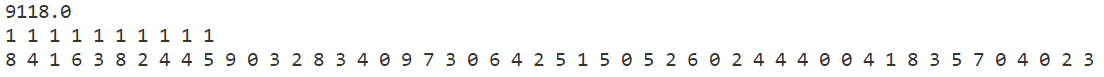
贪心算法
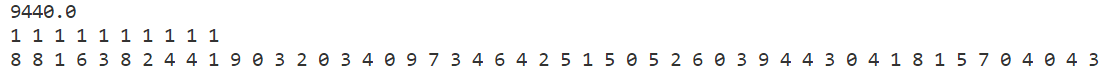
p2
禁忌搜索

模拟退火

贪心算法
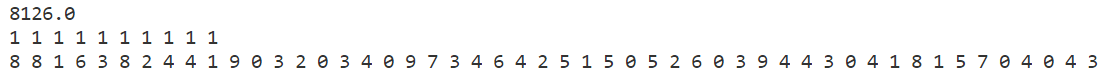
p3
禁忌搜索
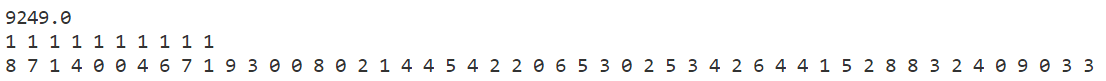
模拟退火
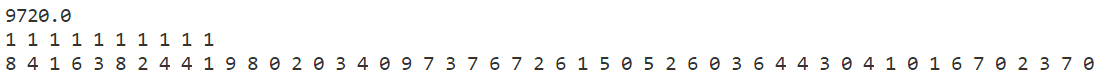
贪心算法
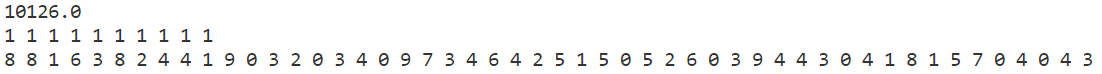
p4
禁忌搜索

模拟退火
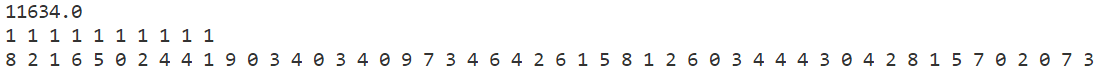
贪心算法
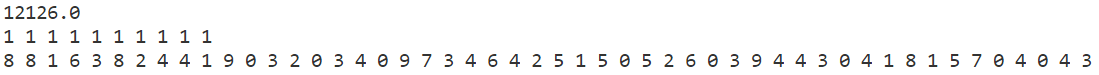
p5
禁忌搜索
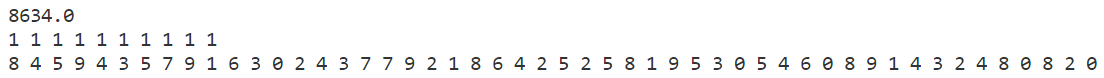
模拟退火
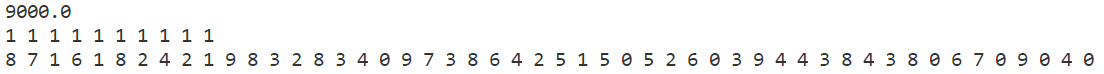
贪心算法
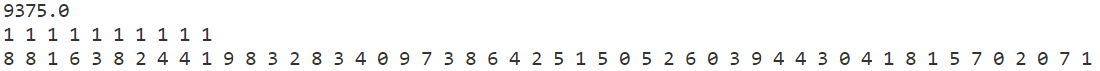
看来禁忌搜索又比模拟退火好很多呀~