版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24133491/article/details/86541889
Description:
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
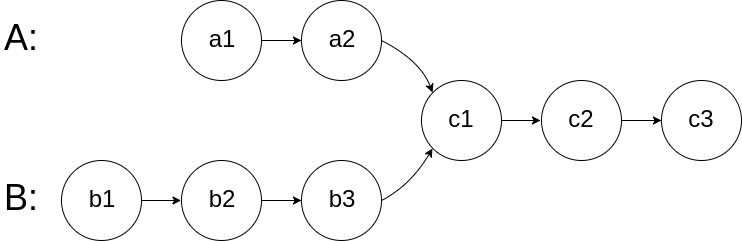
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
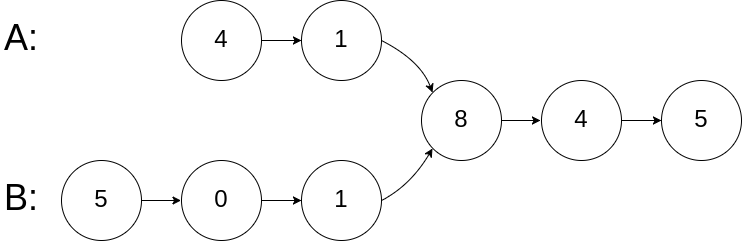
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
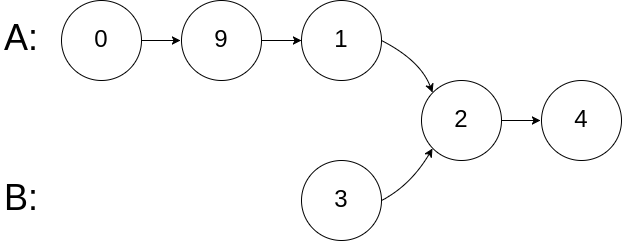
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
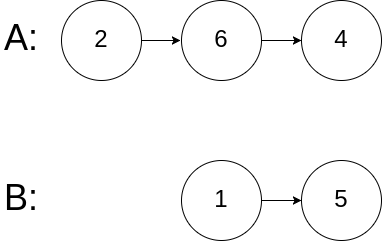
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
题意:找出两个链表的交点;并且不可以改变两个原有的链表且时间复杂度为O(n),空间复杂度为O(1);
解法:假设两个链表有交点的话,那么两个链表的最后一个元素必然是相同的;以最后一个相同元素对齐的话,当同时遍历两个链表,短的那个链表首先遍历结束,其下个结点转向长的链表头结点;而长的链表同时继续遍历知道结束后,其下个结点转向短的链表头结点;这个时候相当于第二遍遍历链表,直到找到相同的那个结点终止遍历;
eg.
- A = {a1, a2, c1, c2, c3}
- B = {b1, b2, b3, c1, c2, c3}
最终的遍历如图所示,相同数字表示同一时刻;
Java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null)
return null;
ListNode ptr1 = headA;
ListNode ptr2 = headB;
while (ptr1 != ptr2) {
ptr1 = ptr1 == null ? headB : ptr1.next;
ptr2 = ptr2 == null ? headA : ptr2.next;
}
return ptr1;
}
}
