Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
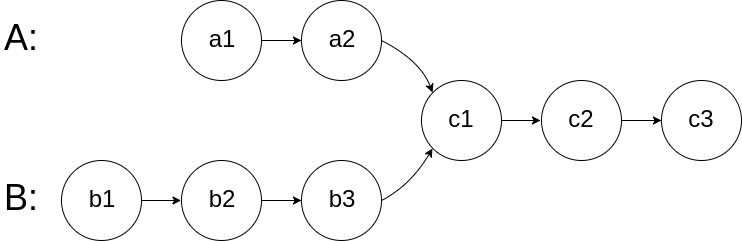
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
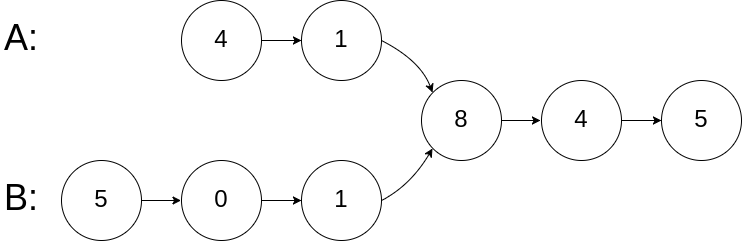
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
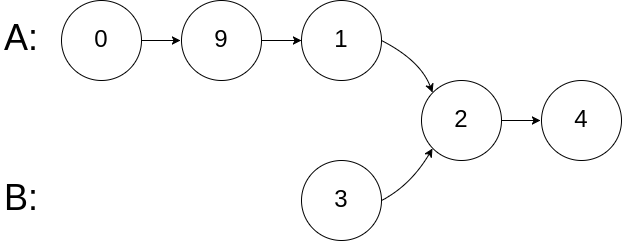
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
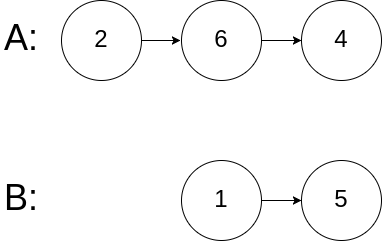
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
思路:
通过两次遍历求出A和B两个链表的长度,然后在两者长度相等的情况下看其是否相等。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode *pA, *pB;
int lenA = 0, lenB = 0;
pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA) {
lenA++;
pA = pA->next;
}
while (pB) {
lenB++;
pB = pB->next;
}
pA = headA, pB = headB;
while (pA && pB) {
if (lenA > lenB) {
lenA--;
pA = pA->next;
continue;
}
else if (lenA < lenB) {
lenB--;
pB = pB->next;
continue;
}
else {
if (pA == pB) return pA;
else {
pA = pA->next;
pB = pB->next;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
};