个人博客地址:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41907991
本文如有不懂可参考如下博客
集合源码解析:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011240877/article/details/52752589
JavaConcurrentModificationException异常原因和解决方法:
https://blog.csdn.net/androidboy365/article/details/50540202/
文章重点在于解析在迭代过程中出现的 java.lang.IllegalStateException。
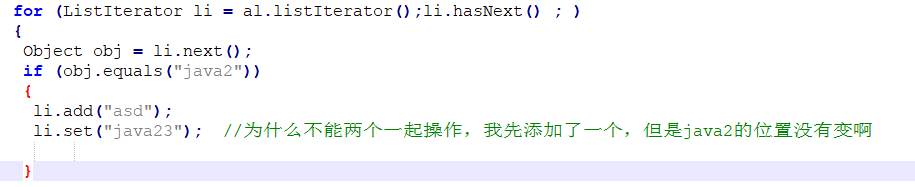
问题代码如下:
以下为ListIterator中add();set();remove();,next();
private final class FullListIterator extends SimpleListIterator implements ListIterator<E> {
//根据 start 指定游标位置
FullListIterator(int start) {
if (start >= 0 && start <= size()) {
pos = start - 1;
} else {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
//在游标前面添加元素
public void add(E object) {
if (expectedModCount == modCount) {
try {
//调用子类的添加操作,ArrayList, LinkedList,Vector 的添加操作实现有所不同
AbstractList.this.add(pos + 1, object);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
//游标后移一位
pos++;
//!注意! 添加后 上次迭代位置又变回 -1 了,说明 add 后调用 remove, set 会有问题!
lastPosition = -1;
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
expectedModCount = modCount;
}
} else {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//当游标不在初始位置(-1)时返回true
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return pos >= 0;
}
//游标后面的元素索引,就是游标 +1
public int nextIndex() {
return pos + 1;
}
//游标前面一个元素
public E previous() {
if (expectedModCount == modCount) {
try {
E result = get(pos);
lastPosition = pos;
pos--;
return result;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
//游标前面元素的索引,就是游标的位置,有点晕的看开头那几张图
public int previousIndex() {
return pos;
}
//更新之前迭代的元素为 object
public void set(E object) {
if (expectedModCount == modCount) {
try {
//调用子类的set
AbstractList.this.set(lastPosition, object);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
} else {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
从源码中可以看出:
add方法跟remove方法在运行中,将lastpostion的位置重置到-1,并且remove方法自身在
运行时会进行lastpostion的判定,set方法修改元素的位置也是lastpostion,所以在add方法或
者remove方法后调用set方法会报错,连续调用两次remove方法也会报错,但是连续调用add方法不会报错,add的定位依赖
的是postion指针。