Spark2.3 源码解析 之 梯度提升树 gradient boosting tree
一、理论
理论部分源自 Machine Learning-A Probabilistic Perspective(MLAPP)和 Elements of Statistical Machine Learning(ESML)1、boosting
boosting是一种greedy算法,书中也称作一种adaptive basis-function model (ABM),形式如下:
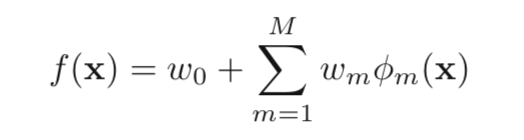
2、gradient boosting
gradient boosting的伪代码如下(摘自MLAPP):
梯度提升(gradient boosting)是一种改进的boosting方法。boosting算法的目标是让模型输出逼近真实值,即最小化Loss=L(y,f)。那么boosting每一步的目标就是:通过 弱学习器φm 来改进f,使得loss逐步减少。
那么问题就来了:f 应该向什么方向改进呢?即φm取什么值才能让loss下降最快呢?这就离梯度gradient很近了,因为loss下降最快的方向就是对f的一阶导数 即梯度gradient。因此根据gradient梯度来更新f就是gradient boosting的目的。
那么具体怎么更新呢:每次根据gradient(伪代码中 r )拟合一个弱学习器φ,并累加给f(乘以学习速率)。即gradient boosting模型中每个弱学习器都是对gradient的拟合。
(1)损失函数定义loss
根据任务类型不同,损失函数Loss的定义也不同,具体见下图(MLAPP 556页 table16.1):

(2)Logloss推导
平方损失和绝对值损失不详细介绍,Expoential指数损失过于关注错误样本,因此受到错误样本的干扰很大(比如非常离谱的数据),这里也不做介绍。
此处主要讨论gradient boosting的Logloss如何得来的,不啰嗦,直接赋上ESML的介绍:

其中,根据p(x)推导出损失函数 l(Y,p(x))不难,根据p(x)也可以推导出f(x)=1/2的log-odds
但问题是:p(x)如何而来?为什么不是LR一样的sigmoid函数?
注意:这里的Loss是 y与f之间的loss,其中导数也是对f求导(因为每个f是一个弱分类器,目的是f拟合梯度gradient),这里的loss和gradient都与x无关
(3)spark中损失函数
在spark采用的损失函数为:
3、扩展cross-entropy,KL,logistic
假设两个概率分布p(x)和q(x),其中p是已知分布(比如y),而q是未知分布(比如预测值hat{y})首先cross entropy的定义是:
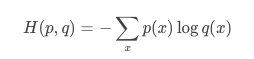
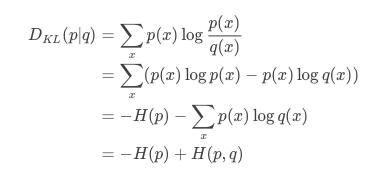
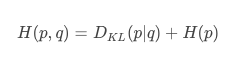
在二分类中,p∈{y,1-y},而q∈{y^,1−y^},这样,cross entropy就可以写成logistic loss
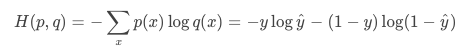
二、源码
spark的梯度提升树为:org.apache.spark.mllib.tree.GradientBoostedTrees1、train
训练每一个弱学习器DecisionTree的时候,都会用到决策树的训练方法(随机森林RandomForest的特例),具体讲解见决策树 decision tree。接下来,涉及到决策树的训练不在赘述。
主要的代码位于GradientBoostedTrees.boost方法中
/**
* Internal method for performing regression using trees as base learners.
* @param input training dataset
* @param validationInput validation dataset, ignored if validate is set to false.
* @param boostingStrategy boosting parameters
* @param validate whether or not to use the validation dataset.
* @param seed Random seed.
* @return tuple of ensemble models and weights:
* (array of decision tree models, array of model weights)
*/
def boost(
input: RDD[LabeledPoint],
validationInput: RDD[LabeledPoint],
boostingStrategy: OldBoostingStrategy,
validate: Boolean,
seed: Long,
featureSubsetStrategy: String): (Array[DecisionTreeRegressionModel], Array[Double]) = {
val timer = new TimeTracker()
timer.start("total")
timer.start("init")
boostingStrategy.assertValid()
// Initialize gradient boosting parameters
val numIterations = boostingStrategy.numIterations
val baseLearners = new Array[DecisionTreeRegressionModel](numIterations)
val baseLearnerWeights = new Array[Double](numIterations)
val loss = boostingStrategy.loss
val learningRate = boostingStrategy.learningRate
// Prepare strategy for individual trees, which use regression with variance impurity.
val treeStrategy = boostingStrategy.treeStrategy.copy
val validationTol = boostingStrategy.validationTol
treeStrategy.algo = OldAlgo.Regression
treeStrategy.impurity = OldVariance
treeStrategy.assertValid()
// Cache input
val persistedInput = if (input.getStorageLevel == StorageLevel.NONE) {
input.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
true
} else {
false
}
// Prepare periodic checkpointers
val predErrorCheckpointer = new PeriodicRDDCheckpointer[(Double, Double)](
treeStrategy.getCheckpointInterval, input.sparkContext)
val validatePredErrorCheckpointer = new PeriodicRDDCheckpointer[(Double, Double)](
treeStrategy.getCheckpointInterval, input.sparkContext)
timer.stop("init")
logDebug("##########")
logDebug("Building tree 0")
logDebug("##########")
// Initialize tree
//***第一棵树的拟合目标就是label,而非梯度***
timer.start("building tree 0")
val firstTree = new DecisionTreeRegressor().setSeed(seed)
val firstTreeModel = firstTree.train(input, treeStrategy, featureSubsetStrategy)
//***第一个树的权重设置为1***
val firstTreeWeight = 1.0
baseLearners(0) = firstTreeModel
baseLearnerWeights(0) = firstTreeWeight
var predError: RDD[(Double, Double)] =
computeInitialPredictionAndError(input, firstTreeWeight, firstTreeModel, loss)
predErrorCheckpointer.update(predError)
logDebug("error of gbt = " + predError.values.mean())
// Note: A model of type regression is used since we require raw prediction
timer.stop("building tree 0")
var validatePredError: RDD[(Double, Double)] =
computeInitialPredictionAndError(validationInput, firstTreeWeight, firstTreeModel, loss)
if (validate) validatePredErrorCheckpointer.update(validatePredError)
var bestValidateError = if (validate) validatePredError.values.mean() else 0.0
var bestM = 1
var m = 1
var doneLearning = false
//***逐步构建m个树,每个树都是对当前梯度的拟合***
while (m < numIterations && !doneLearning) {
// Update data with pseudo-residuals
//***修改数据类型,利用负梯度(-gradient)替换label,从而利用负梯度来构建决策树***
val data = predError.zip(input).map { case ((pred, _), point) =>
LabeledPoint(-loss.gradient(pred, point.label), point.features)
}
timer.start(s"building tree $m")
logDebug("###################################################")
logDebug("Gradient boosting tree iteration " + m)
logDebug("###################################################")
//***根据替换后的数据,训练决策树,即根据负梯度训练决策树***
//***这里其实利用随机森林RandomForest类进行训练(一棵树的森林)***
val dt = new DecisionTreeRegressor().setSeed(seed + m)
val model = dt.train(data, treeStrategy, featureSubsetStrategy)
timer.stop(s"building tree $m")
// Update partial model
baseLearners(m) = model
// Note: The setting of baseLearnerWeights is incorrect for losses other than SquaredError.
// Technically, the weight should be optimized for the particular loss.
// However, the behavior should be reasonable, though not optimal.
//***这里将学习速率learning rate当作了权重weight***
baseLearnerWeights(m) = learningRate
predError = updatePredictionError(
input, predError, baseLearnerWeights(m), baseLearners(m), loss)
predErrorCheckpointer.update(predError)
logDebug("error of gbt = " + predError.values.mean())
if (validate) {
// Stop training early if
// 1. Reduction in error is less than the validationTol or
// 2. If the error increases, that is if the model is overfit.
// We want the model returned corresponding to the best validation error.
validatePredError = updatePredictionError(
validationInput, validatePredError, baseLearnerWeights(m), baseLearners(m), loss)
validatePredErrorCheckpointer.update(validatePredError)
val currentValidateError = validatePredError.values.mean()
if (bestValidateError - currentValidateError < validationTol * Math.max(
currentValidateError, 0.01)) {
doneLearning = true
} else if (currentValidateError < bestValidateError) {
bestValidateError = currentValidateError
bestM = m + 1
}
}
m += 1
}
timer.stop("total")
logInfo("Internal timing for DecisionTree:")
logInfo(s"$timer")
predErrorCheckpointer.unpersistDataSet()
predErrorCheckpointer.deleteAllCheckpoints()
validatePredErrorCheckpointer.unpersistDataSet()
validatePredErrorCheckpointer.deleteAllCheckpoints()
if (persistedInput) input.unpersist()
if (validate) {
(baseLearners.slice(0, bestM), baseLearnerWeights.slice(0, bestM))
} else {
(baseLearners, baseLearnerWeights)
}
}
-
代码比较容易理解,这里只强调几点:
- 回归树:梯度提升树的弱学习器永远是回归树,利用回归树拟合梯度(连续值)
- 第一棵树:第一棵树的学习目标是label,因为此时没有梯度
- 拟合梯度:从第二棵树开始,每个决策树学习的目标都是梯度,因此代码中每次循环都要修改data的标签列为当前梯度
- 权重:第一棵树的权重是1,之后每棵树的权重=学习速率。其实权重weight也应该根据loss优化产生,但是此处利用学习速率也存在合理性,因为每次 f 的更新都是弱学习器*学习速率,因此最终的 f 构成,利用学习速率=权重,也可以理解
2、predict
(1)predict策略:
spark中的组合树模型如随机森林模型RandomForestModel和梯度提升模型GradientBoostedTreesModel,都是继承TreeEnsembleModel,在该模型中定义了预测predice的各种策略的实现。-
主要定义了两种预测predict策略:
- 加权求和sum:每棵树的输出*权重之后,求和
- 投票vote:统计每个prediction的权重weight和,权重和最大的prediction就是结果
/** * Predicts for a single data point using the weighted sum of ensemble predictions. * * @param features array representing a single data point * @return predicted category from the trained model */ private def predictBySumming(features: Vector): Double = { val treePredictions = trees.map(_.predict(features)) blas.ddot(numTrees, treePredictions, 1, treeWeights, 1) } /** * Classifies a single data point based on (weighted) majority votes. */ private def predictByVoting(features: Vector): Double = { val votes = mutable.Map.empty[Int, Double] trees.view.zip(treeWeights).foreach { case (tree, weight) => val prediction = tree.predict(features).toInt votes(prediction) = votes.getOrElse(prediction, 0.0) + weight } votes.maxBy(_._2)._1 }
-
针对不同的问题和策略,预测的代码如下:
- 回归问题:求和sum或者取平均值
- 分类问题:求和sum或者投票vote
/** * Predict values for a single data point using the model trained. * * @param features array representing a single data point * @return predicted category from the trained model */ def predict(features: Vector): Double = { (algo, combiningStrategy) match { //回归+求和sum case (Regression, Sum) => predictBySumming(features) //回归+平均 case (Regression, Average) => predictBySumming(features) / sumWeights //分类+sum case (Classification, Sum) => // binary classification val prediction = predictBySumming(features) // TODO: predicted labels are +1 or -1 for GBT. Need a better way to store this info. //标签转换为{0,1} if (prediction > 0.0) 1.0 else 0.0 //分类+vote case (Classification, Vote) => predictByVoting(features) case _ => throw new IllegalArgumentException( "TreeEnsembleModel given unsupported (algo, combiningStrategy) combination: " + s"($algo, $combiningStrategy).") }
(2)概率Probability:
spark的predict中返回的是label的预测值,而非预测概率,预测值不够灵活如无法排序等。根据理论部分的公式,预测为正类的概率P=1.0 / (1.0 + math.exp(-2.0 * margin)),此处的margin即为每棵树输出值的加权和。因此,梯度提升树gbt的预测概率代码如下:
def score(features: Vector,gbdt: GradientBoostedTreesModel): Double = {
val treePredictions = gbdt.trees.map(_.predict(features))
blas.ddot(gbdt.numTrees, treePredictions, 1, gbdt.treeWeights, 1)
}
val labelAndPreds = testData.map { point =>
var margin = score(point.features,model)
prediction = 1.0 / (1.0 + math.exp(-2.0 * margin))
(point.label, Vectors.dense(1.0-prediction, prediction))
}